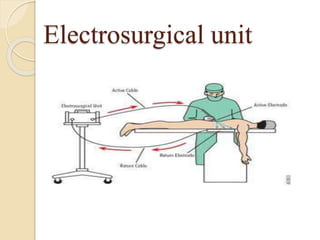
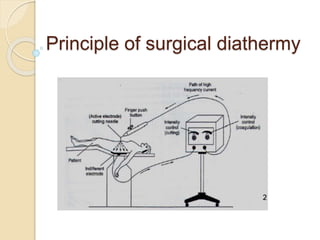
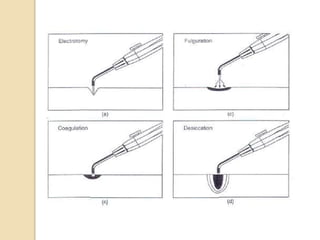
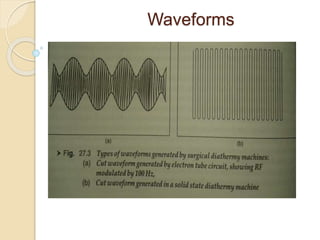
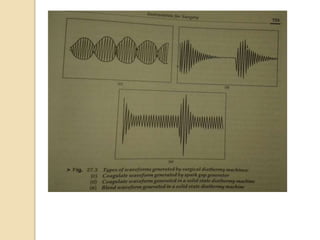
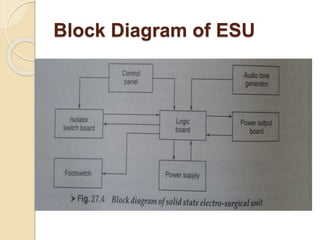
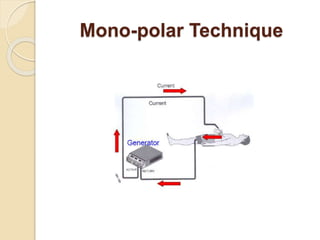
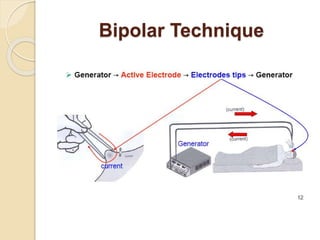
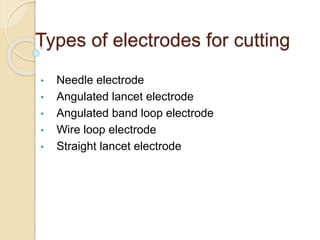
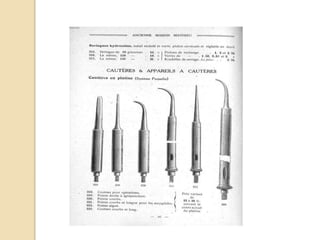
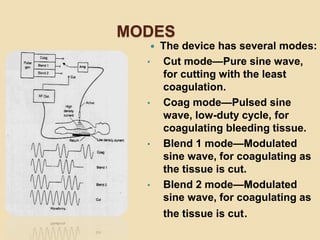
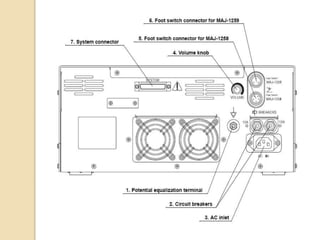
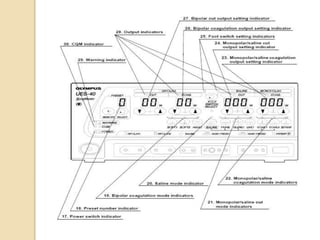
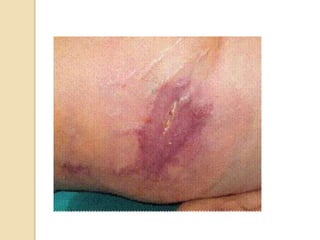
The document discusses electrosurgical units, which utilize high-frequency electric currents for cutting, coagulating, and desiccating biological tissue during surgical procedures. It outlines various techniques, device modes, safety precautions, and advantages over traditional methods. Key points include the importance of grounding the equipment, using protective gear, and the effectiveness of different electrode types.