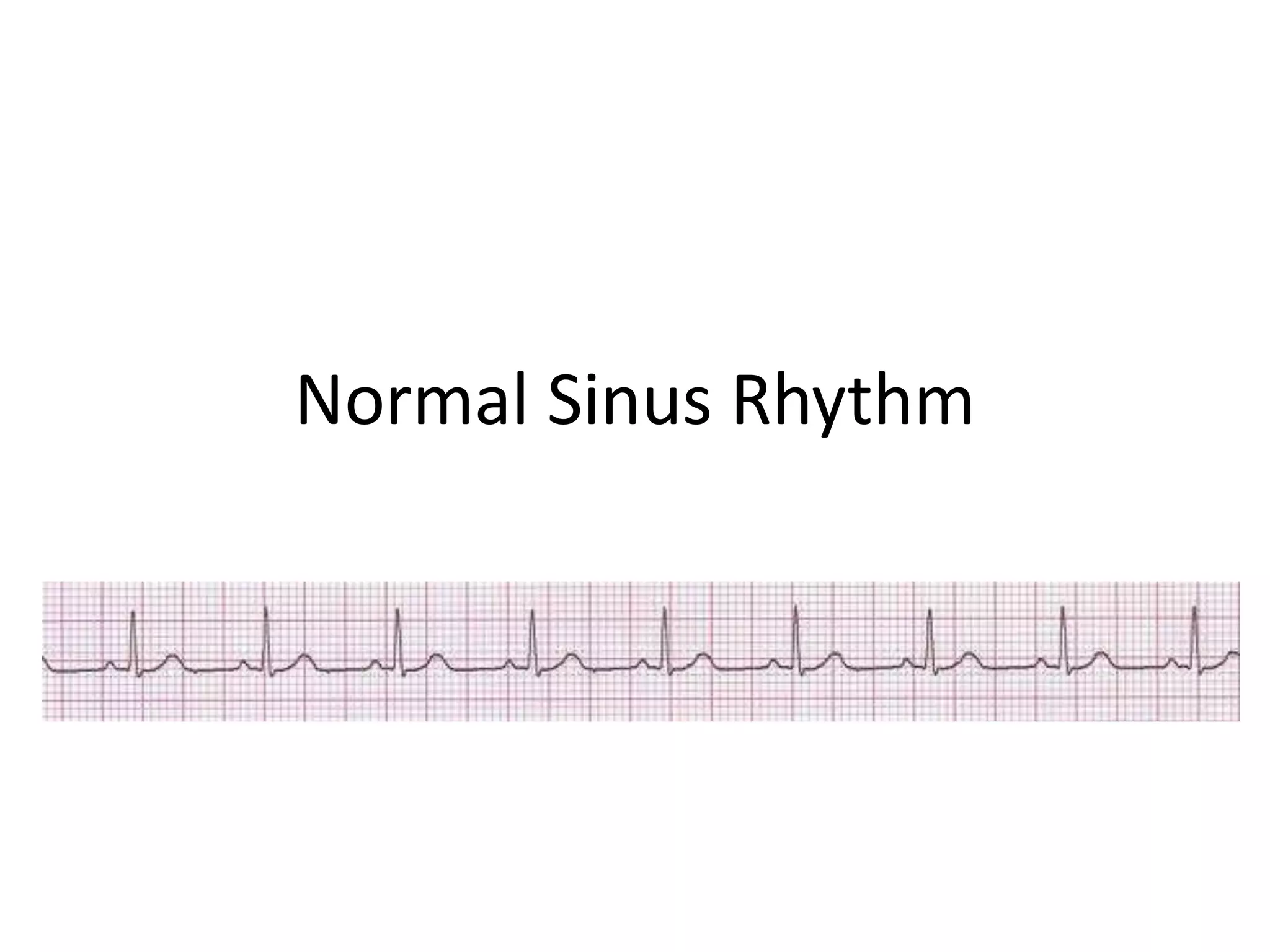
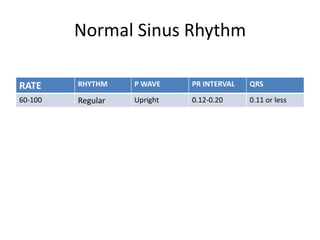
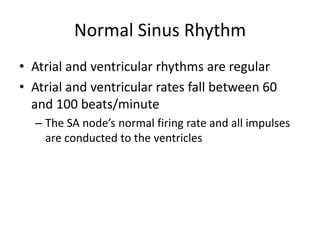
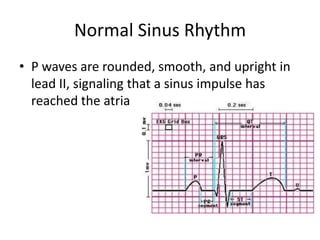
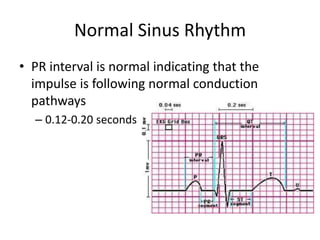
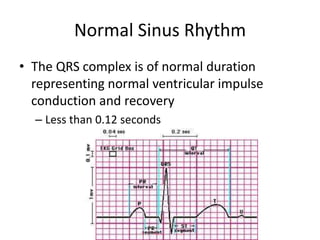
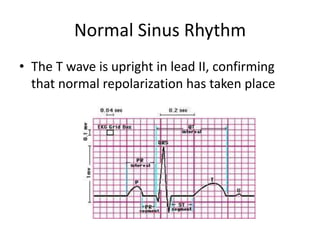
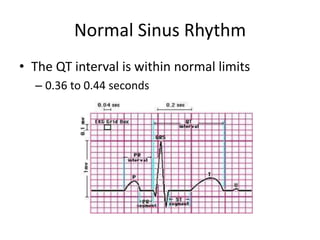
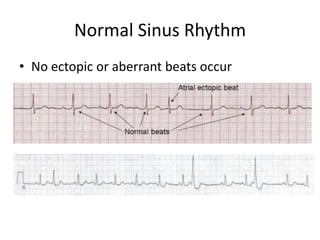
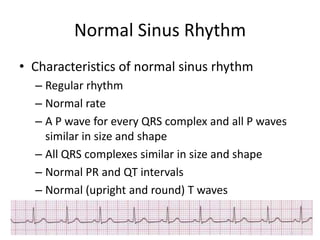
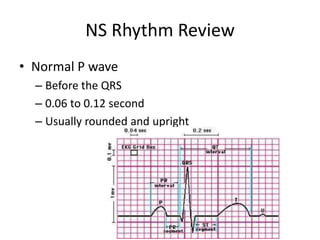
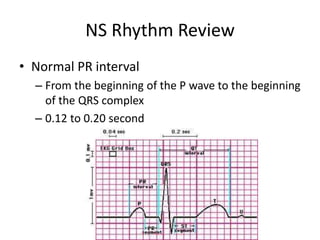
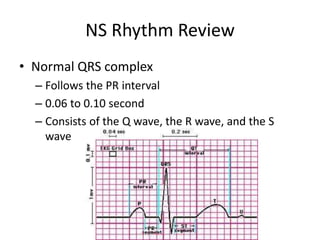
