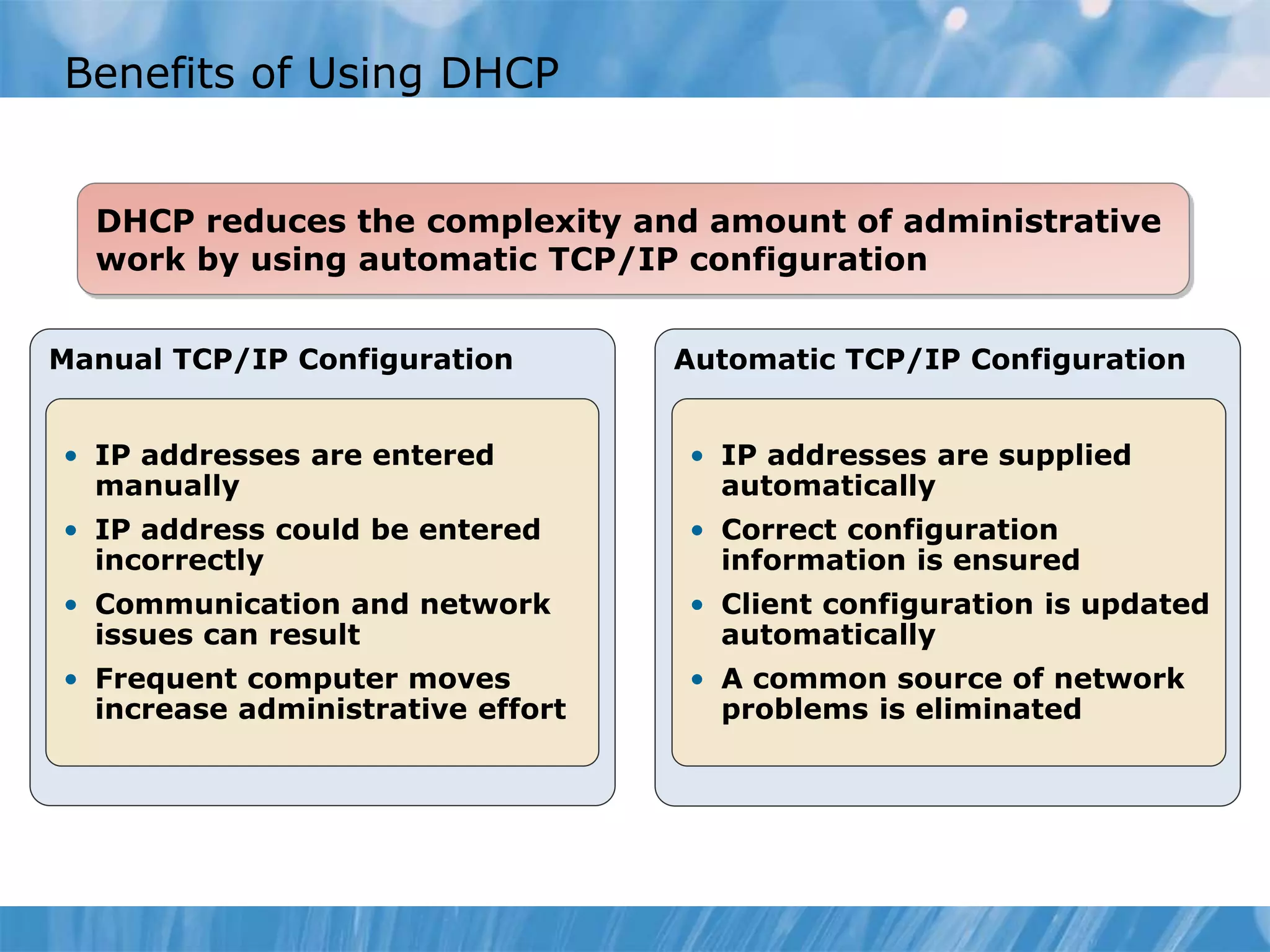
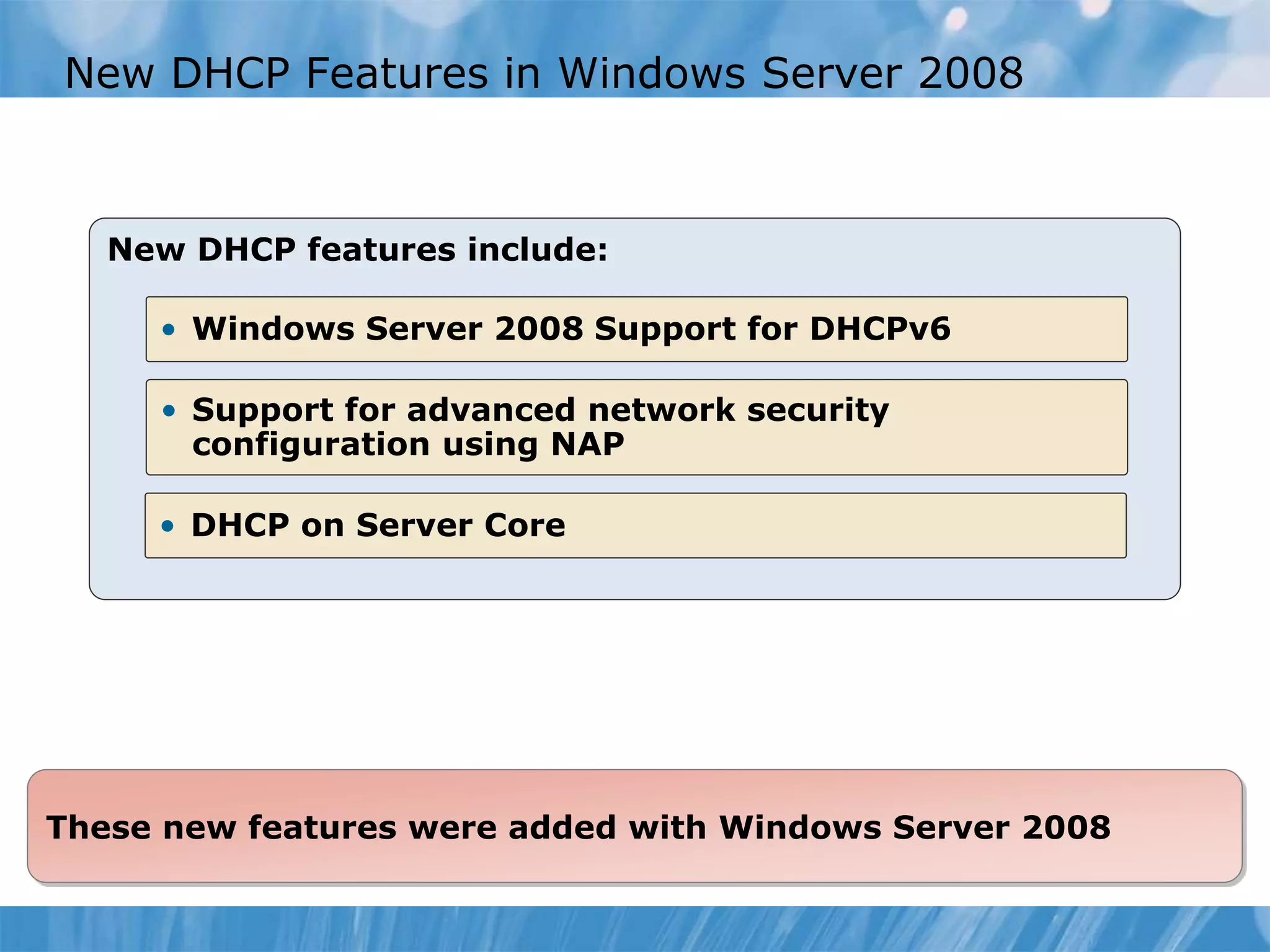
