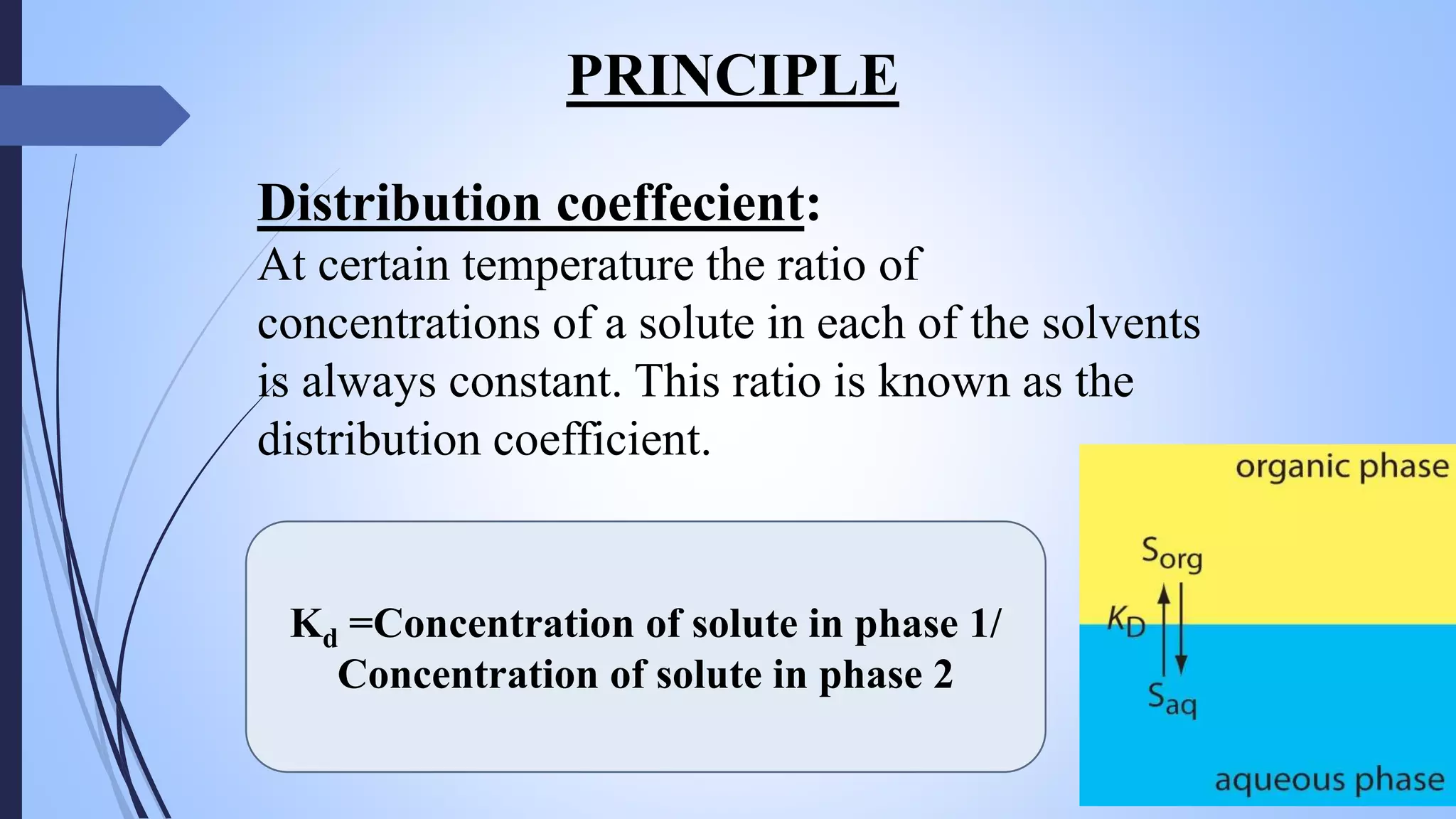
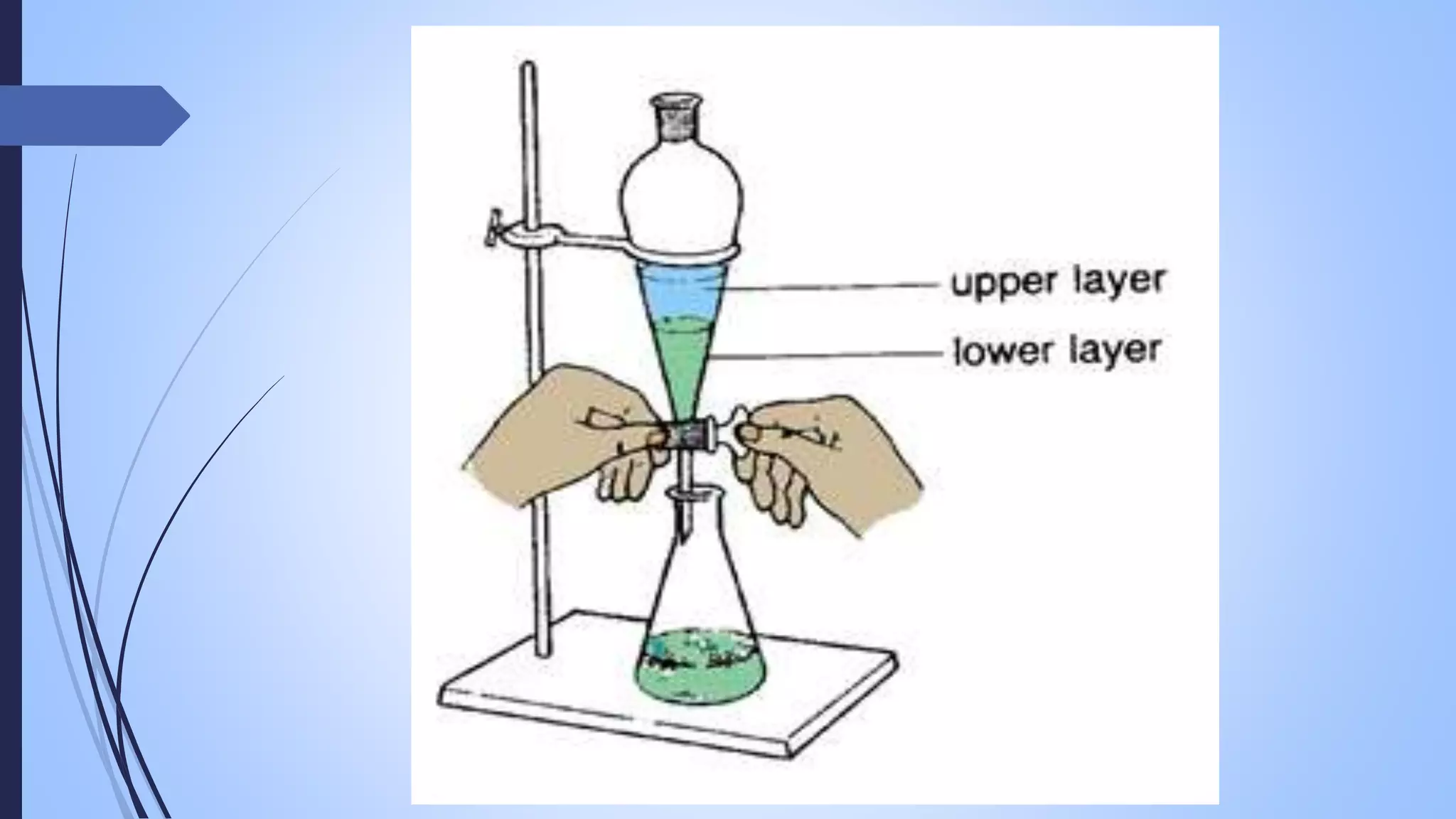
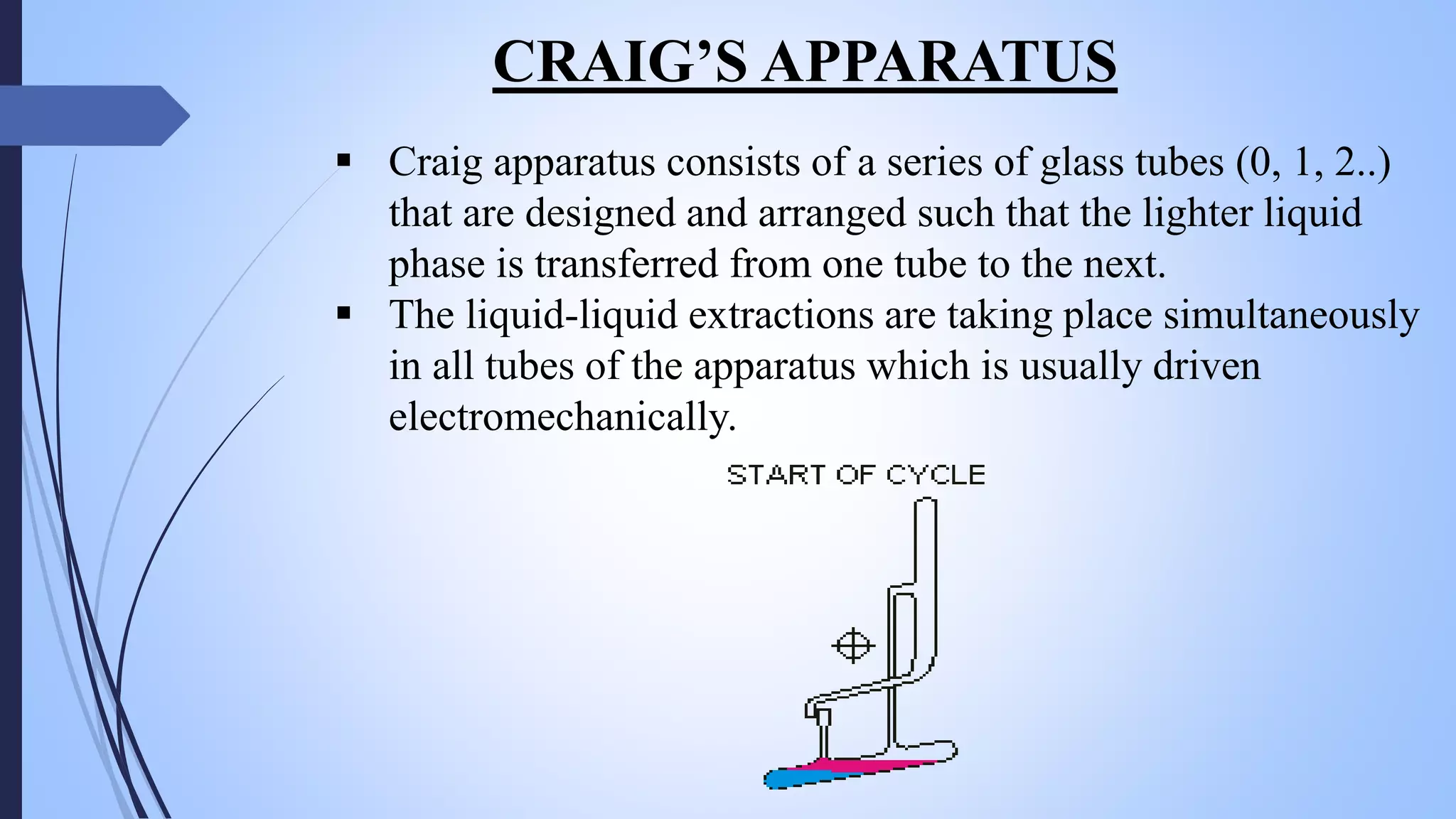
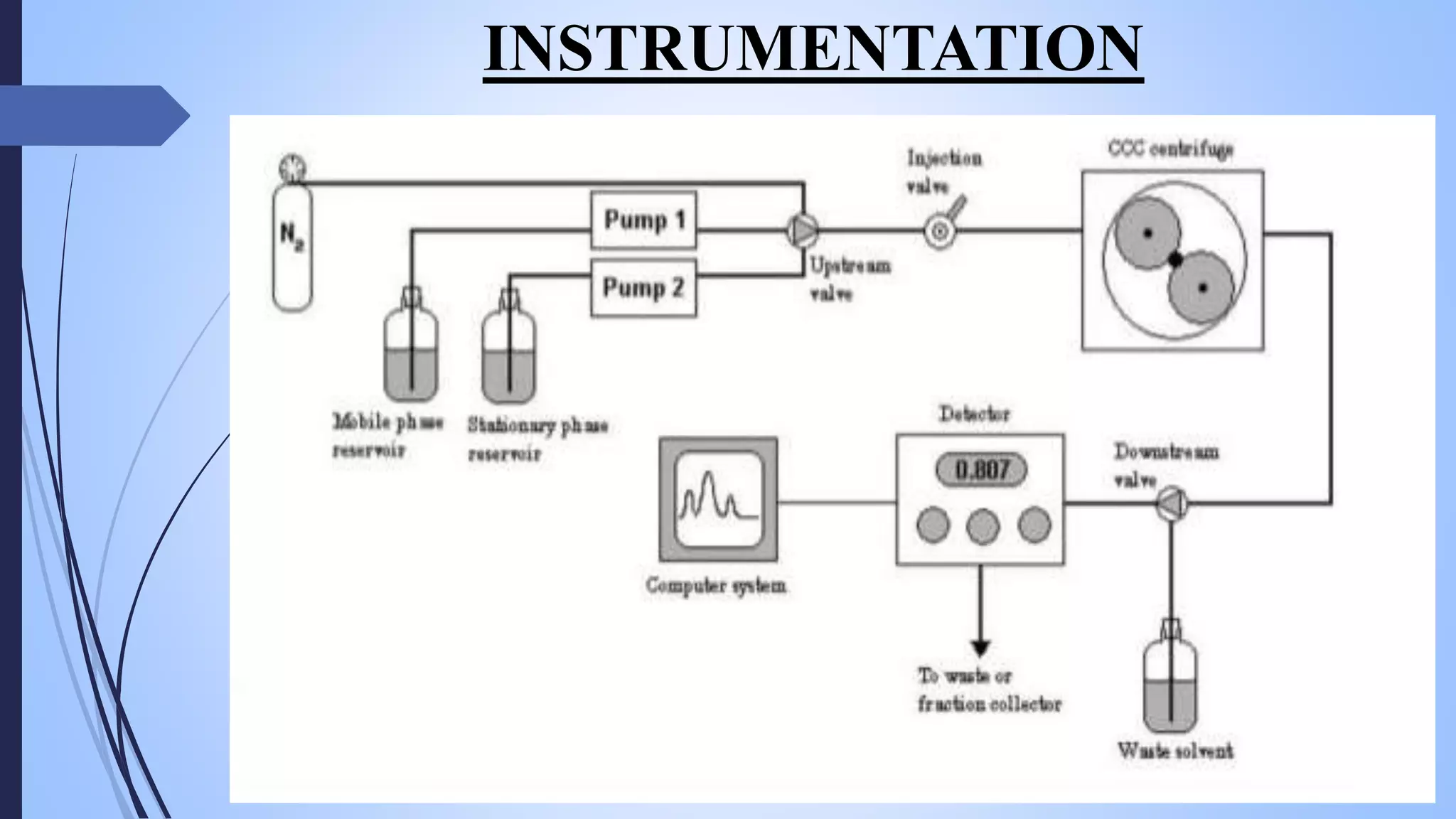
