The document describes Linux containerization and virtualization technologies including containers, control groups (cgroups), namespaces, and backups. It discusses:
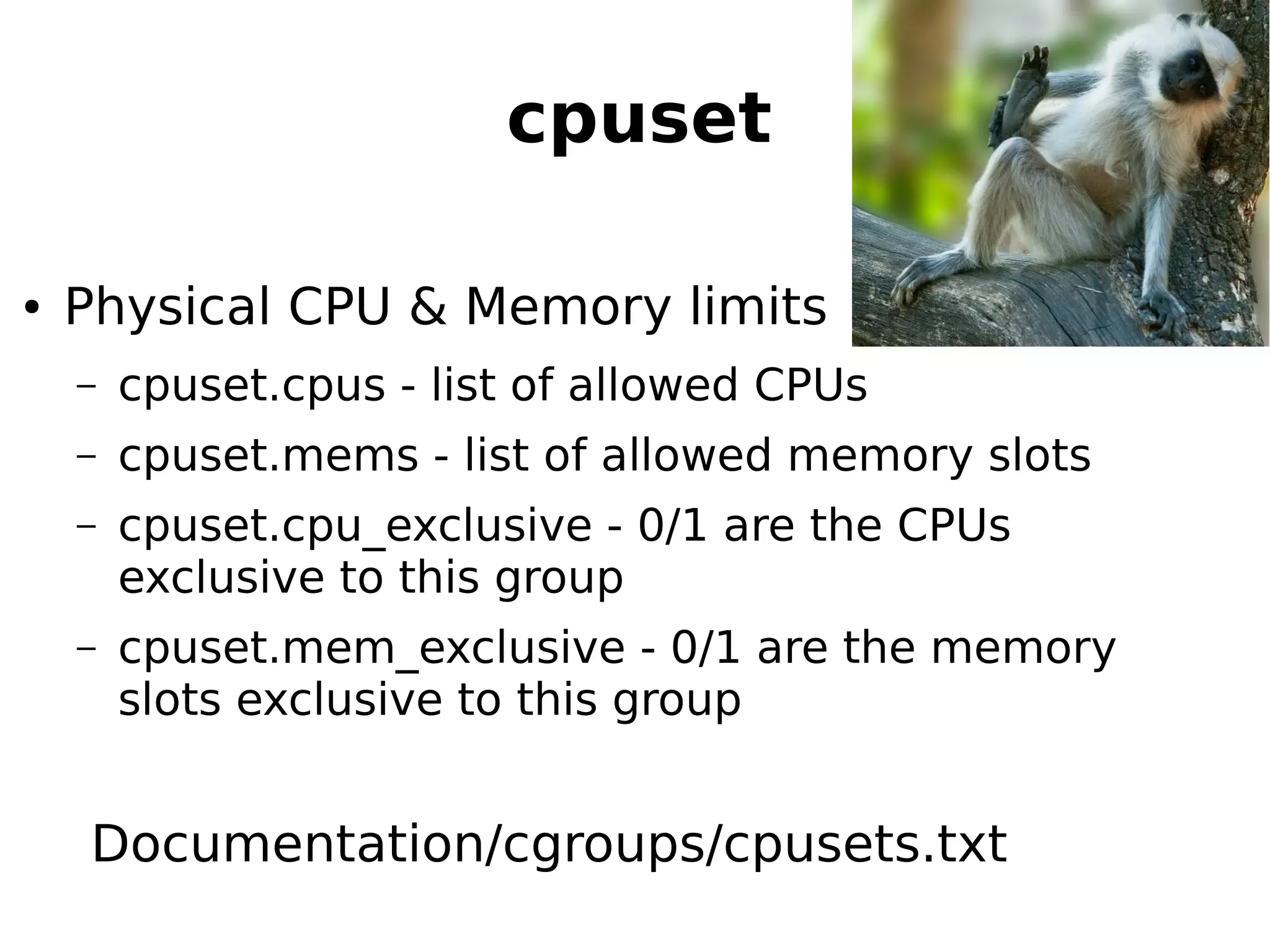