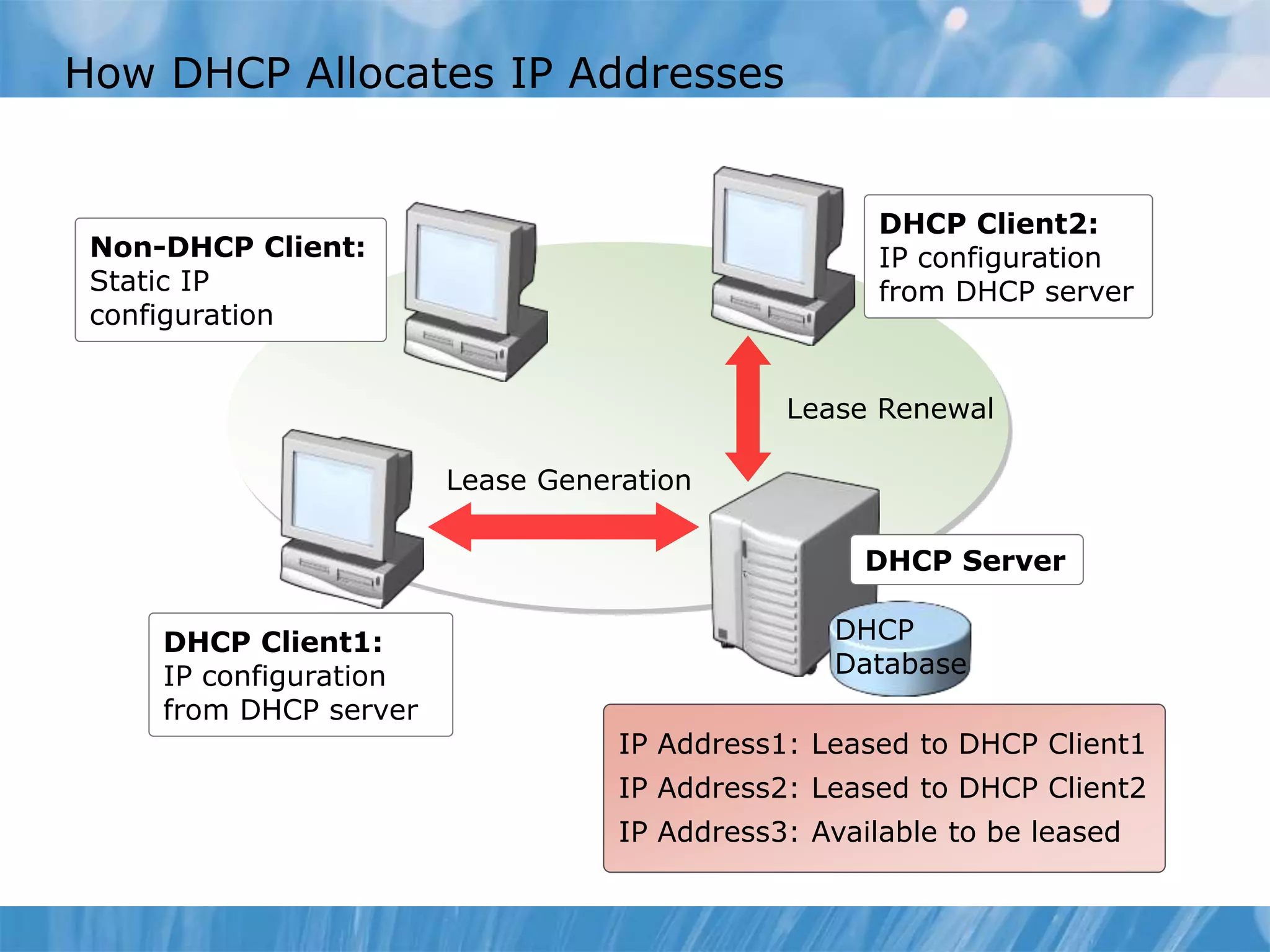
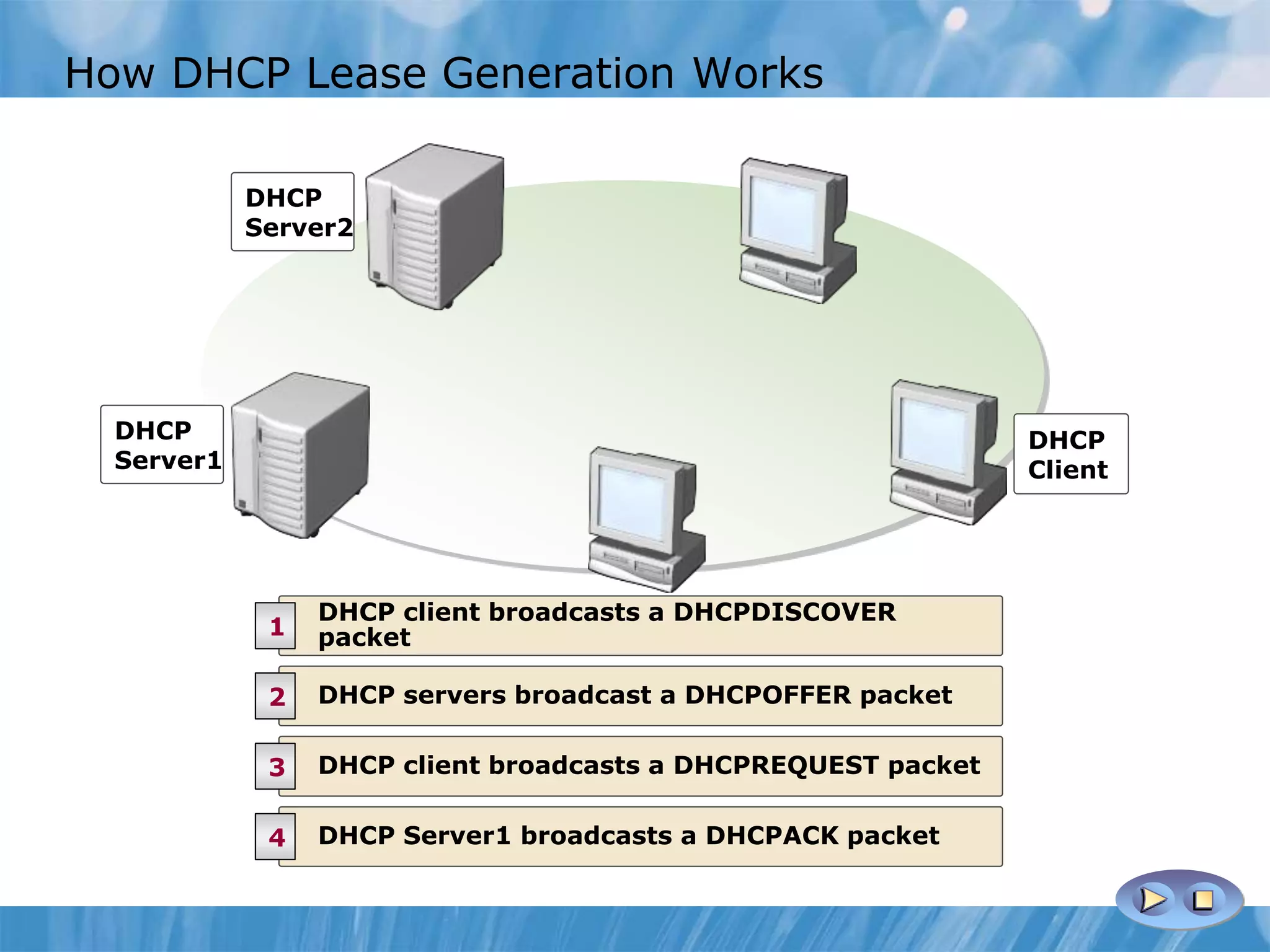
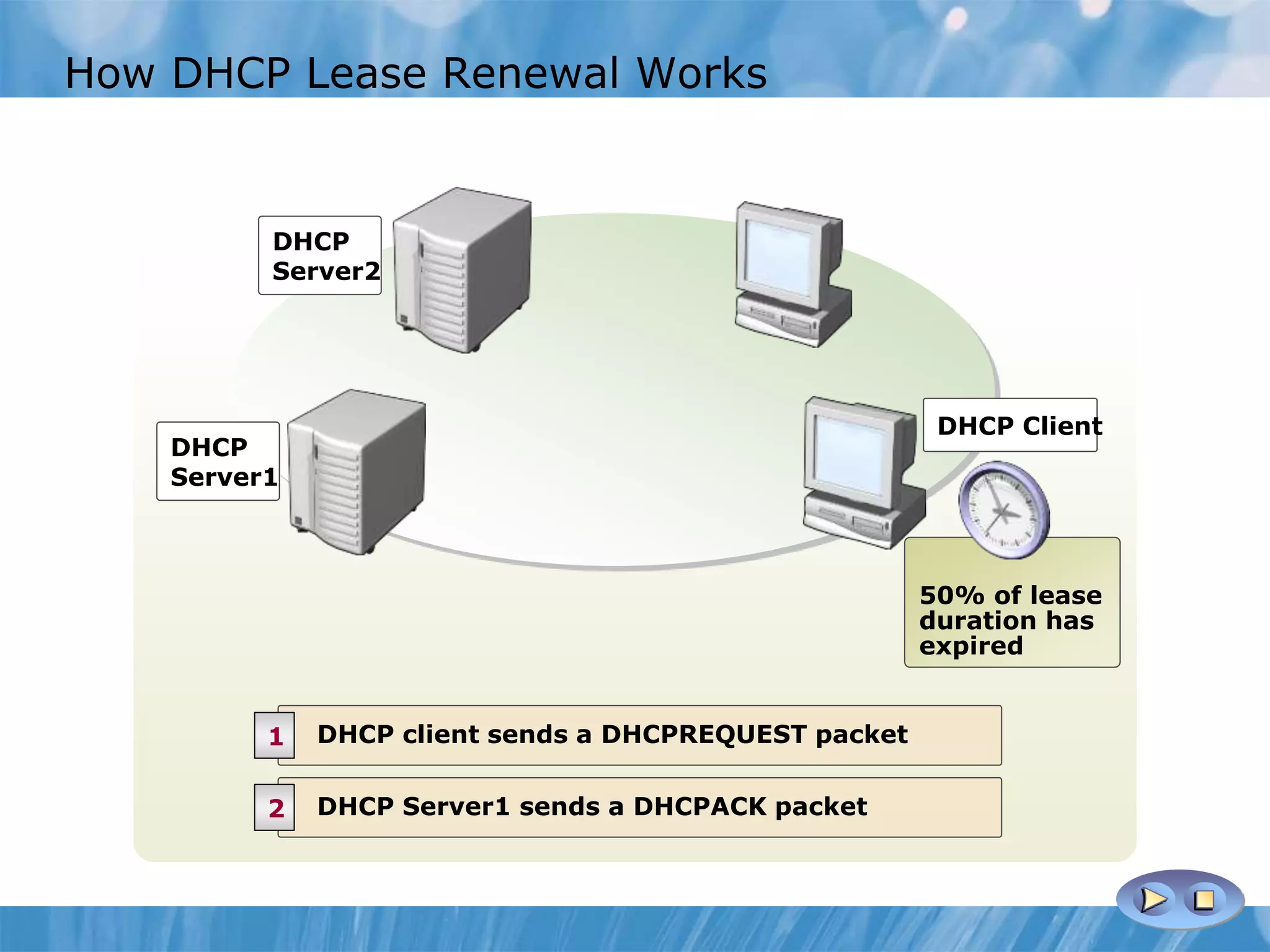
