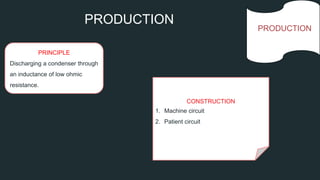
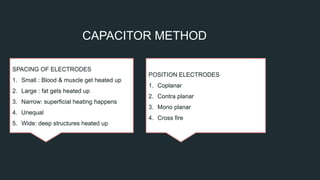
Short wave diathermy uses electromagnetic waves between 107-108 Hz to induce heating in tissues. It has both thermal and non-thermal physiological effects and can be used to treat inflammatory conditions, infections, muscle injuries and more. The document describes the production of short wave diathermy through an oscillating circuit, and discusses methods of application including capacitor and cable techniques which create electric and magnetic fields. Precautions are outlined to avoid risks like burns. In summary, it provides an overview of short wave diathermy including its mechanisms, effects, indications and application methods.