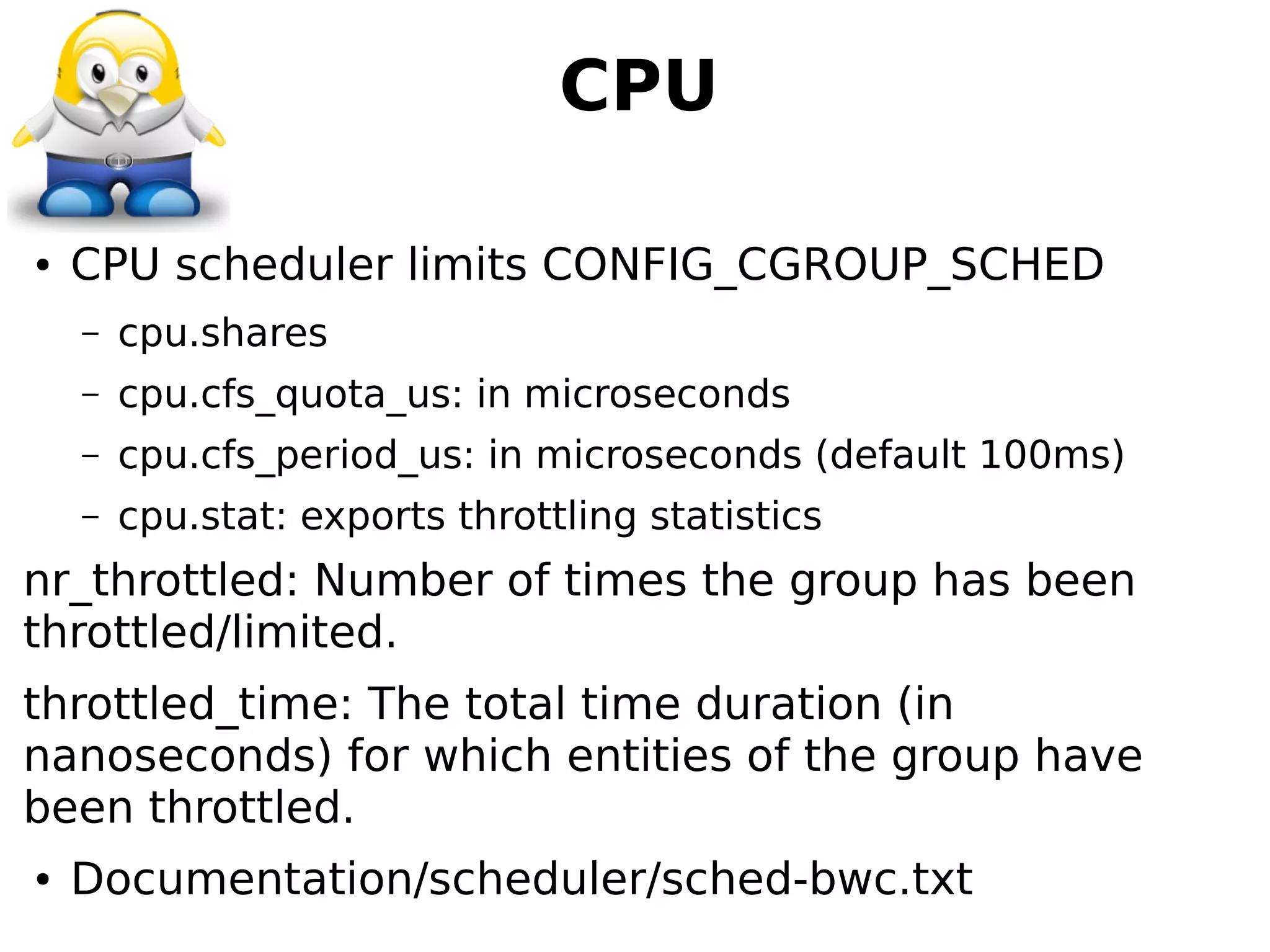
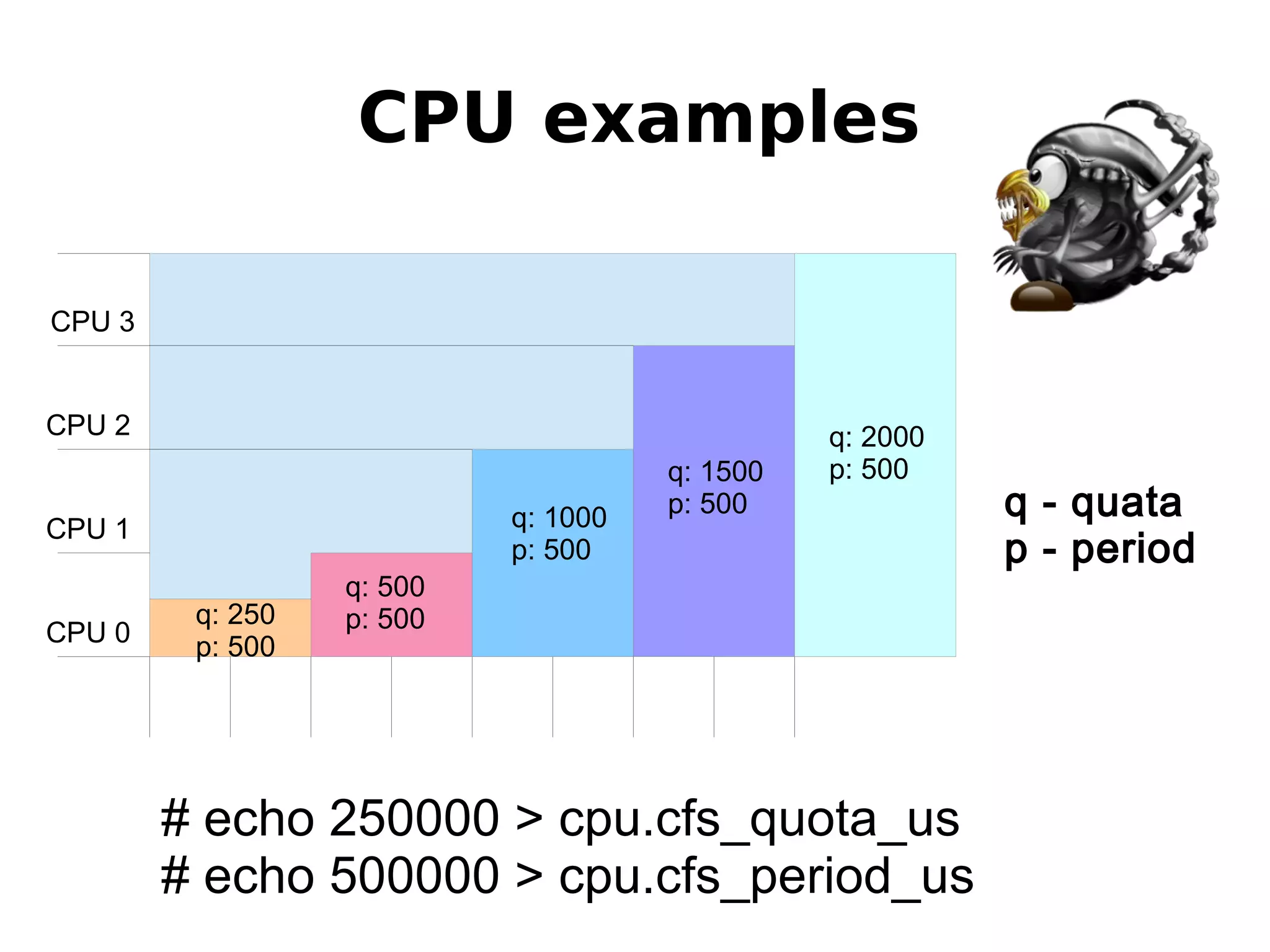
1) How cgroups isolate and limit system resources for containers through mechanisms like cpuset, cpuacct, cpu, memory, blkio, and freezer.
