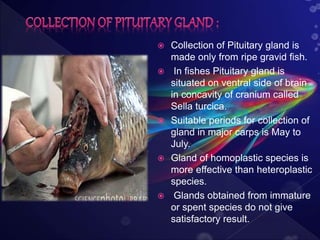
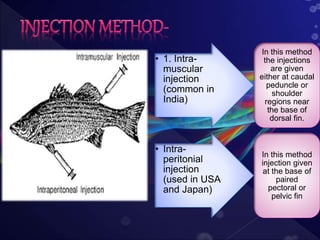
This document discusses induced breeding techniques in fish. It provides background on the historical development of induced breeding starting in the 1930s. The key steps discussed are collecting pituitary glands from ripe fish, preserving and storing the glands, determining appropriate doses of pituitary gland extract or synthetic hormones to inject into breeding fish, and collecting eggs and sperm. Factors that influence successful induced breeding include water conditions, climate, turbidity, and light levels.