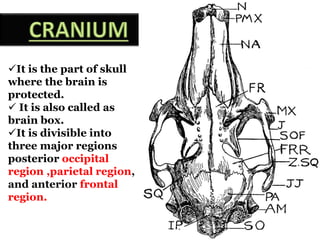
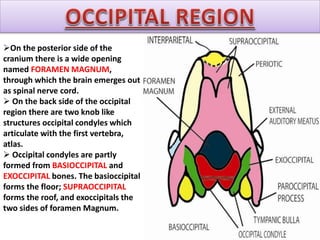
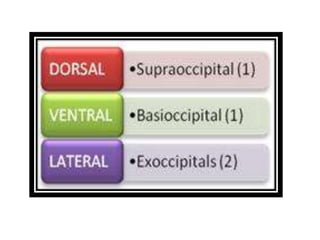
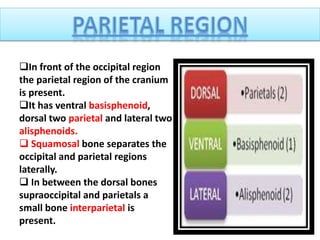
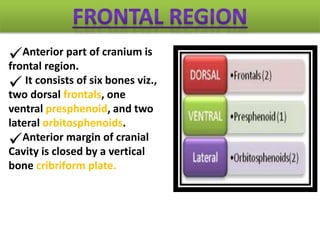
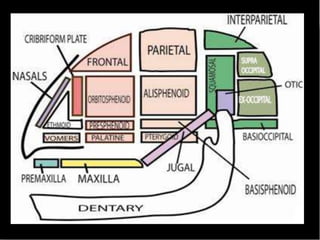
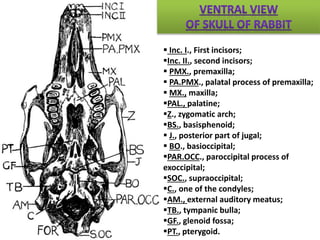
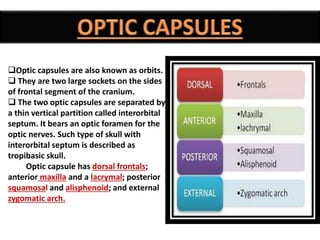
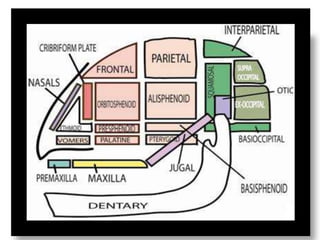
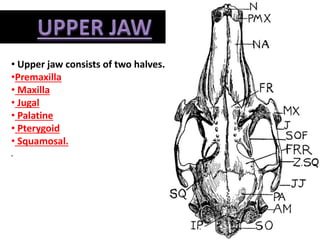
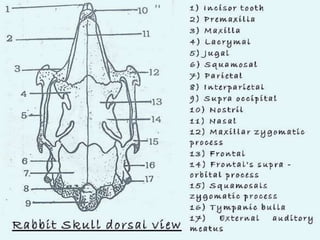
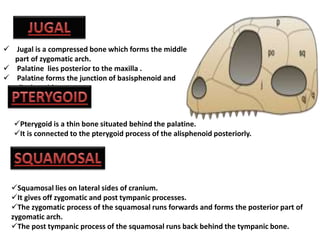
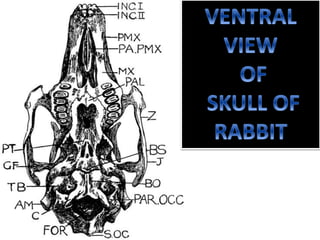
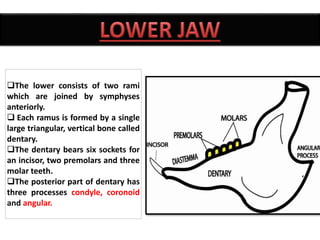
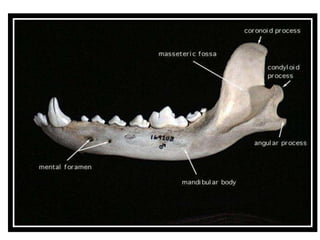
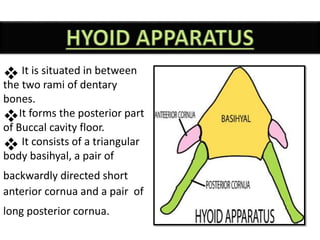
The document provides a detailed overview of the rabbit skull, highlighting its structure, including the cranium and mandible, and its role in protecting the brain and housing sensory organs. It describes the division of the skull into the posterior cranial part and anterior facial part and details the major regions, sensory capsules, and various bones that comprise the skull. Key features include the presence of olfactory, optic, and auditory capsules, as well as the arrangement of the upper and lower jaws.