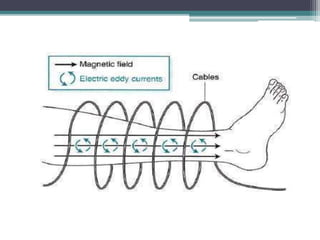
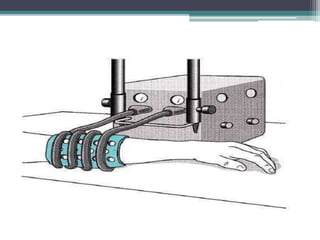
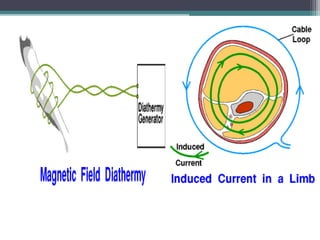
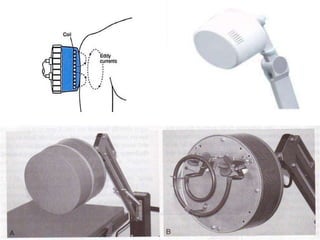
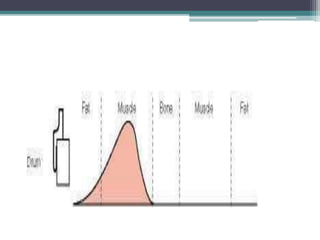
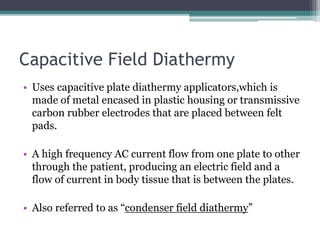
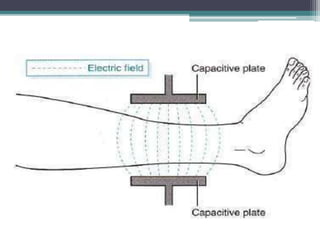
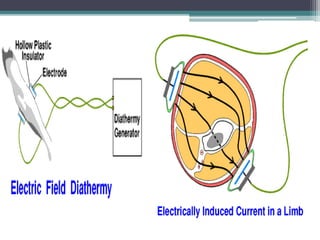
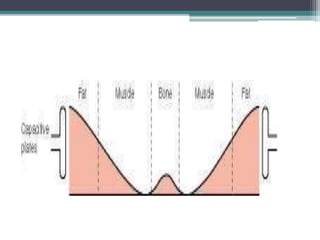
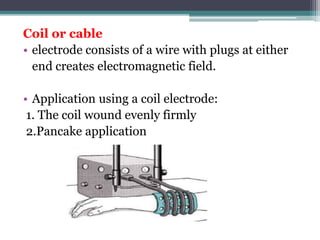
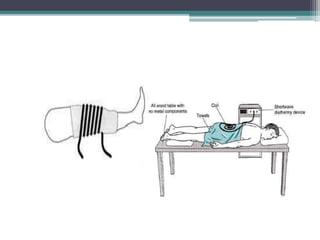
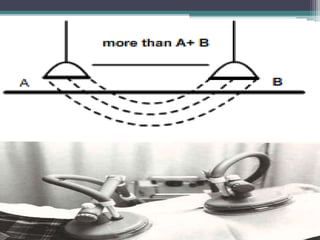
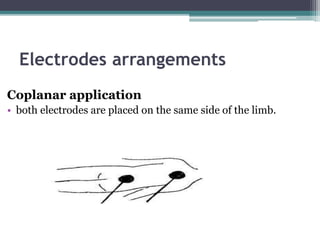
The document discusses shortwave diathermy, a therapeutic modality that uses electromagnetic energy to generate heat within body tissues, promoting physiological changes such as increased blood flow and reduced inflammation. It details various methods of application, the physiological effects, types of diathermy, and considerations for safe use, highlighting its benefits for musculoskeletal disorders and chronic pain management. Additionally, the document presents findings on the efficacy of shortwave diathermy in comparison with other treatments for conditions like osteoarthritis and low back pain.