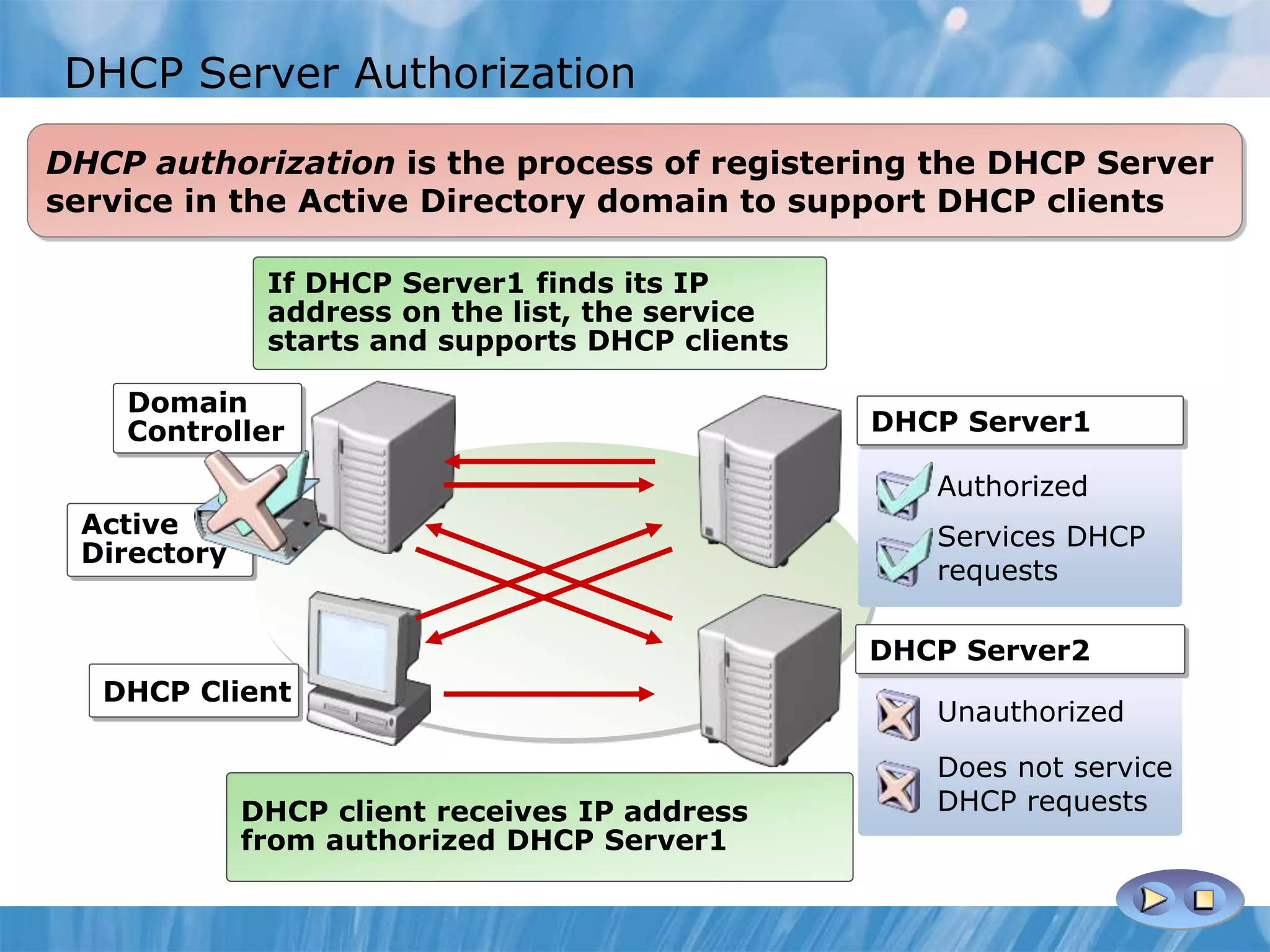
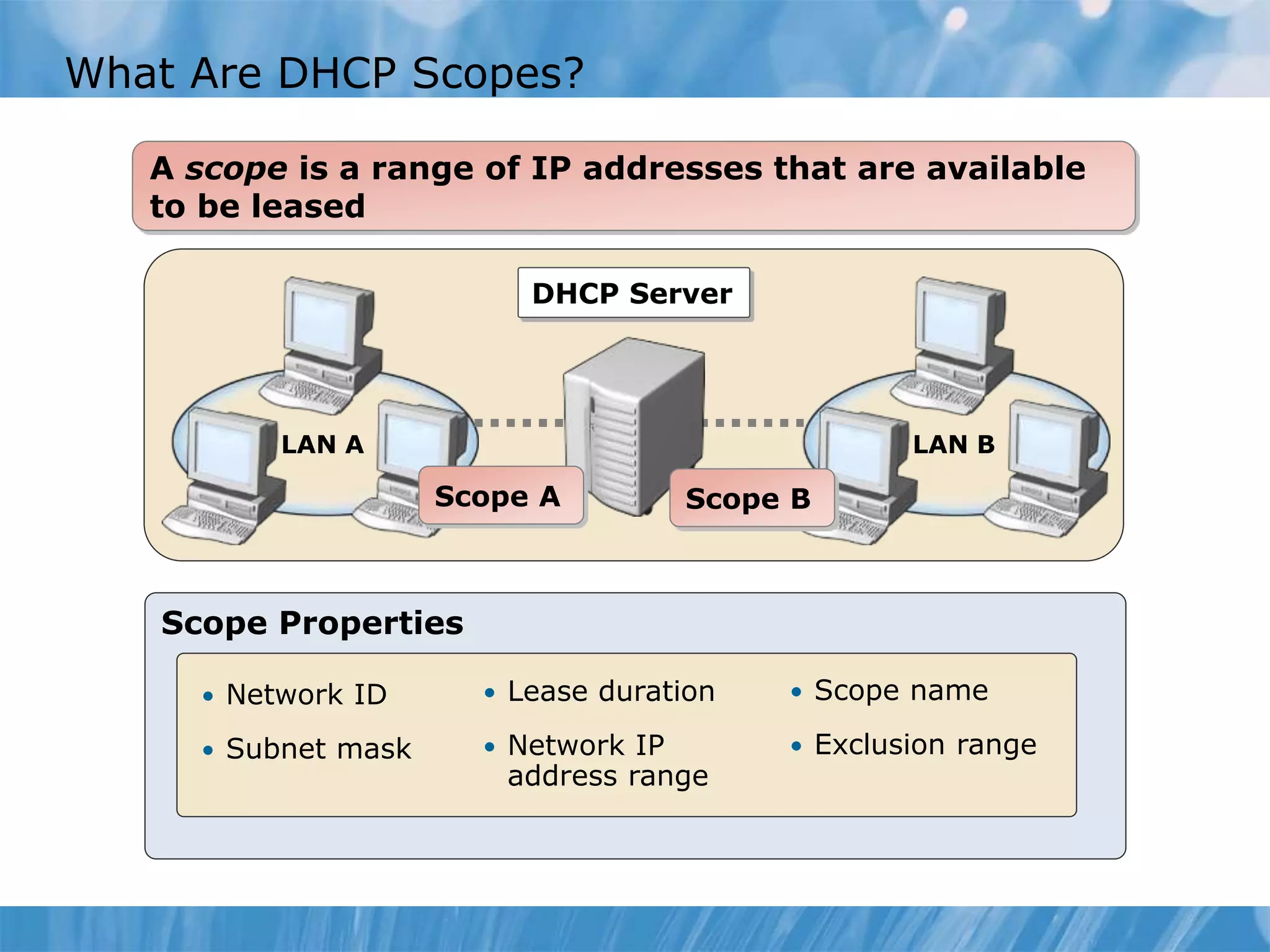