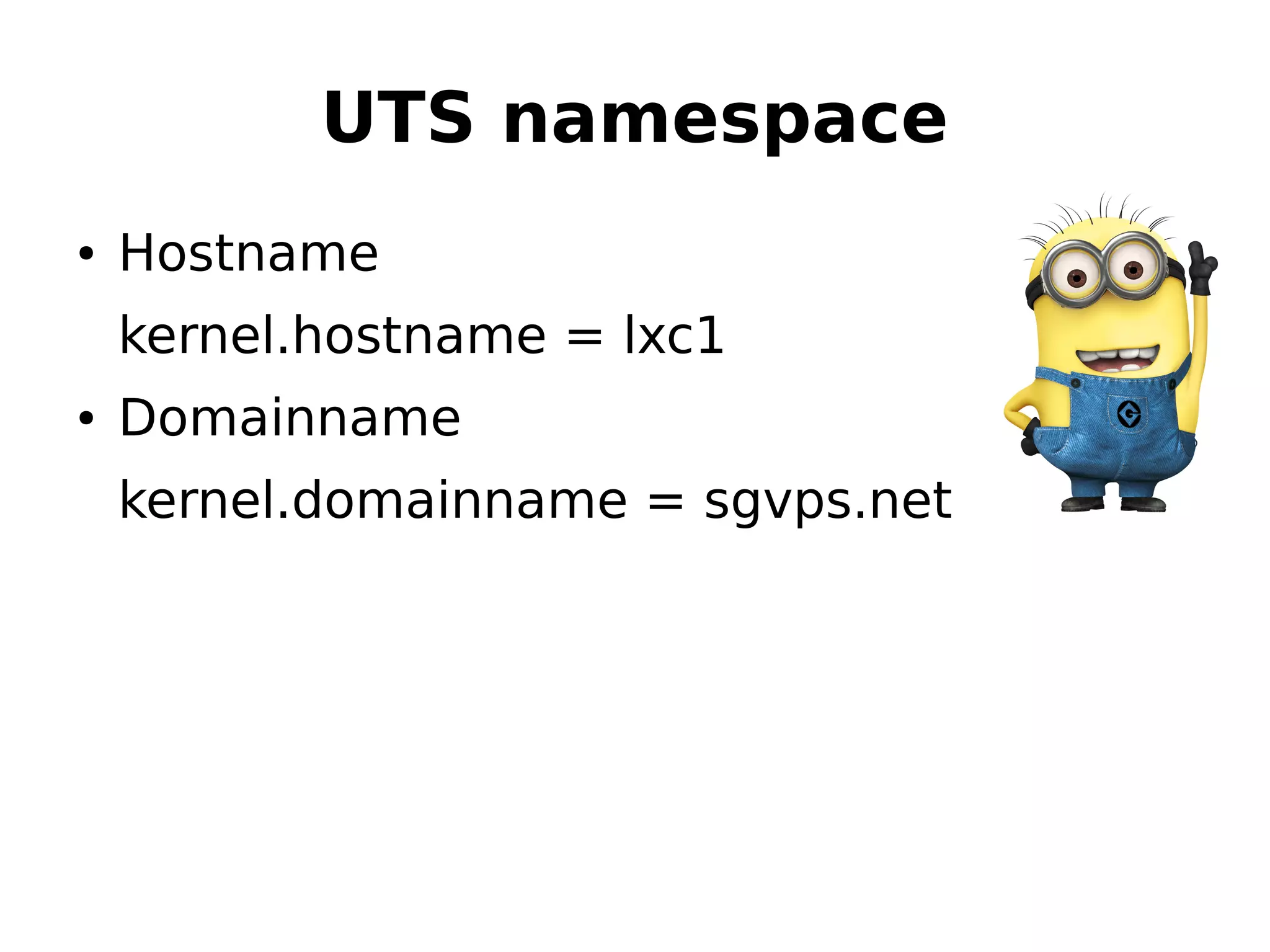
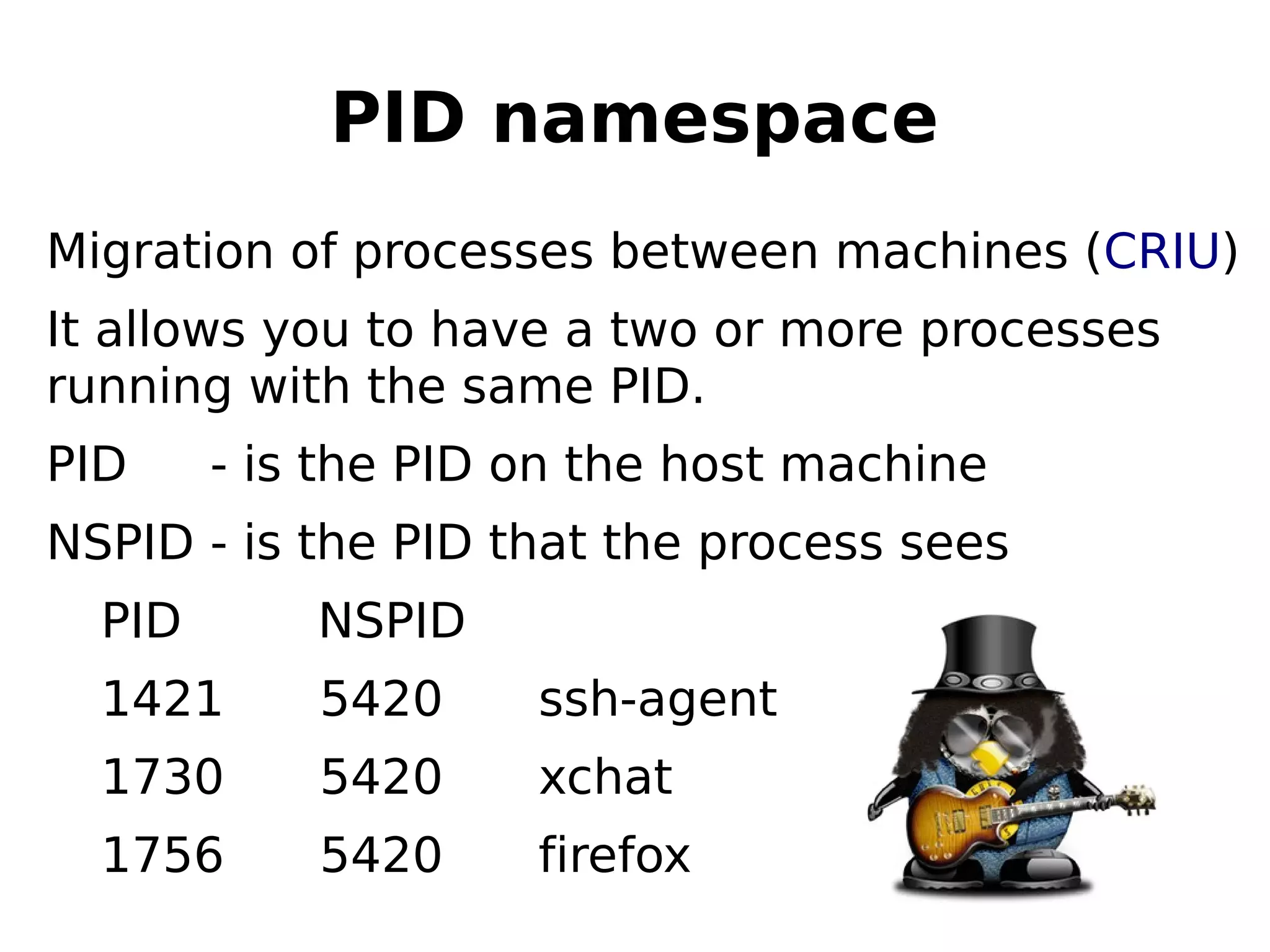
2) How namespaces isolate processes by