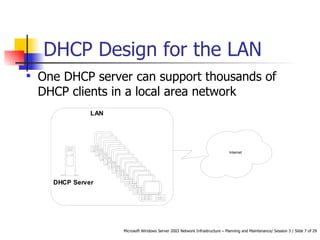
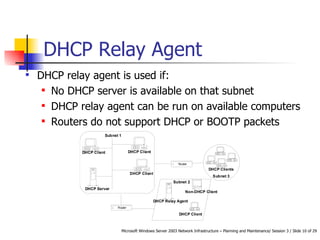
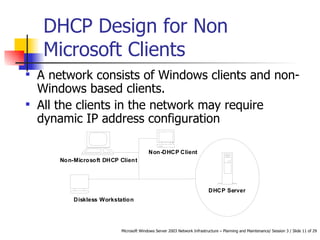
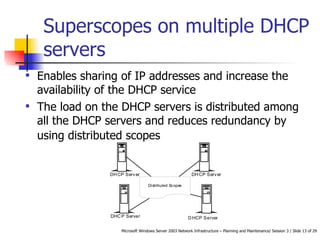
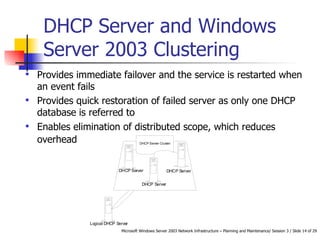
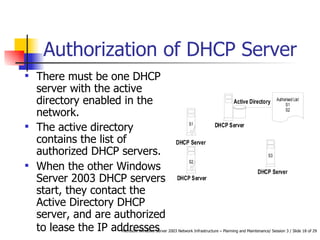
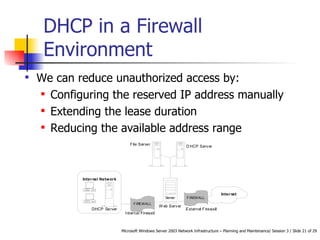
DHCP automates the allocation of IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, and other network configuration parameters. It uses four messages - DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPOFFER, DHCPREQUEST, DHCPACK - to allocate addresses dynamically or statically. DHCP can be designed for LANs, routed networks, and non-Microsoft clients. It enhances availability through features like superscopes across multiple servers and Windows Server 2003 clustering. Security involves authorizing servers, controlling access, and using firewalls. Performance is increased by shortening response times, distributing load across servers, and optimizing lease times.