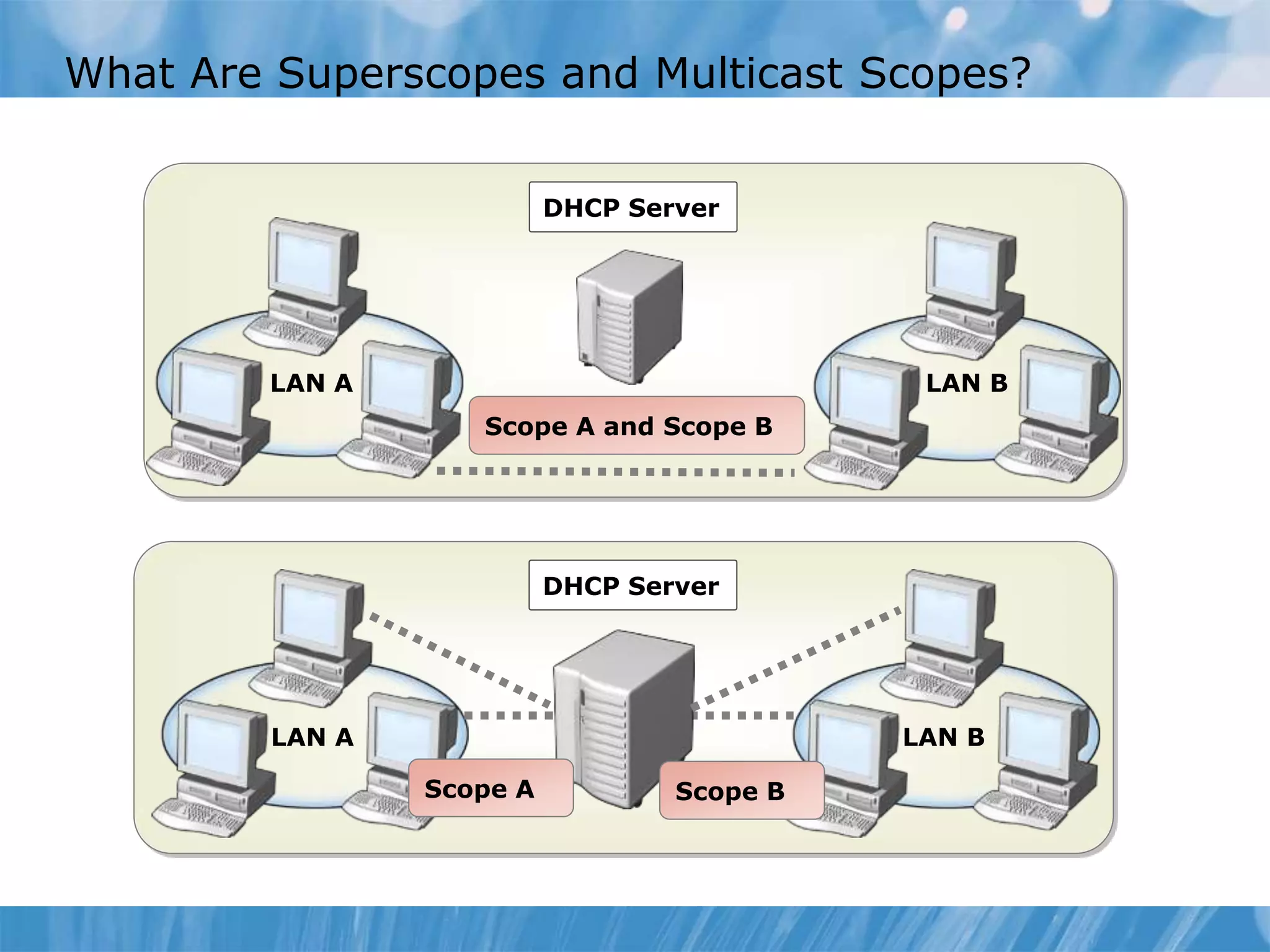
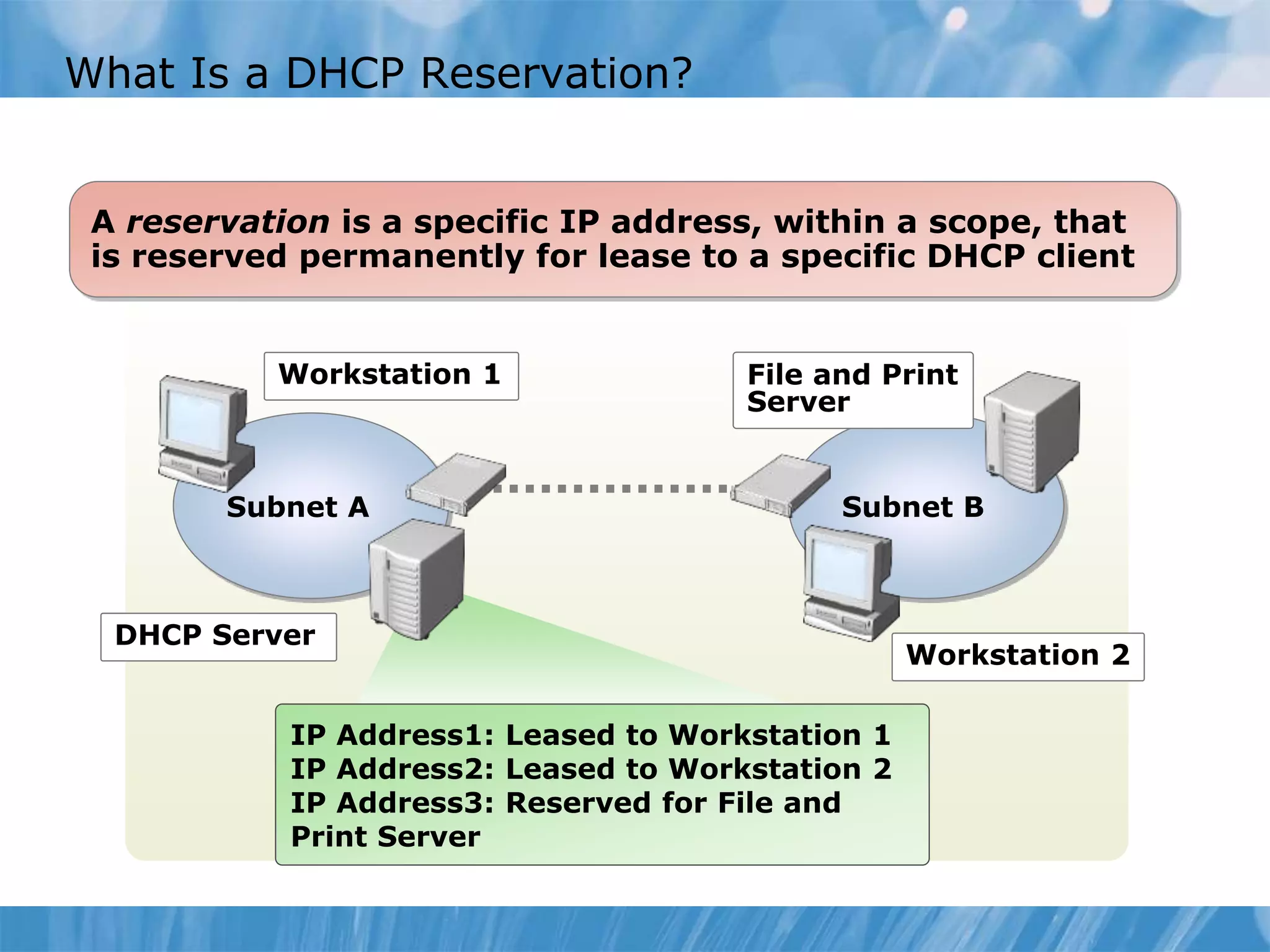
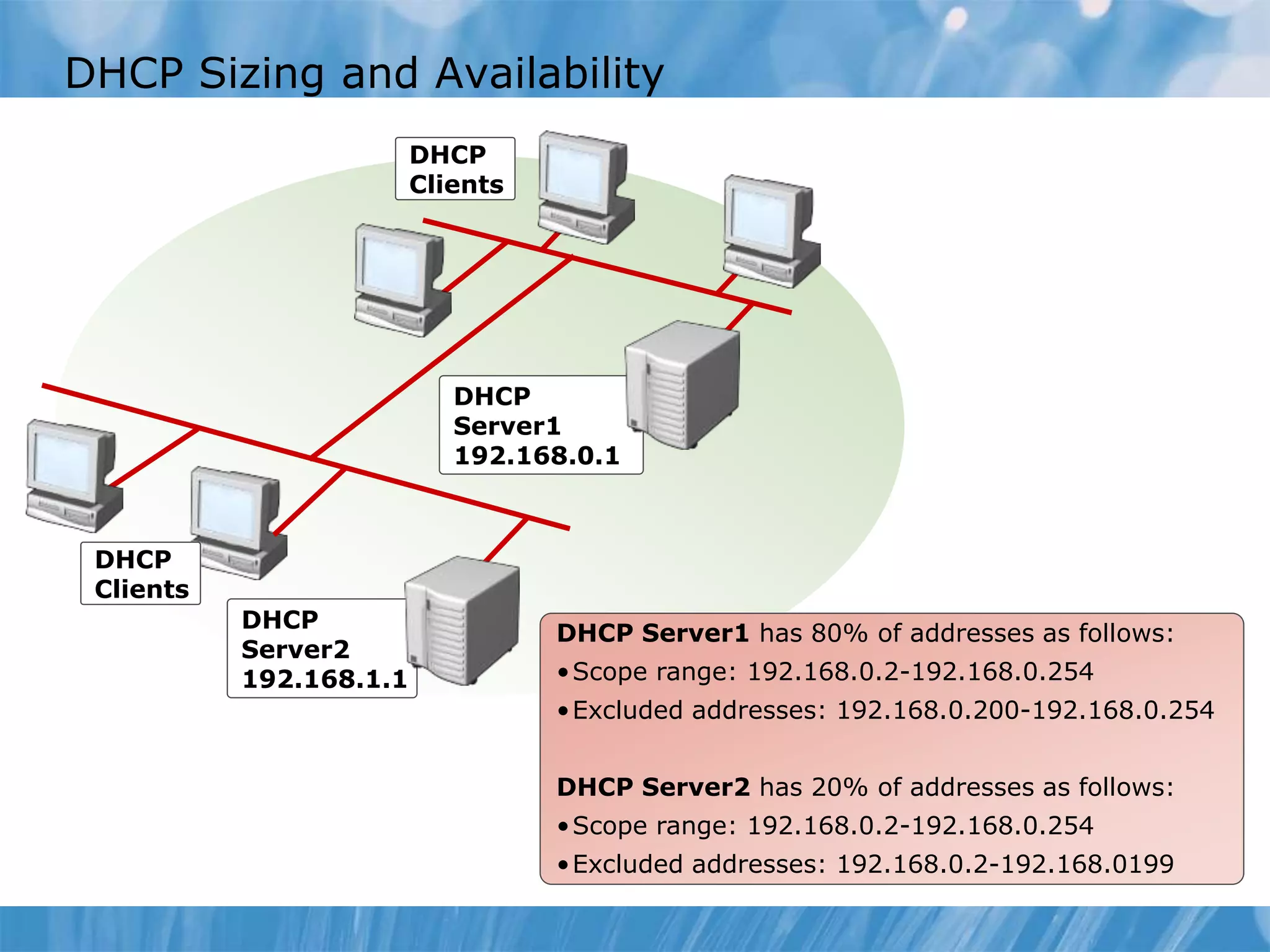
