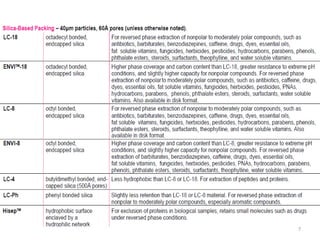
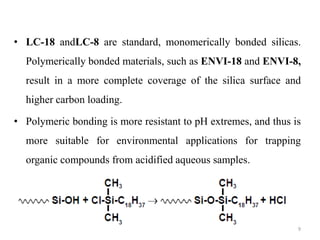
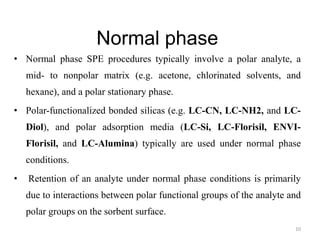
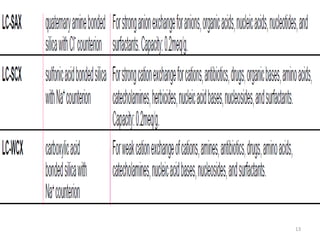
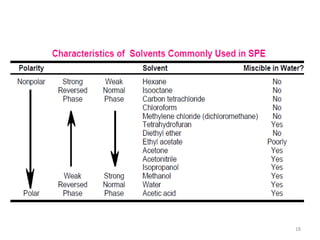
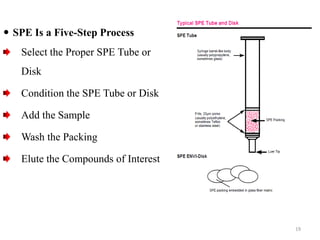
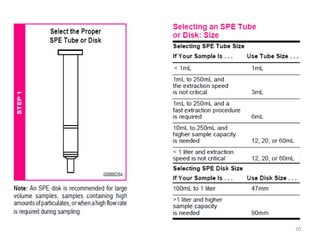
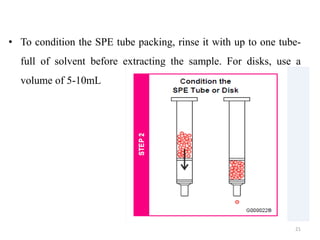
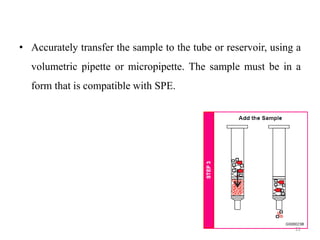
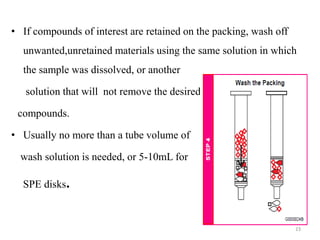
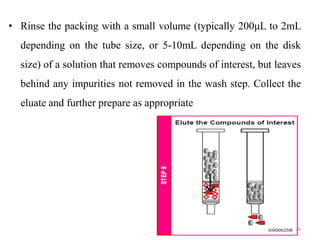
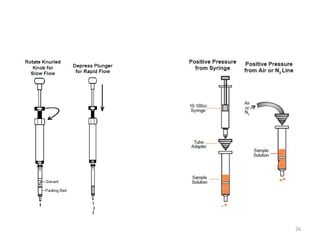
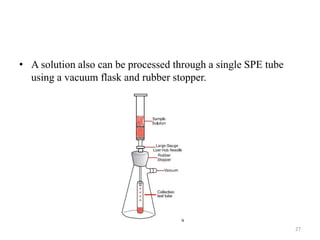
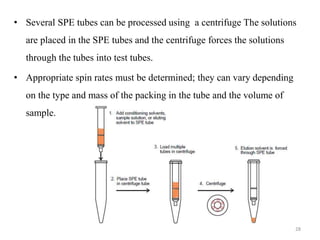
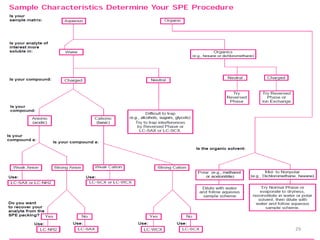
Solid phase extraction (SPE) is a sample preparation technique used to extract analytes from liquid samples. It offers advantages over liquid-liquid extraction such as being more efficient, quantitative, easy to perform, rapid, and able to be automated with reduced solvent use and time. SPE works by retaining analytes on a solid stationary phase while allowing interfering substances to pass through. Key steps involve conditioning the SPE material, adding the sample, washing away unwanted materials, and then eluting the target analytes. Common SPE materials include reversed phase, normal phase, ion exchange, and adsorbent types which separate compounds based on interactions like hydrophobicity, polarity, and charge.