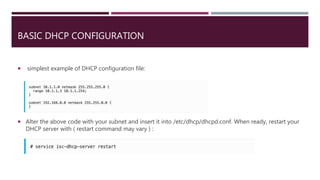
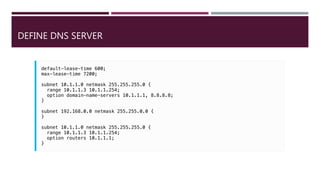
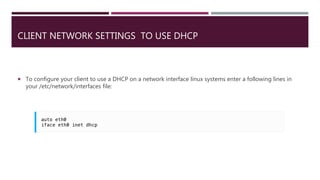
DHCP is a protocol that dynamically assigns IP addresses and other network configuration parameters to clients on a network. It allows for centralized management of IP addresses and helps conserve IP addresses. A DHCP server manages pools of IP addresses and related configurations to hand out to DHCP client software installed on other devices on the network to automatically obtain IP addresses and other networking settings as needed. A DHCP relay agent can help extend DHCP services to remote subnets that don't have direct access to the DHCP server.