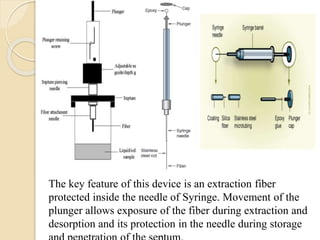
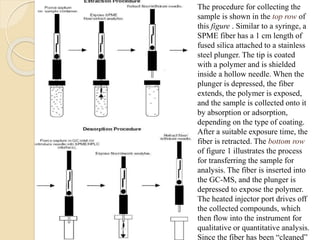
This presentation provides an overview of solid phase microextraction (SPME), including its history, basic principles, and applications. SPME was invented in 1990 as a simple, solvent-free technique for isolating and concentrating analytes from samples. It uses coated fibers that are exposed to a sample to absorb analytes, then thermally desorbed in a gas chromatograph. Some advantages are its simplicity, speed, and ability to directly analyze extracted analytes. Main applications include analysis of explosives, foods, plastics, biomedicine, and flavors.