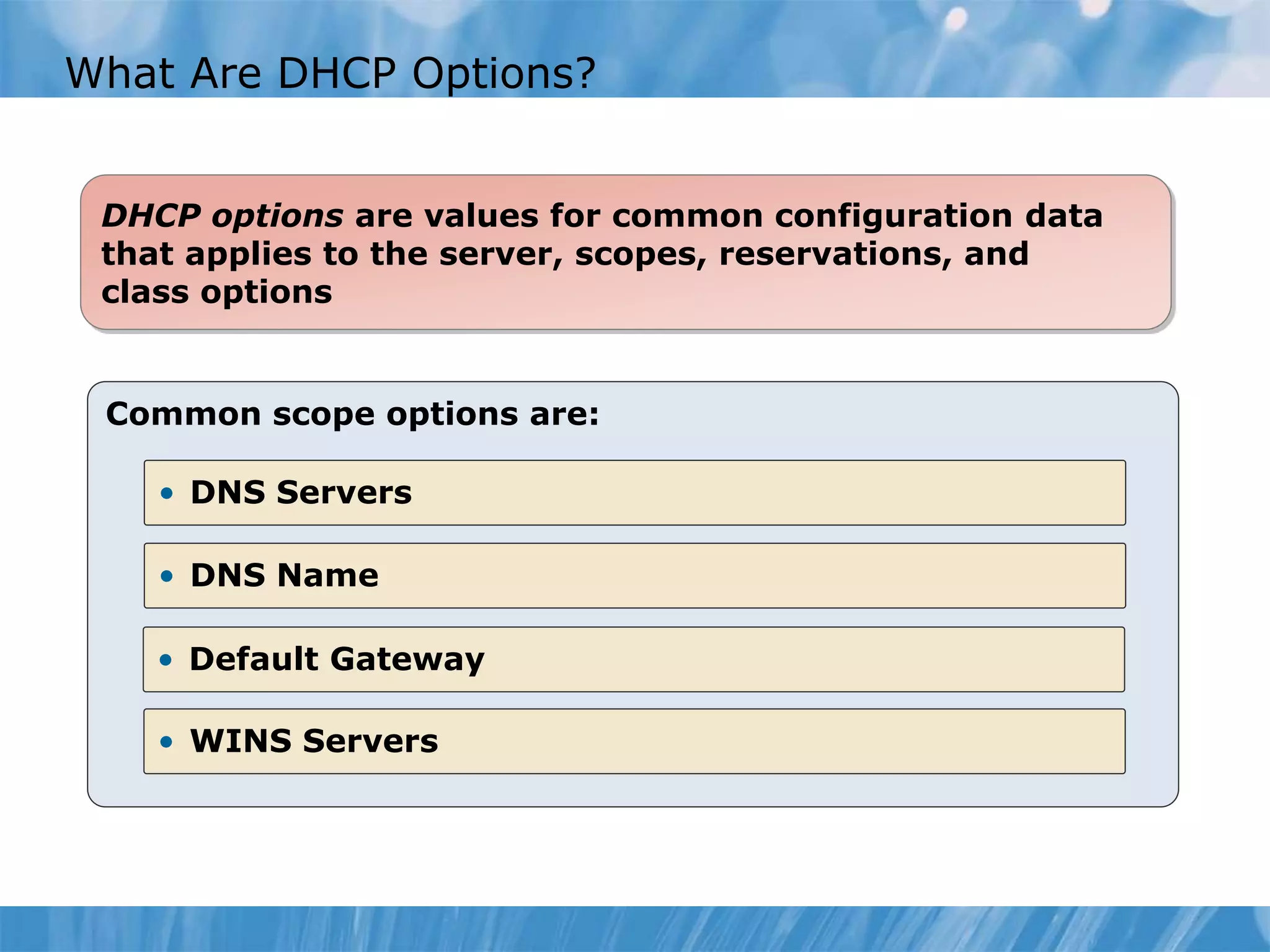
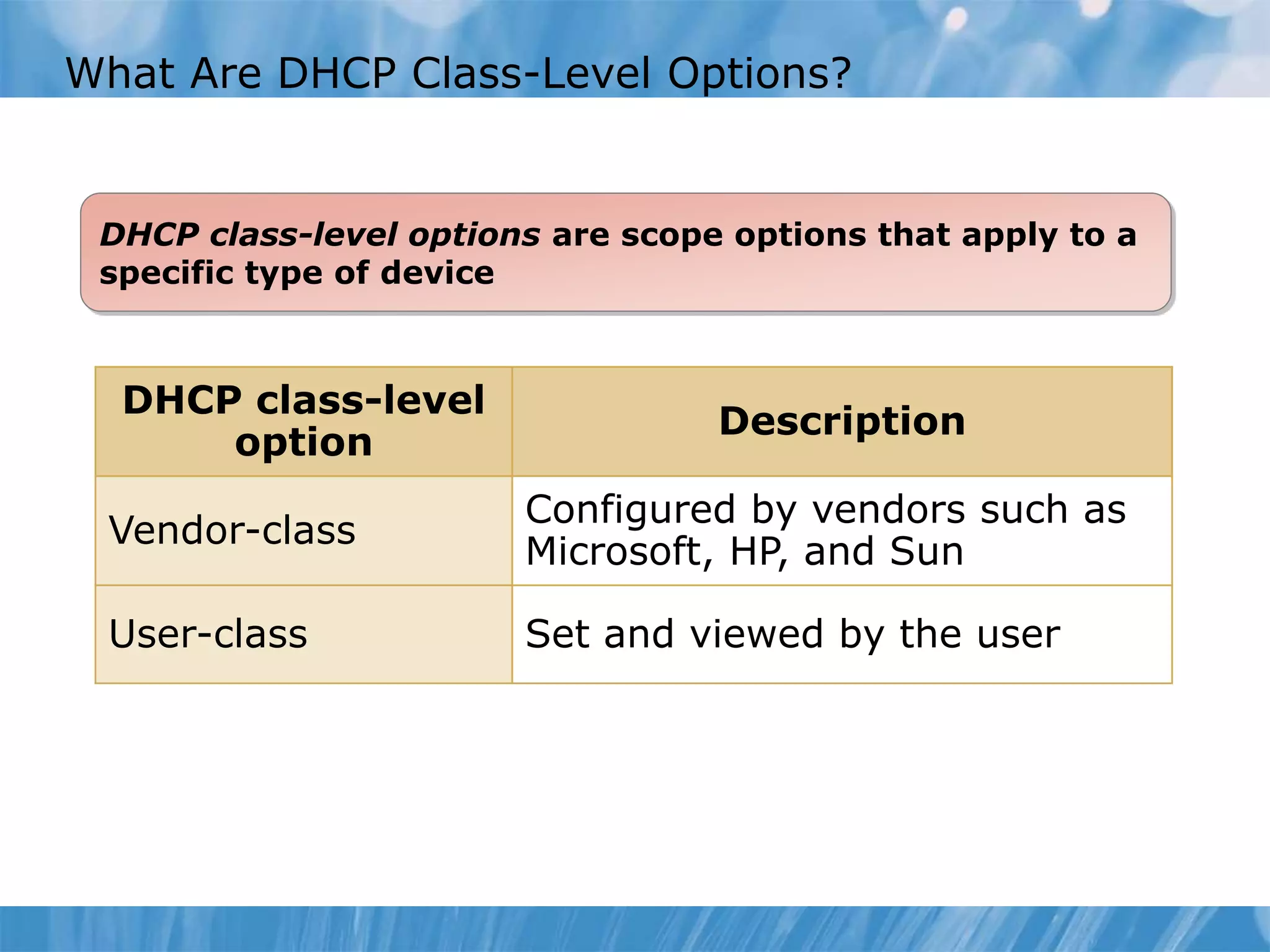
