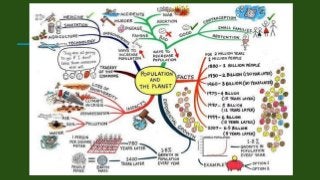
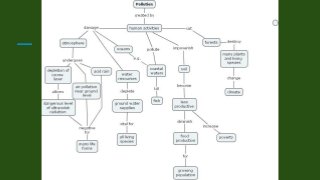
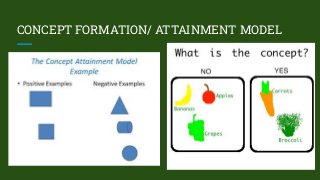
The document discusses the concept and techniques of set induction, emphasizing its importance in preparing students for learning by connecting new ideas to their prior knowledge. It outlines various methods for effectively introducing lessons, such as asking lower-order questions, using demonstrations, and employing multimedia resources. Additionally, it highlights the significance of engaging students through storytelling, role play, and audio-visual aids to enhance understanding across subjects.