ID, mounting, networking, IPC, and other resources to separate environments for containers.
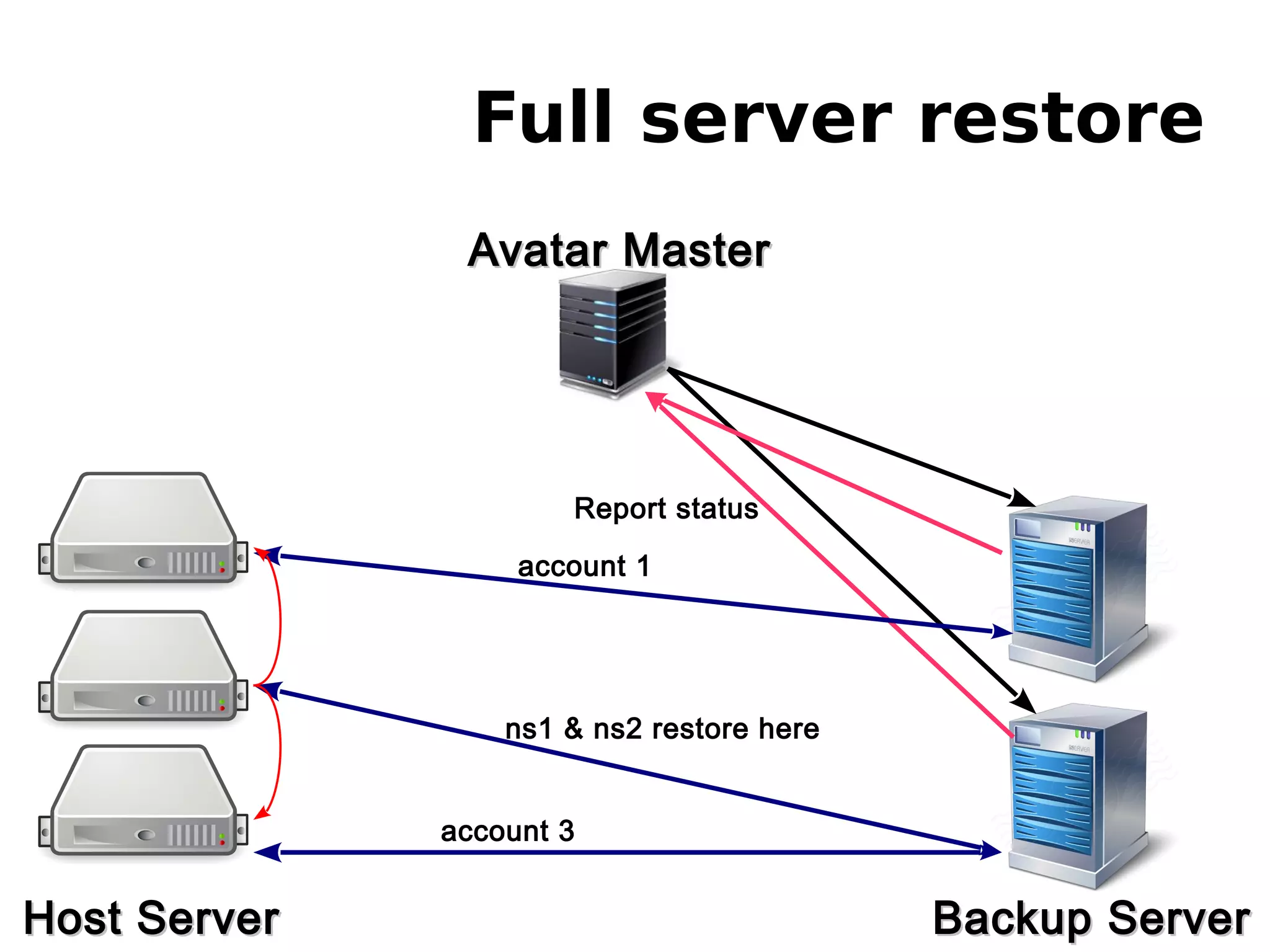