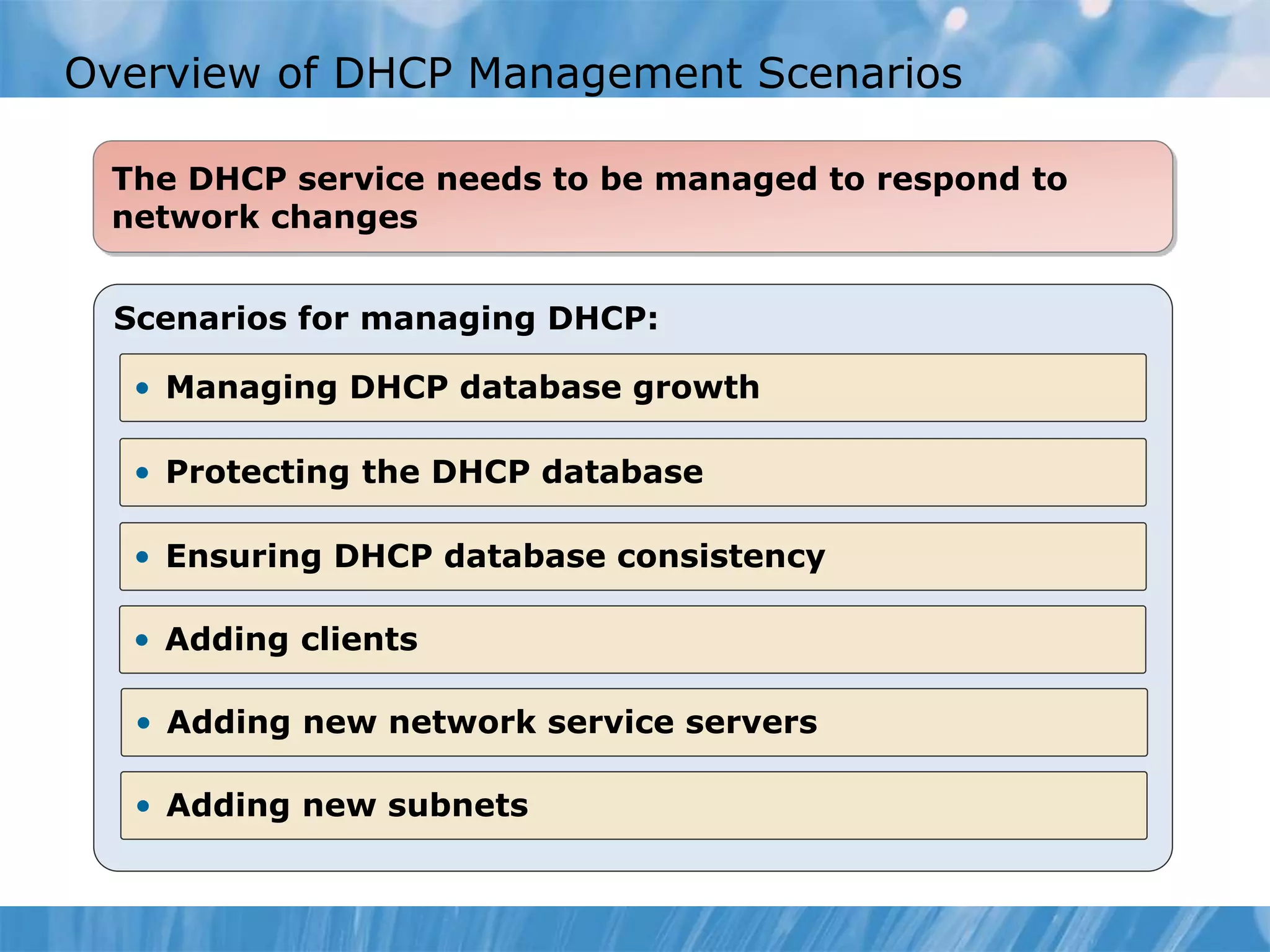
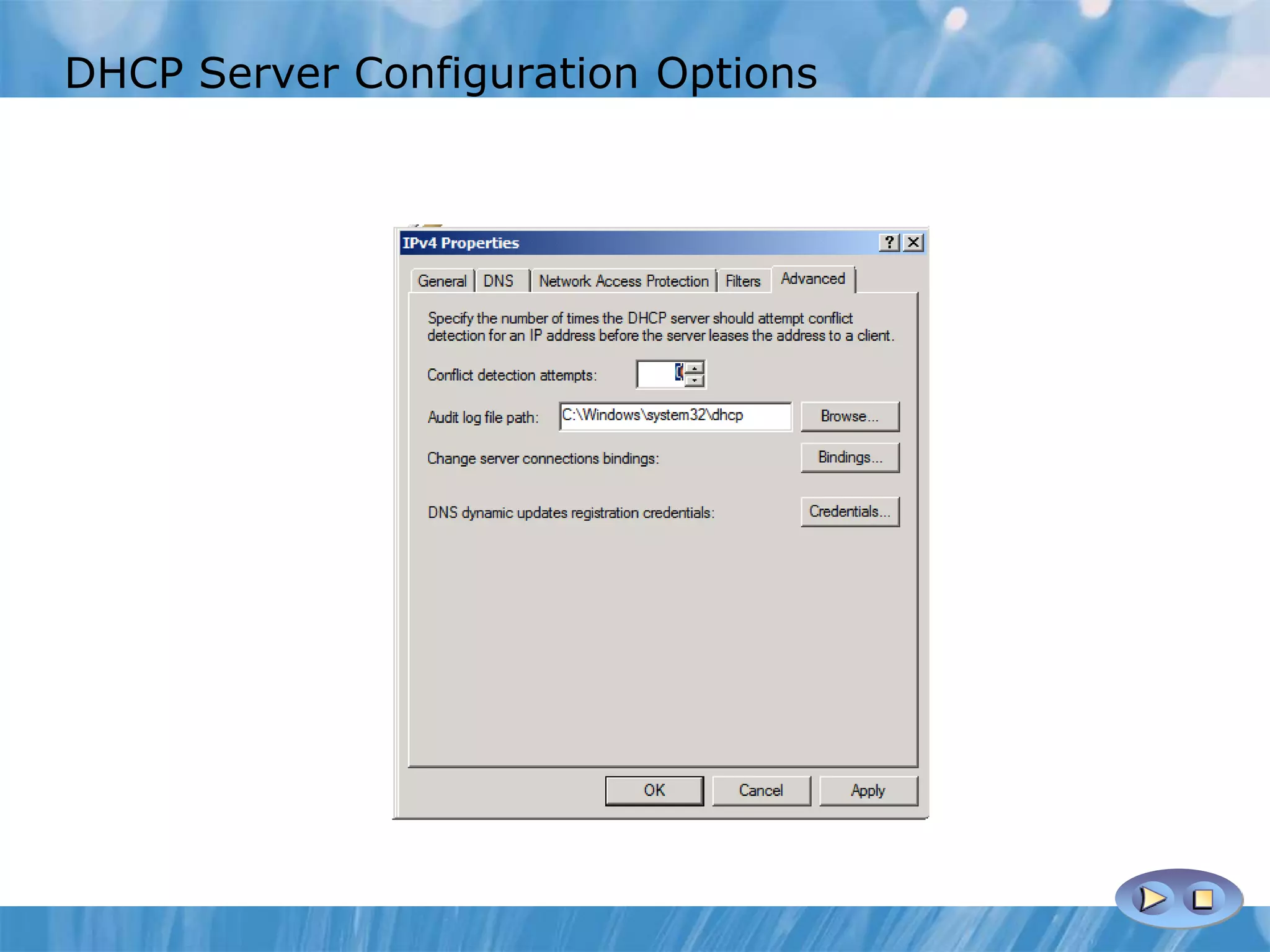
