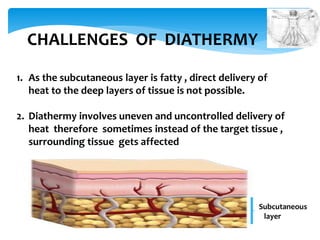
Diathermy is a therapeutic treatment that uses electric currents to generate deep heat inside tissues up to two inches below the skin's surface. It works by using electromagnetic fields to cause body tissues' dipole molecules to rearrange and generate heat, which increases blood flow and promotes healing. There are several types of diathermy that use different electromagnetic wavelengths, including shortwave, microwave, ultrasound, and longwave diathermy, which are used to treat various musculoskeletal conditions and injuries. While diathermy provides benefits like pain relief, improved flexibility and circulation, it also carries risks if used improperly or by those with implanted metal devices.