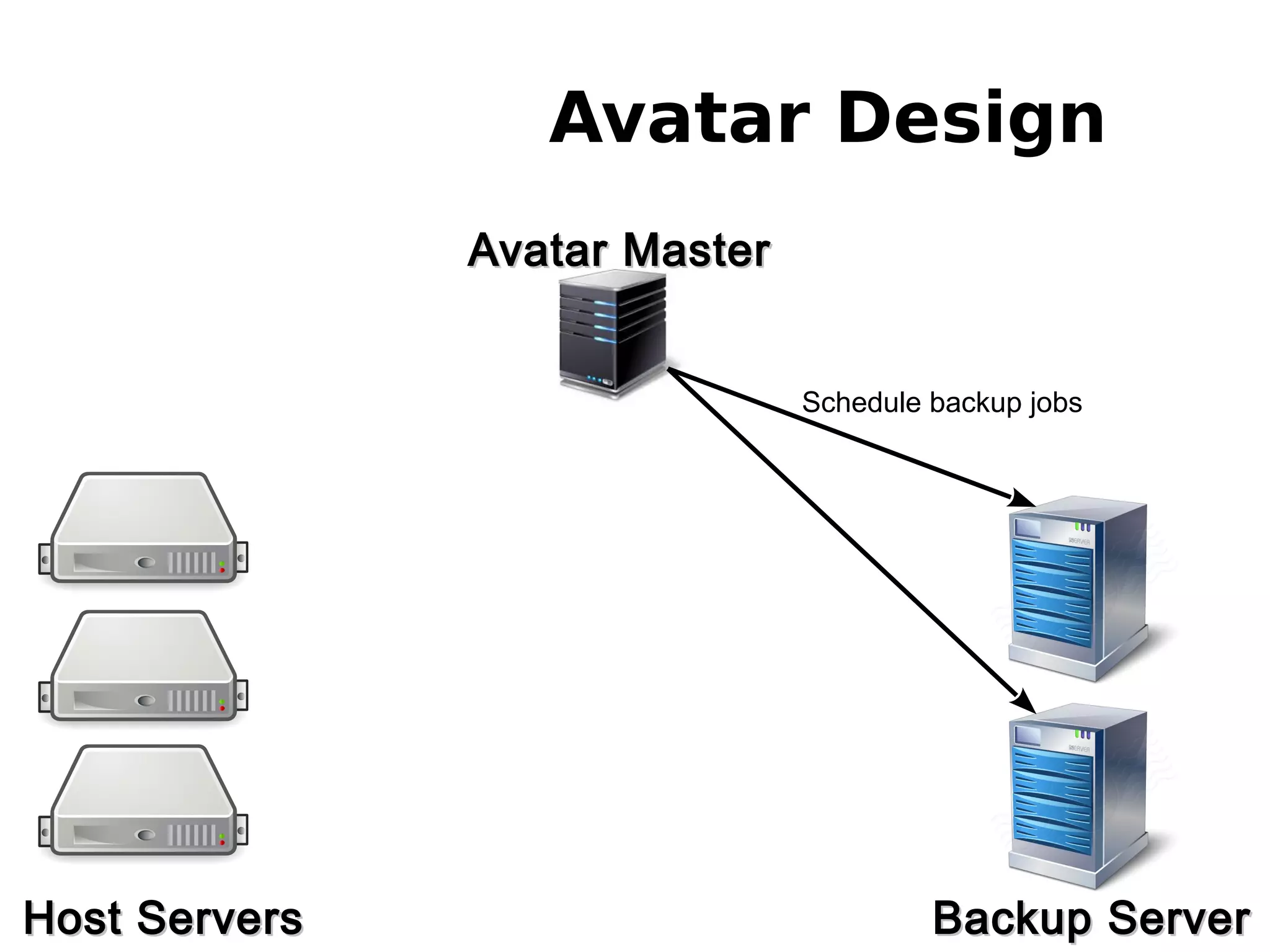
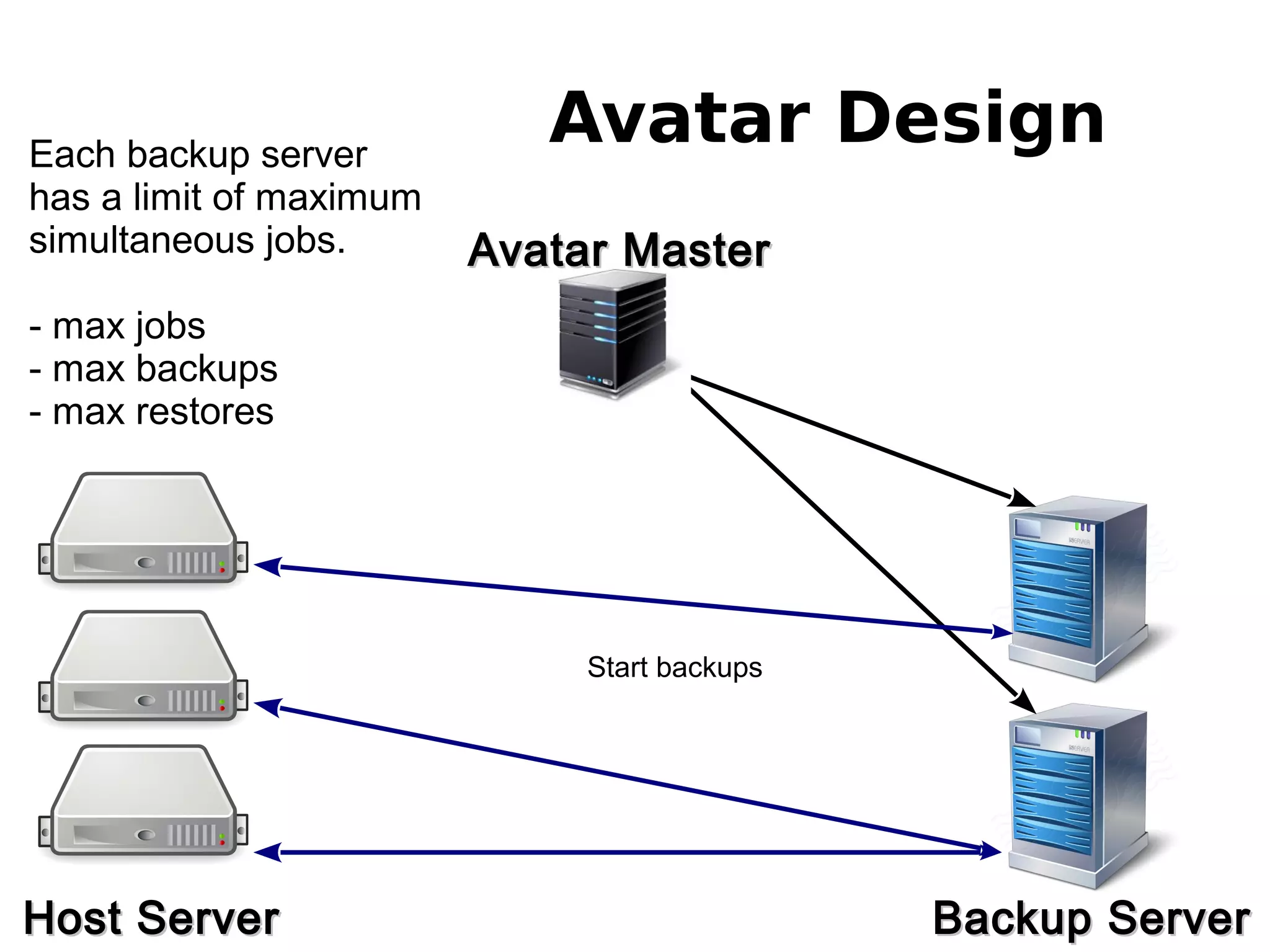
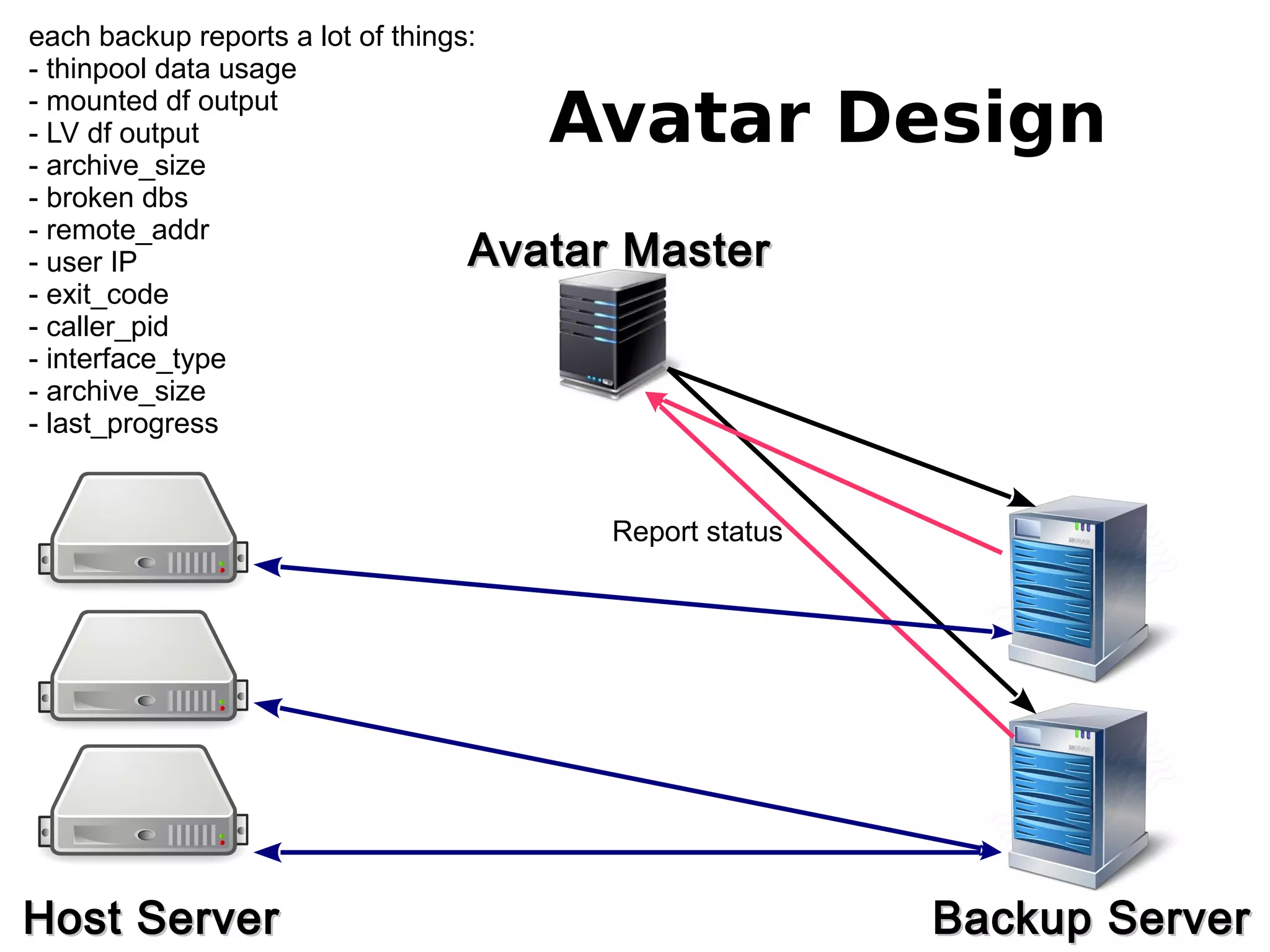