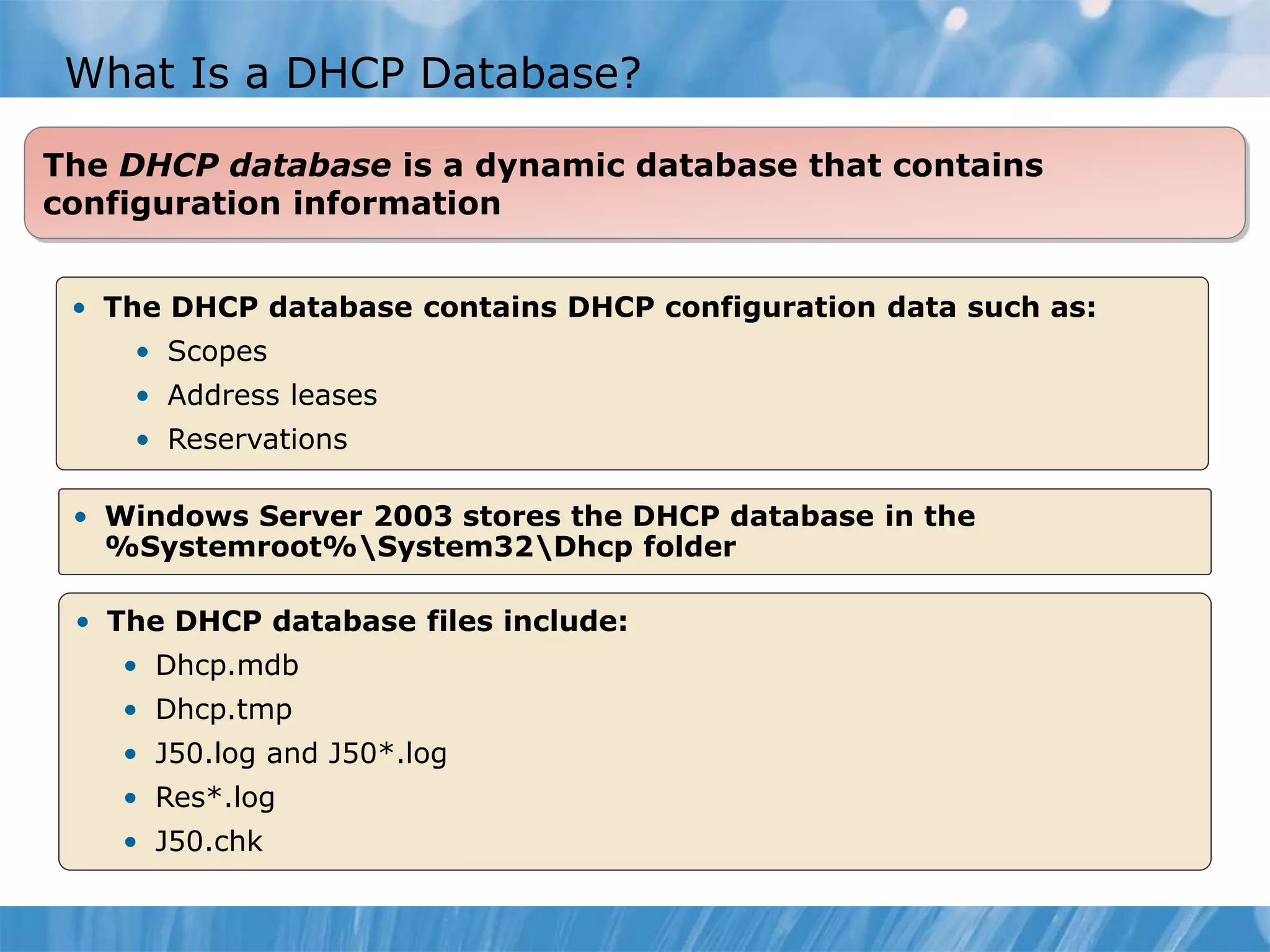
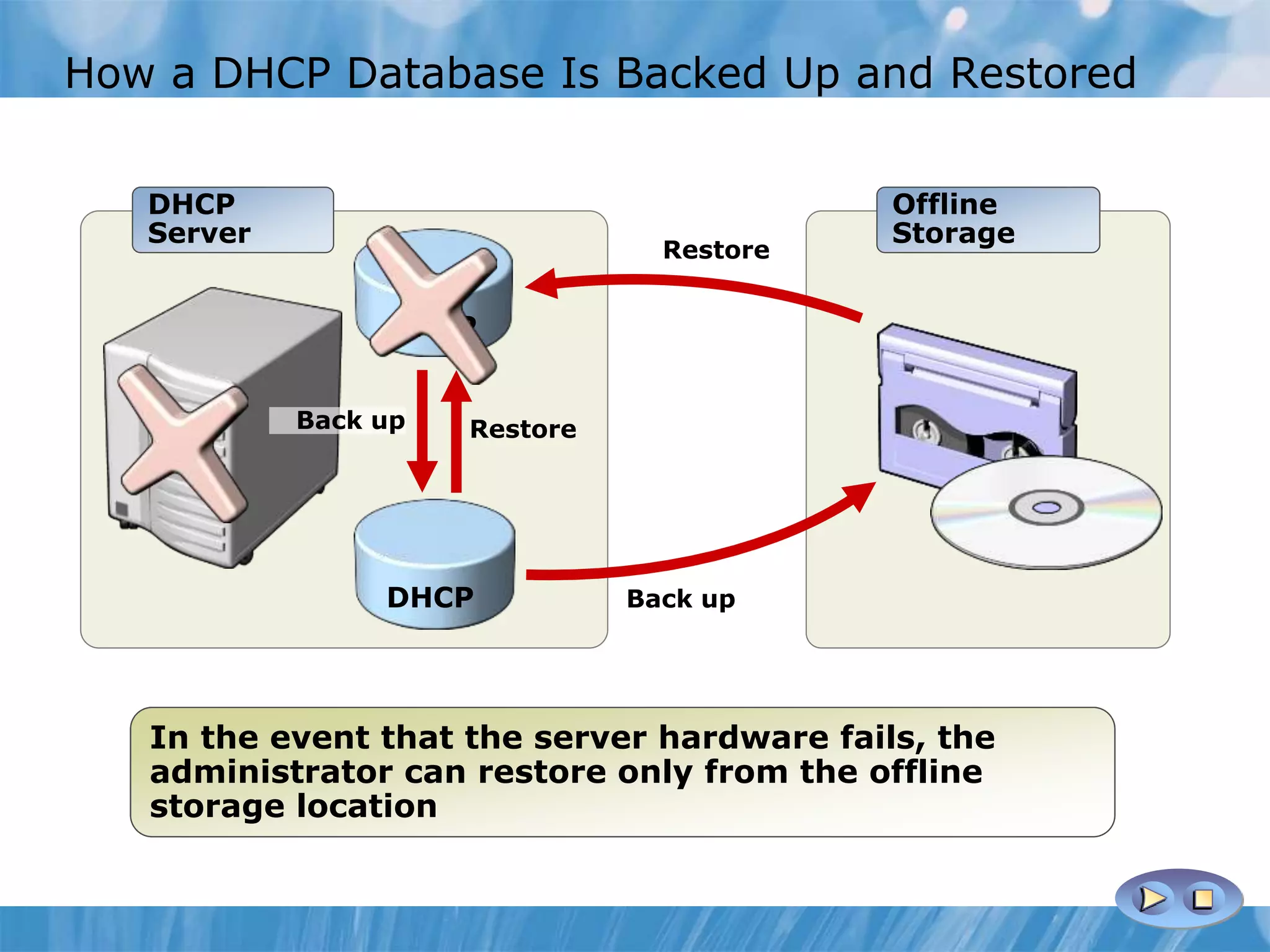
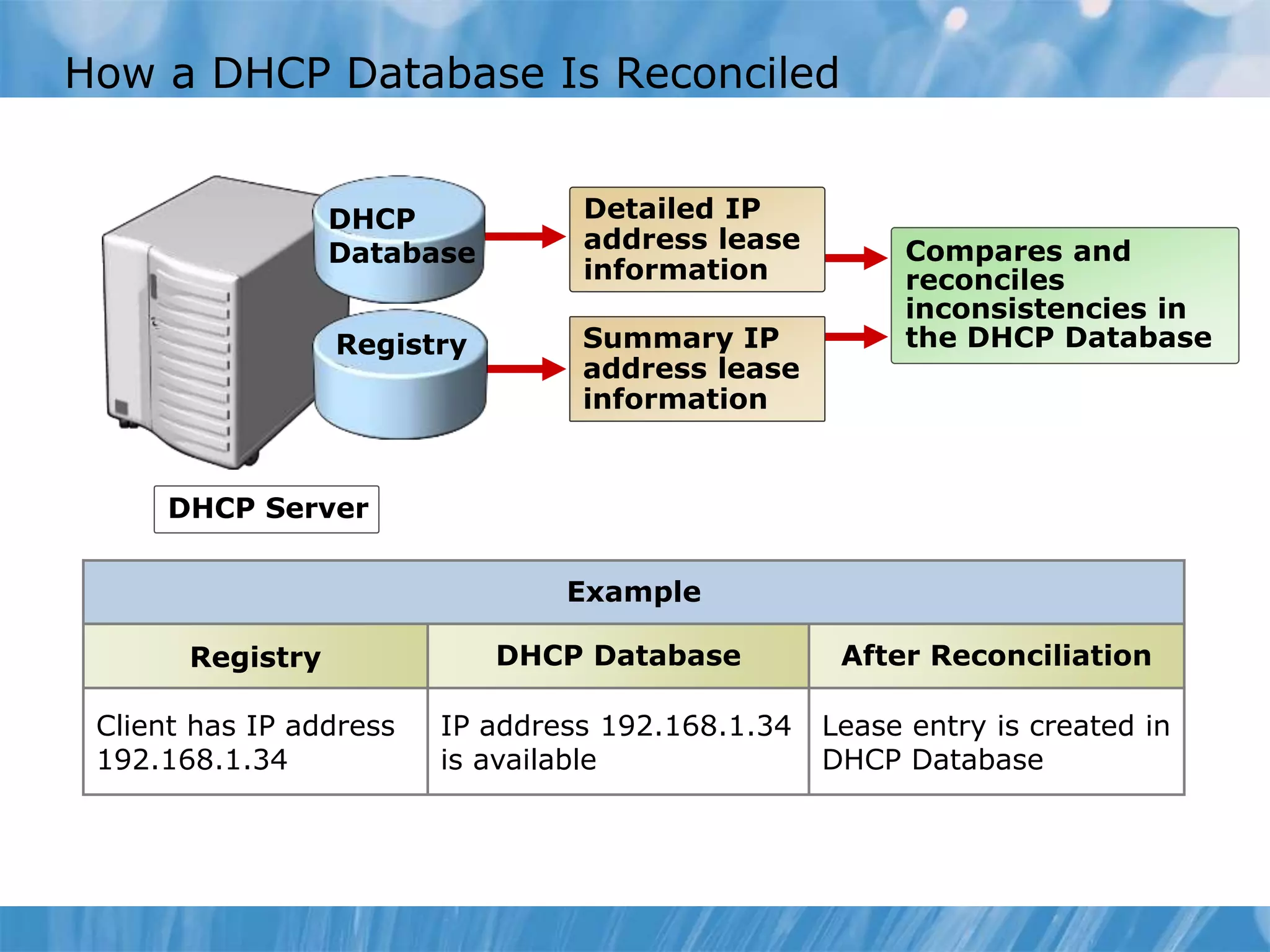
