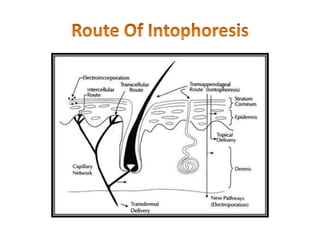
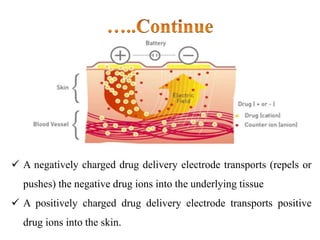
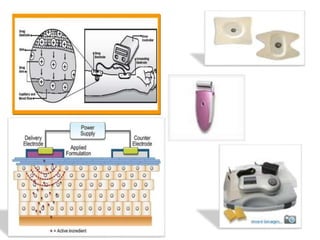
Iontophoresis is a technique that uses a low-level electrical current to introduce ions into the body across the skin. Positively or negatively charged drug ions are repelled into the skin by their respective electrodes. Factors like drug concentration, pH, charge, and molecular size influence transport. While it is a painless, sterile method for delivering certain charged drugs through the skin with small dosages, it also has drawbacks like potential irritation and device failures that require skilled operation. Iontophoresis has applications in areas like analgesia, wound healing, and inflammatory conditions.