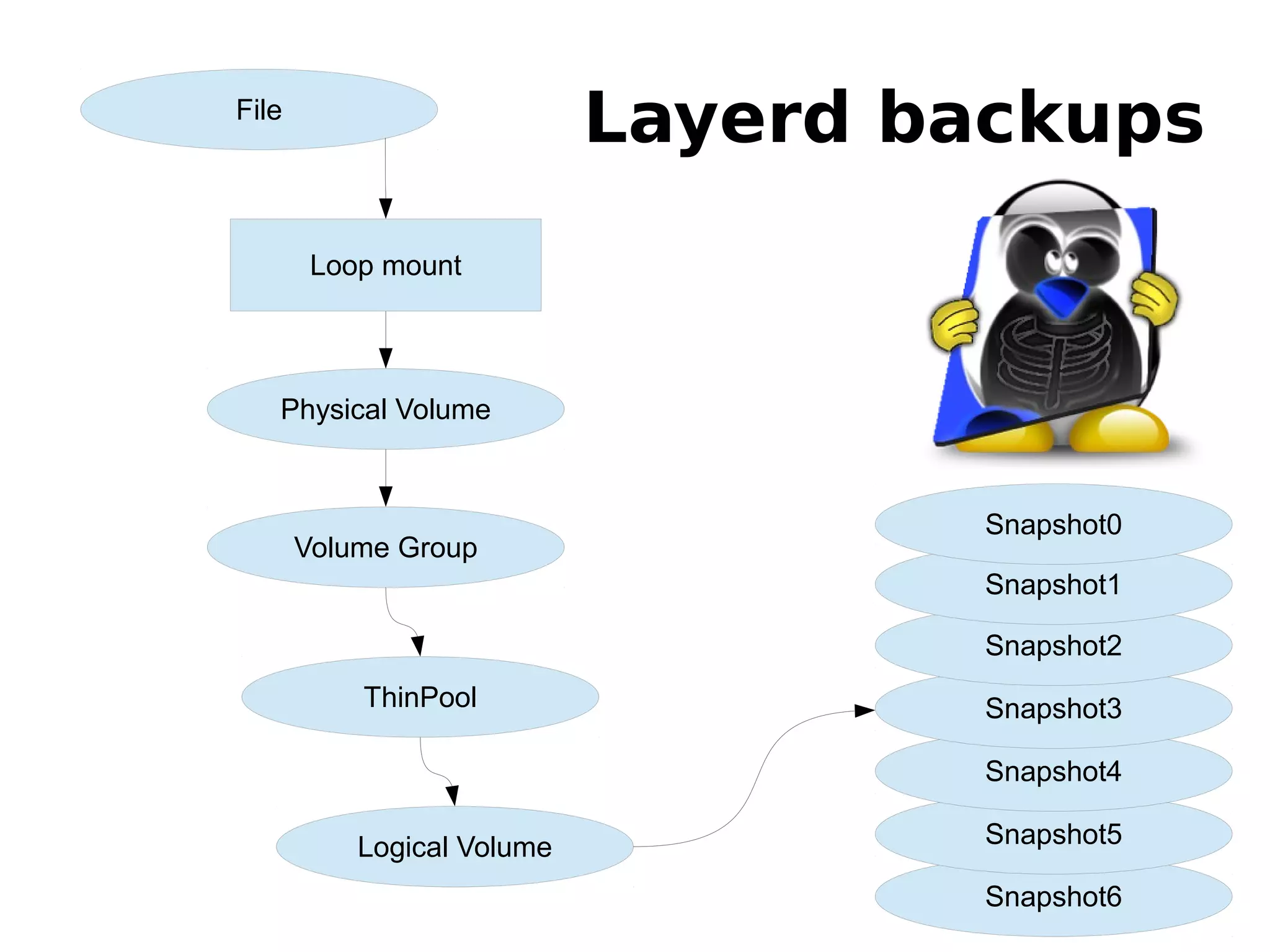
3) The new backup system which uses thin provisioning and snapshotting to efficiently backup container environments to backup servers and restore individual accounts or full servers as needed.



















