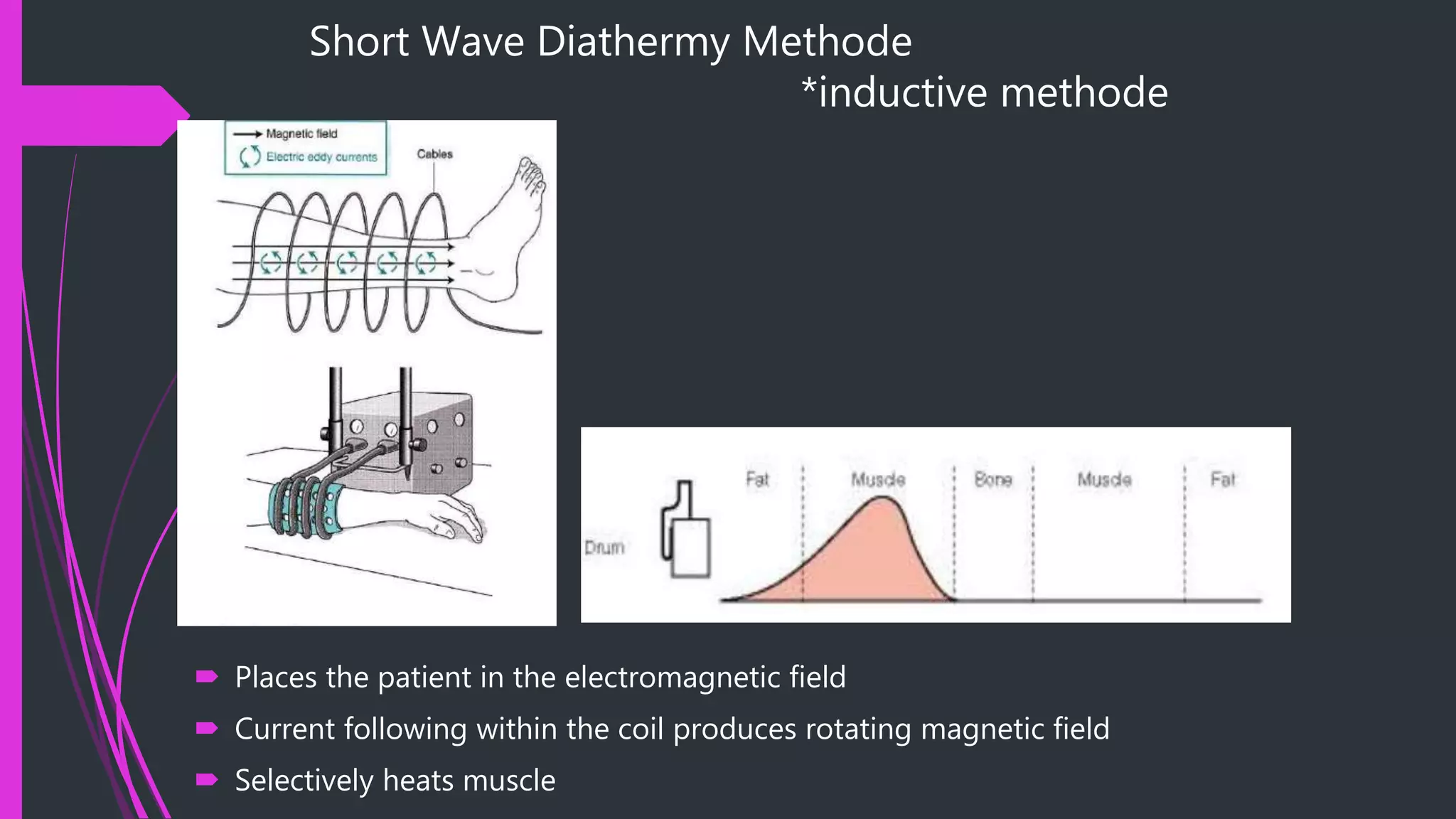
Short wave diathermy uses electromagnetic waves to generate heat deep in tissues for therapeutic purposes. It works by causing molecular vibration that increases temperature. Different tissue types heat differently due to varying densities. Treatment involves placing electrodes on the skin to create electromagnetic or electrostatic fields using various techniques. Proper electrode placement and factors like body size influence field distribution. Short wave diathermy increases blood flow, metabolism and reduces pain. It is used for mild chronic conditions but has contraindications like acute injuries, tumors or pregnancy.