This paper explores the side lobe reduction of circular array antennas used in VHF/UHF band radar applications through amplitude-weighted methods, specifically focusing on Taylor and Gaussian window functions. It discusses the advantages of circular arrays over traditional linear arrays in terms of performance metrics such as angular resolution and anti-jamming capabilities. The findings suggest that using Taylor distribution significantly lowers the side lobe levels while maintaining effective beam width.




![Side Lobe Reduction of Circular Array Using Taylor Distribution Function In Radar
Applications
http://www.iaeme.com/IJECET/index.asp 7 editor@iaeme.com
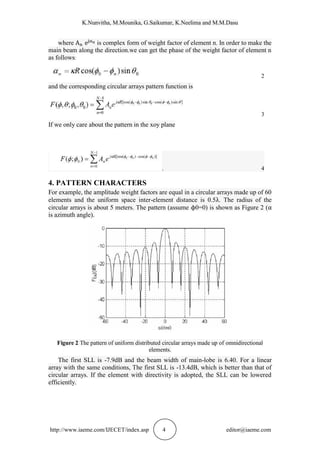
Figure 4 The pattern of uniform distributed circular arrays made up of directional elements
with Taylor distribution function as weighting factor
The first SLL is -28.7dB and the width of main-beam is 73degrees. To sum up,
Taylor distribution weighting can help to lower SLL obviously, and the main beam at
the cost of a little expanding of main beam width. In engineering, we can improve the
angle resolution by enlarging the radius of circular arrays.
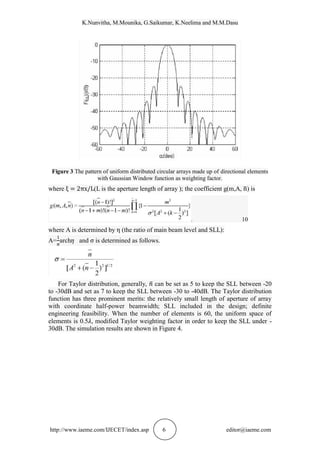
8. CONCLUSION
The circular arrays are key factors which have an influence on the performance of
radar. Circular arrays have a relatively high SLL and we prove that the SLL can be
lowered by weighting on array elements. Recently, the measurement of circular arrays
is under investigation. With the development of digital beam forming, the circular
arrays will show a great prospect.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We are thankful to God for being bestowed to undertake project in the field of
Circular Array in radar Appliaction development. The never ending support of our
parents and their blessings led us to this stage of knowledge and we are greatly
thankful to them. We are greatly thankful to our guide, Asst Professor M.M.Dasu for
his guidance and thrust provided to lift us to accomplish the project.
REFERENCES
[1] Constantine A. Balanis,“Antenna Theory, 3rd ed., Wiley- India publications.
[2] John D. Kraus, Ronald J. Marhefka, Ahmad S. Khan, “Antennas and Wave
Propagation”, 4th ed., Tata McGraw Hill Education Pvt. Ltd.
[3] V. R. Anitha, S. Narayana Reddy, Design of an 8×1 square microstrip patch
antenna array, International Journal of Electronic Engineering Research, Vol. 1.
No. 1, 2009, pp.71-77.
[4] Md. Tanvir Ishtaique-ul Huque, Md. Kamal Hosain; Md.Shihabul Islam, Md. Al-
Amin Chowdhury, Design and performance analysis of microstrip array antenna
with optimum parameters for X-band applications, (IJACSA) International
Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, Vol. 2, No. 4, 2011.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ijecet0702001-160307083217/85/SIDE-LOBE-REDUCTION-OF-CIRCULAR-ARRAY-USING-TAYLOR-DISTRIBUTION-FUNCTION-IN-RADAR-APPLICATIONS-7-320.jpg)
![K.Nunvitha, M.Mounika, G.Saikumar, K.Neelima and M.M.Dasu
http://www.iaeme.com/IJECET/index.asp 8 editor@iaeme.com
[5] K. Praveen Kumar, K. Sanjeeva Rao, T. Sumanth, N. Mohana Rao, R. Anil
Kumar, Y. Harish,“Effect of feeding techniques on the radiation characteristics of
patch antenna: Design and analysis, International Journal of Advanced Research
in Computer and Communication Engineering, Vol. 2, Issue 2, February 2013.
[6] David M. Pozar, Sean M. Duffy, A dual-band circularly polarized aperture-
coupled stacked microstrip antenna for global positioning satellite, IEEE
Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, Vol. 45, No. 11, November 1997.
[7] R. Vivek, S. Sreenath Kashyap, Novel inset feed miniaturized fractal patch
antenna for wifi-applications, International Journal of Electronics and
Communication Engineering, Vol. 2. Issue 2, May 2013, pp. 127-134.
[8] R. Rajeswari, P. Sudharshini, S. V. Vidhya Harini, Design of dual band dissimilar
patch size array antenna for wireless applications, Internationa Journal of
Information Sciences and Techniques (IJIST), Vol. 4, No. 3, May 2014.
[9] Anouar Dalli, Lahbib Zenkouar, Seddik Bri, Comparison of circular sector and
rectangular patch antenna arrays in C-band, Journal of Electromagnetic Analysis
and Applications, 2012, 4, pp. 457-467.
[10] Ami Munshi and Srija Unnikrishnan. Performance Analysis of Radar Based on
Ds-Bpsk Modulation Technique. International Journal of Electronics and
Communication Engineering & Technology, 4(2), 2013, pp. 137-143.
[11] Sanjay M Trivedi, B. S. Raman, Pinal Engineer and Dr. Mihir Shah. Design of A
Unified Timing Signal Generator (UTSG) For Pulsed Radar. International
Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology, 3(1),
2012, pp. 252 - 261.
[12] Tanveer Kour Raina, Mrs. Amanpreet Kaur, Rajesh Khanna, Design of aperture
coupled micro-strip patch antenna for wireless communication applications at 10
GHz (X band), International Journal of Electronics Engineering, 4(1), 2012, pp.
25-28.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ijecet0702001-160307083217/85/SIDE-LOBE-REDUCTION-OF-CIRCULAR-ARRAY-USING-TAYLOR-DISTRIBUTION-FUNCTION-IN-RADAR-APPLICATIONS-8-320.jpg)