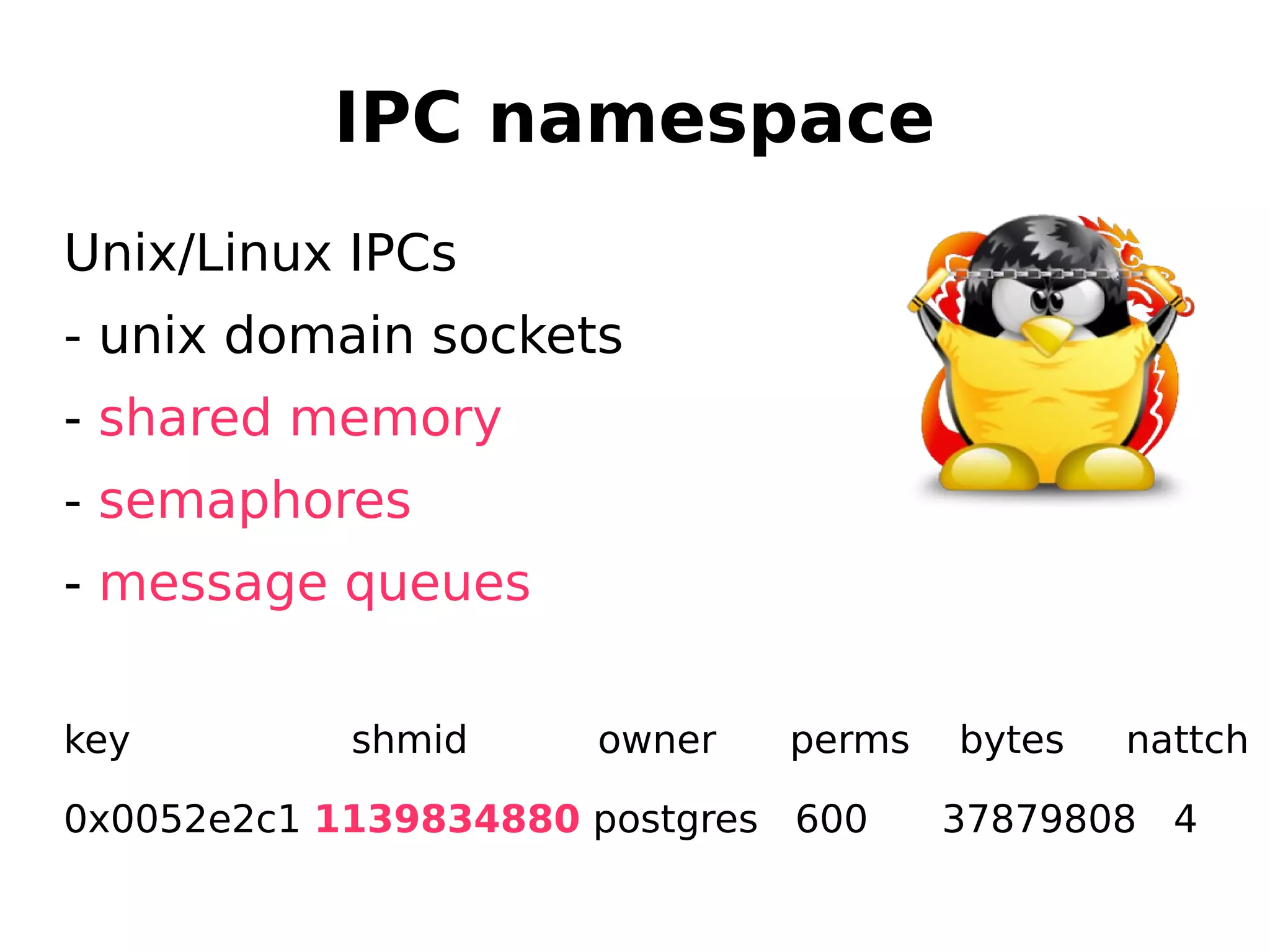
![IPC namespace
Unix/Linux IPCs
- unix domain sockets
- shared memory
- semaphores
- message queues
/proc/PID/fd/
|- 3 -> socket:[3537]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mm-teambuilding-150814083815-lva1-app6891/75/SiteGround-Tech-TeamBuilding-29-2048.jpg)




![Backup Server Structure
/sdb/avatar on /var/backups type none (rw,bind)
# ls /var/backups/siteground200.com/
total 33333656
-rw------- 1 root root 32212254720 Jul 22 04:03 camerafi
-rw------- 1 root root 32212254720 Jul 22 01:36 celticc1
-rw------- 1 root root 32212254720 Jul 22 00:57 citecang
-rw------- 1 root root 32212254720 Jul 21 20:24 ecoshea5
[root@smallvault1 /]#](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mm-teambuilding-150814083815-lva1-app6891/75/SiteGround-Tech-TeamBuilding-42-2048.jpg)
![Backup Server Structure
# losetup -f /var/backups/siteground200.com/exaera30
# losetup -a
/dev/loop0: [0811]:909901835
(/var/backups/siteground200.com/exaera30)
# vgchange -K -ay
2 logical volume(s) in volume group "exaera30" now active
# lvs
LV VG Attr LSize Pool Origin Data% Meta%
1437516546 exaera30 Vwi-a-t--- 30.00g coregroup 2.09
coregroup exaera30 twi-a-t--- 29.82g 2.10 1.54
#](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mm-teambuilding-150814083815-lva1-app6891/75/SiteGround-Tech-TeamBuilding-43-2048.jpg)
![Backup Server Structure
[root@smallvault1 /]# mount /dev/exaera30/1437516546
/mnt/...
[root@smallvault1 /]# ls -l /mnt/exaera30/1437516546
total 40
drwxr-xr-x5 root root 4096 Jul 21 17:09 configs
drwxr-xr-x3 963 959 4096 Dec 23 2014 etc
drwx--x--x14963 959 4096 Dec 23 2014 home
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 Jul 21 17:09 lost+found
drwxr-x--- 9 963 959 4096 Feb 29 2012 mail
drwxr-xr-x2 root root 4096 Jul 21 17:09 mysql
drwxr-xr-x2 root root 4096 Jul 21 17:09 pgsql
[root@smallvault1 /]#](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mm-teambuilding-150814083815-lva1-app6891/75/SiteGround-Tech-TeamBuilding-44-2048.jpg)