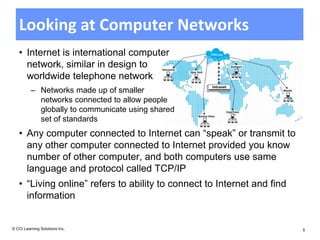
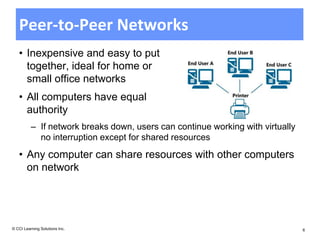
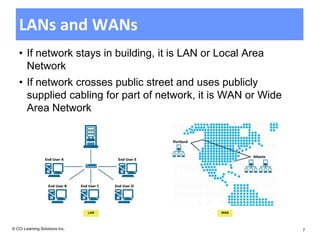
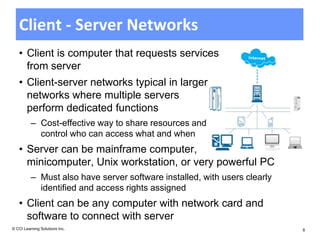
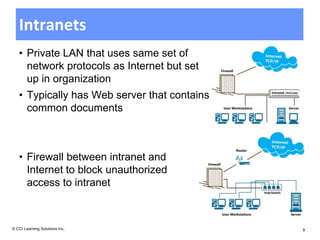
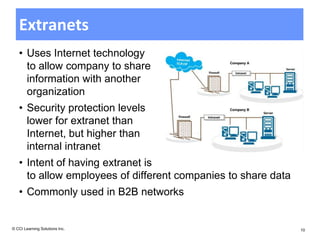
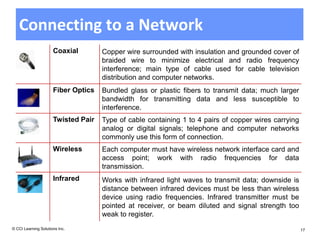
The document discusses networking fundamentals including how computer and telephone networks work, connecting to a network, and email basics. It covers networking topics like peer-to-peer networks, local area networks, wide area networks, client-server models, intranets, and extranets. Benefits of networking include communicating, sharing resources, and dedicated servers. Disadvantages include dependency on the network, security risks, autonomy loss, and vulnerability to viruses. Connections can be made via cable, fiber optics, wireless or other methods, and bandwidth is classified as low or high.