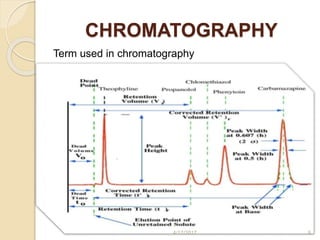
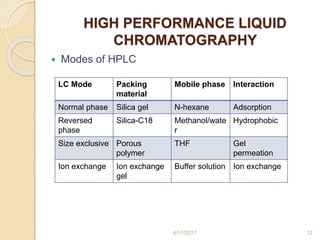
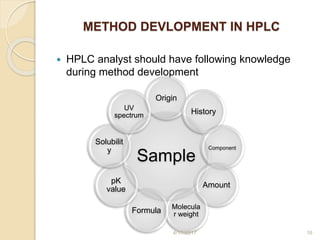
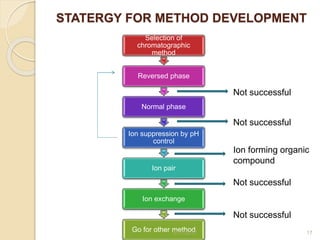
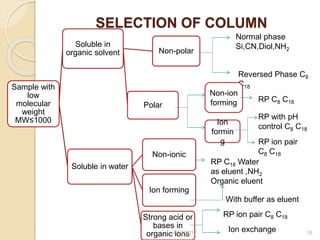
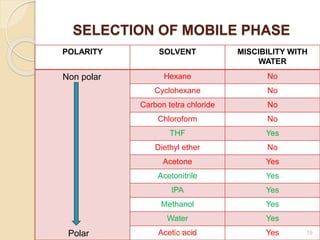
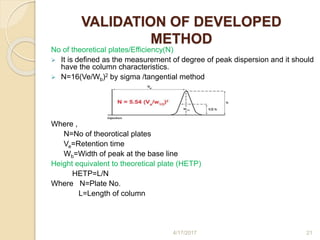
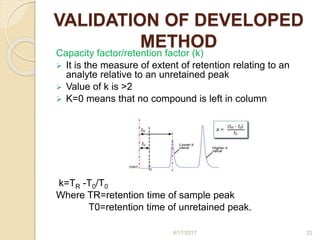
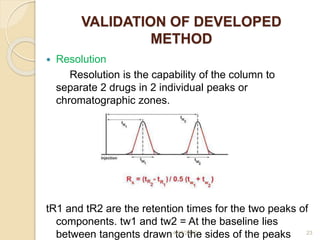
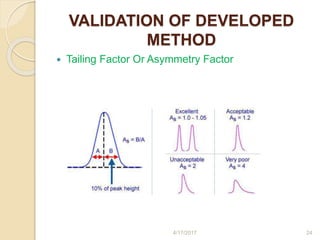
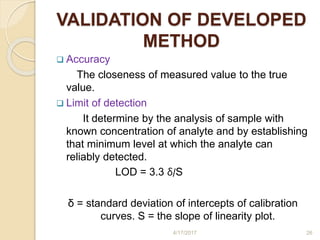
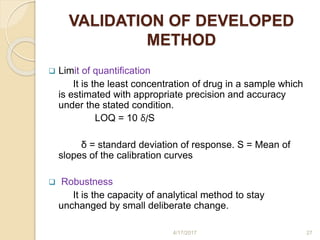
This document presents information on HPLC method development and validation. It begins with an introduction to analytical chemistry and chromatography. It then discusses the principles, types, and modes of HPLC, as well as factors to consider in method development such as column selection and mobile phase selection. The document concludes with a discussion of method validation parameters such as system suitability, specificity, linearity, precision, accuracy, limit of detection, limit of quantification, and robustness. References on the topic are also provided.