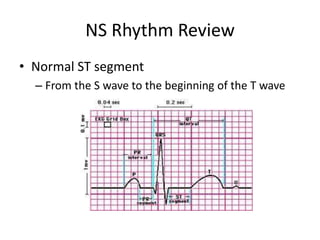
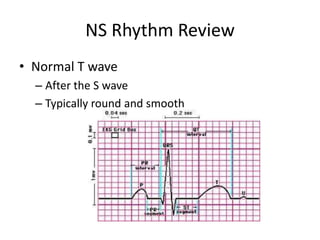
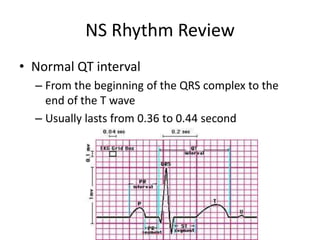
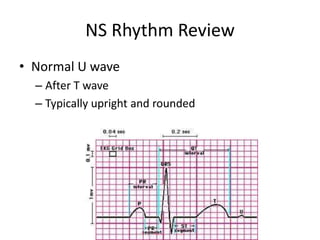
Normal sinus rhythm is characterized by a regular rhythm originating from the sinus node between 60-100 beats per minute. Each impulse follows the normal conduction pathway with visible P waves preceding upright QRS complexes and normal PR and QT intervals. Normal sinus rhythm serves as the standard against which all other cardiac rhythms are compared.