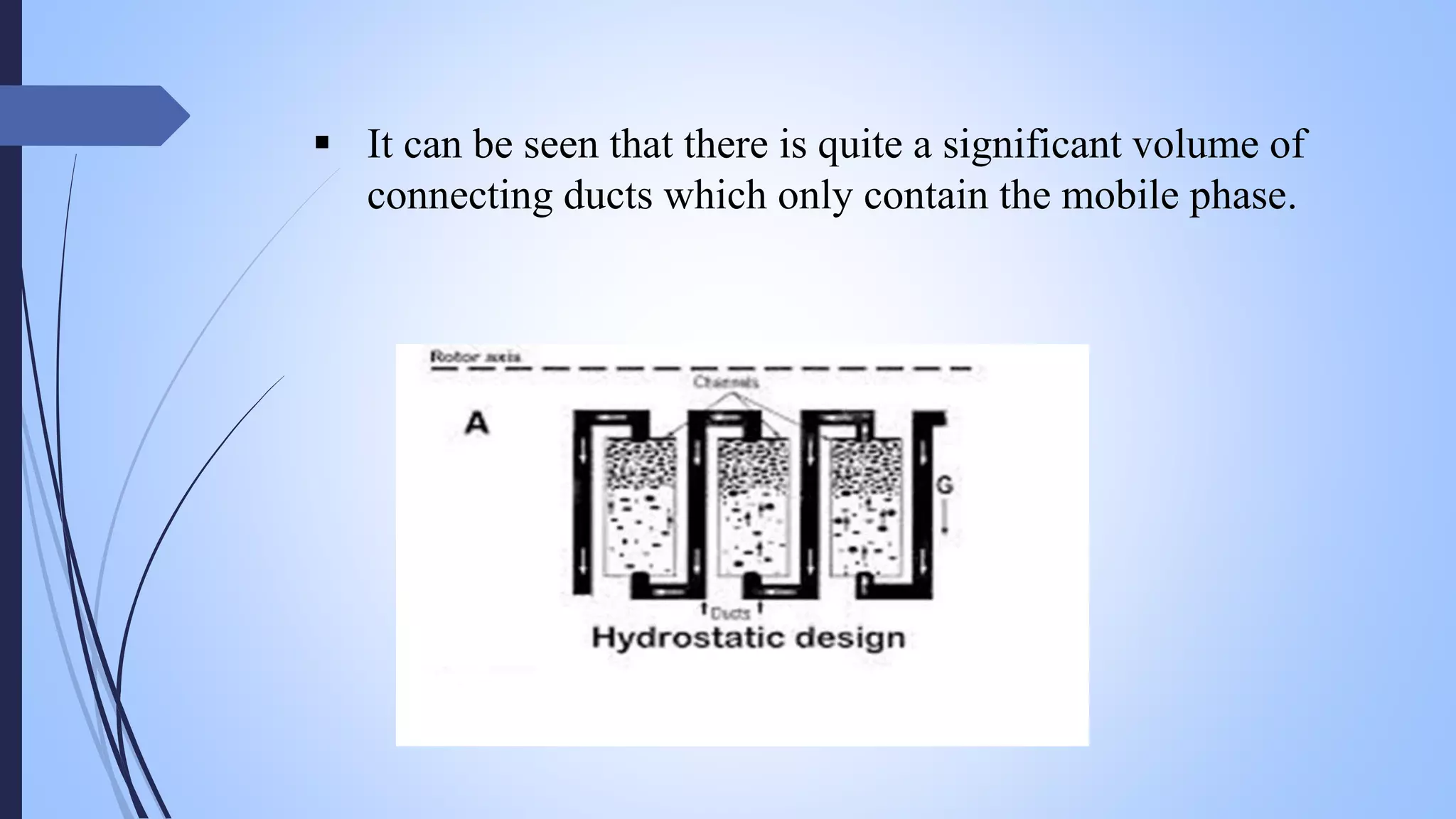
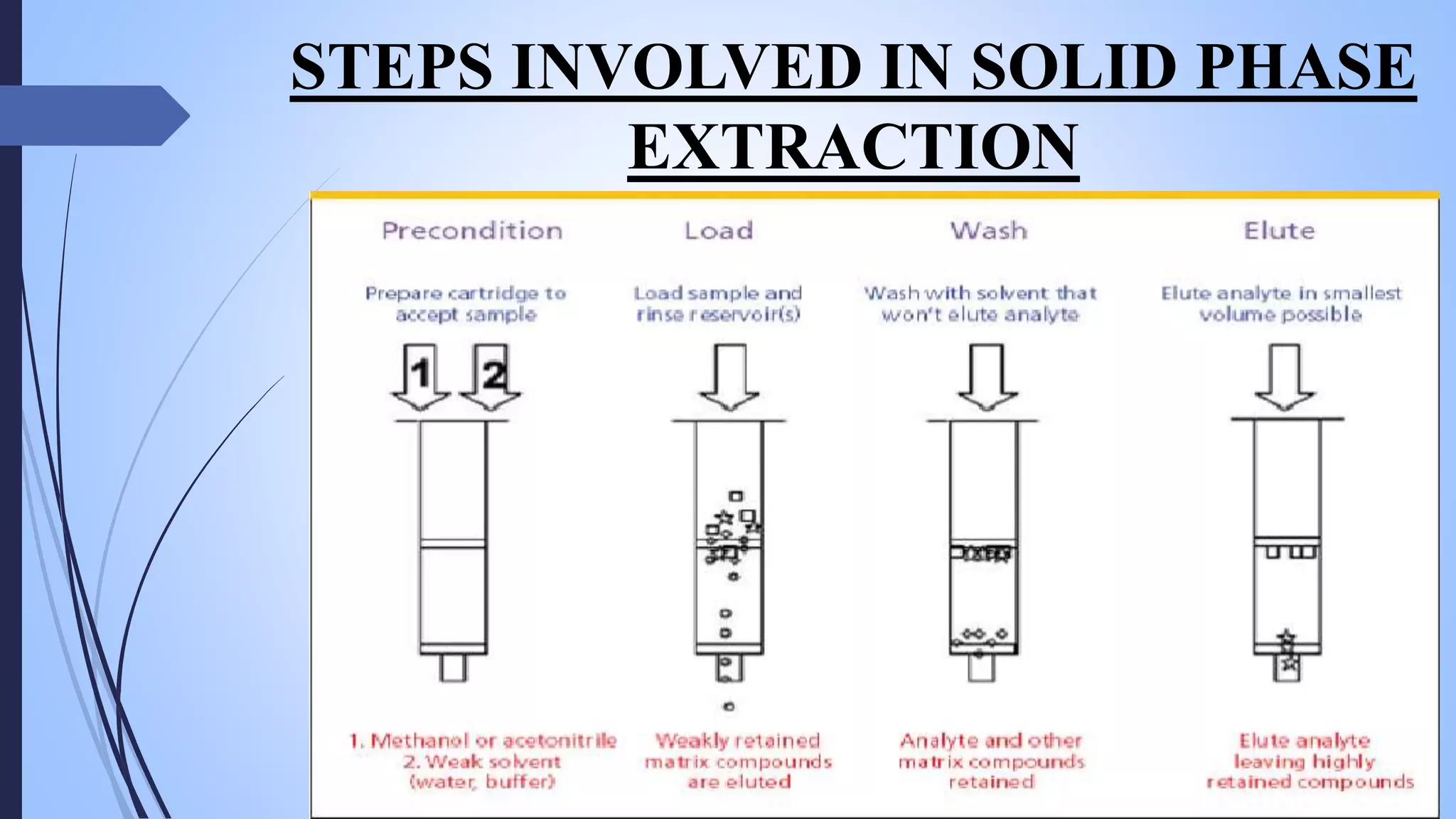
This document provides an overview of counter current extraction, solid phase extraction, and gel filtration chromatography techniques. It discusses the principles, processes, instrumentation, and applications of each technique. Counter current extraction uses a series of tubes to separate mixtures into phases based on solubility differences. Solid phase extraction isolates analytes from samples using adsorption onto a solid phase. Gel filtration separates molecules based on size by allowing larger molecules to pass through column pores. Each technique has advantages for analytical separations and preparative isolation of compounds from complex mixtures.