Embed presentation
Downloaded 38 times


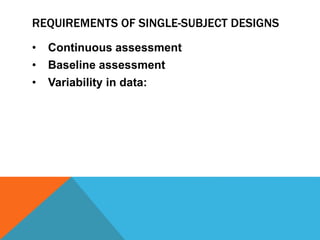
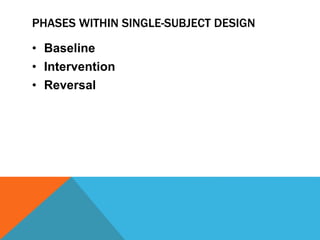

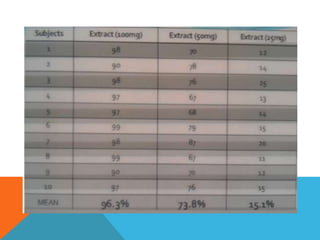



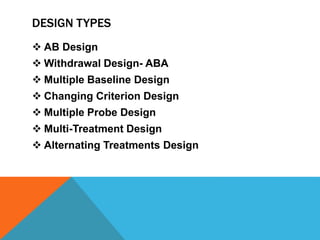


Single-group design involves administering a treatment to a group and measuring the effects, without a control group. It requires continuous assessment before, during, and after intervention to measure variability in responses. Advantages include ease of implementation and illustrating dramatic changes, while disadvantages are lack of controls and limited application. Common single-subject designs include AB, withdrawal, multiple baseline, changing criterion, and multiple probe designs.