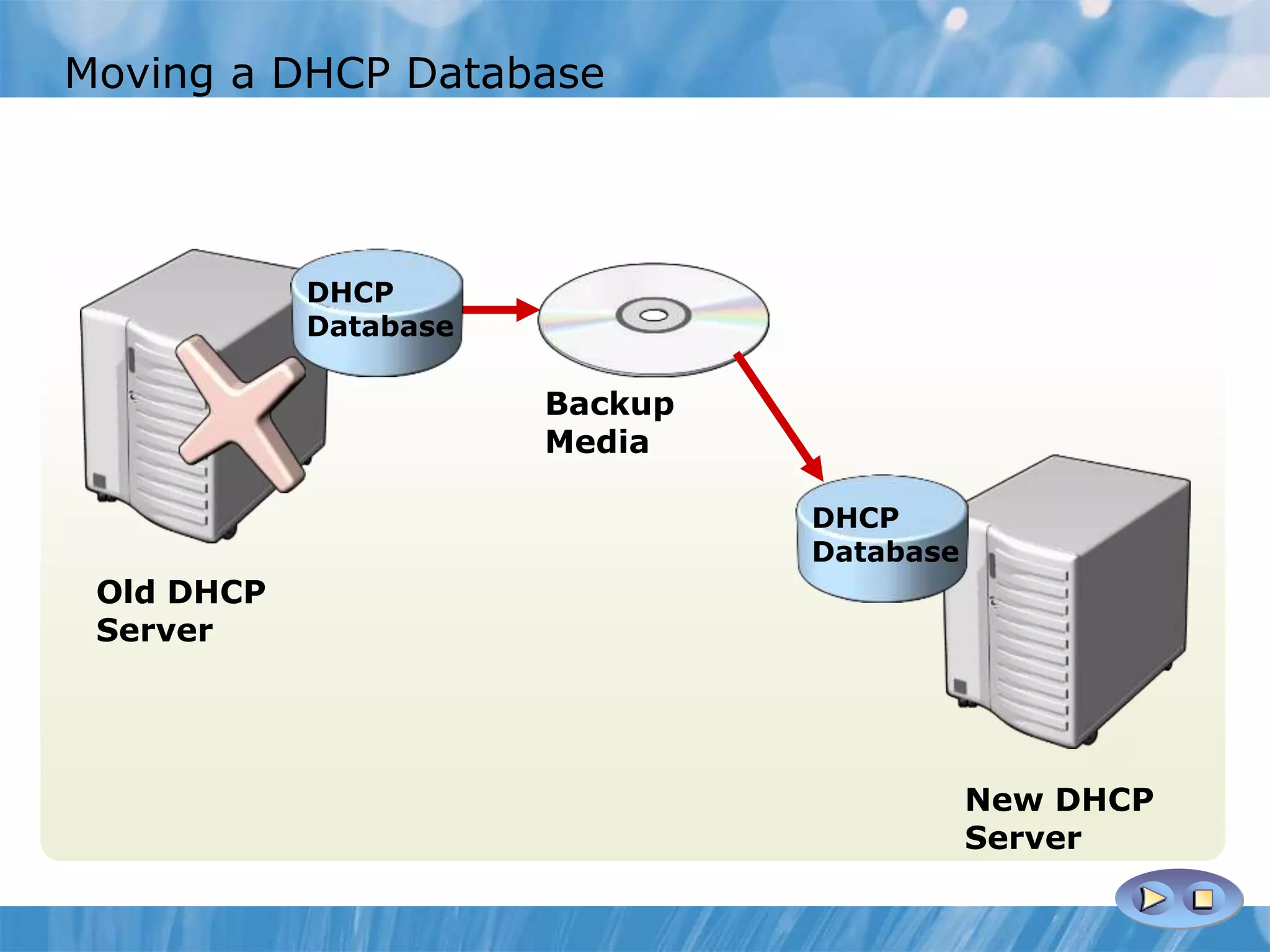
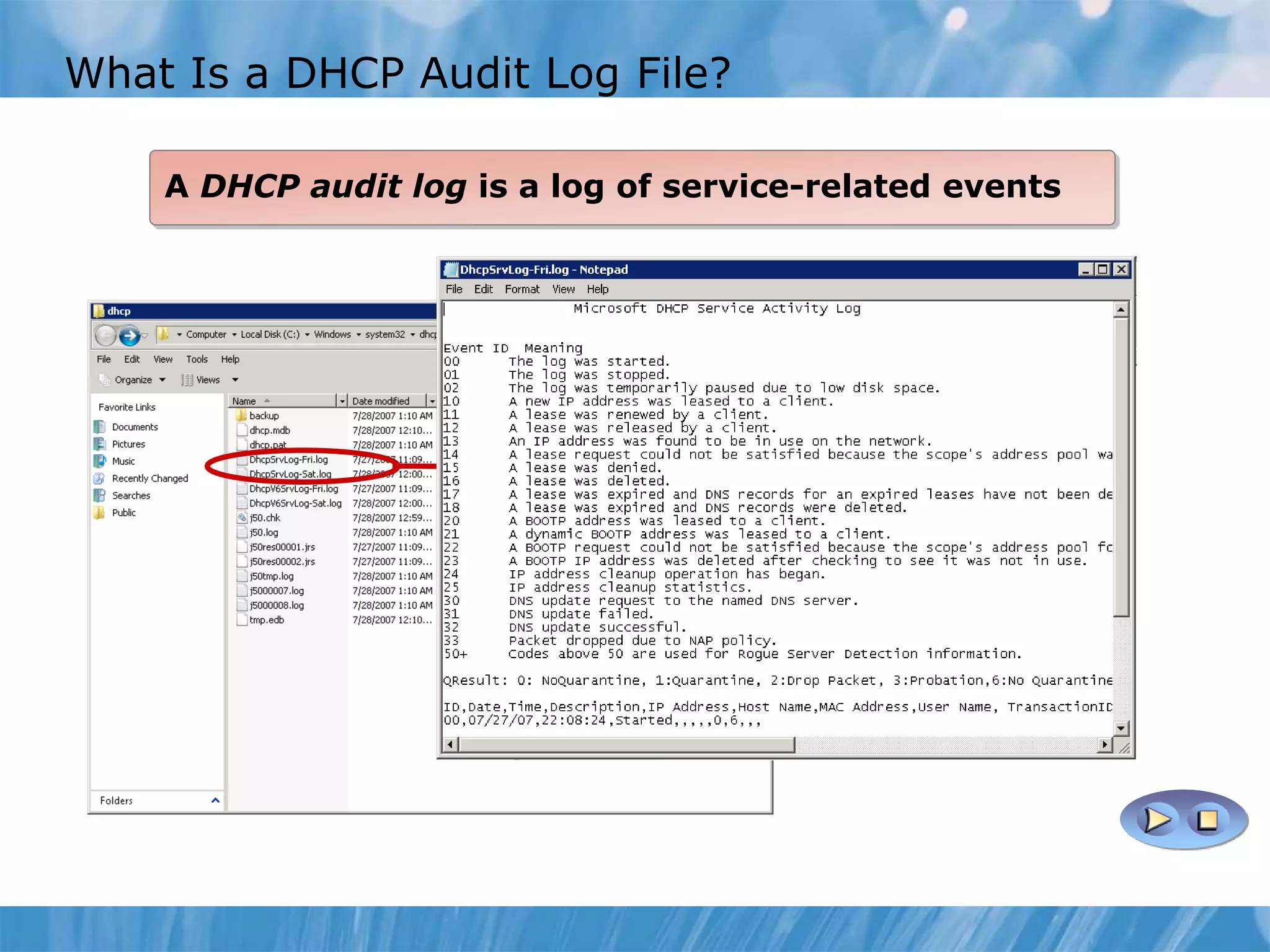
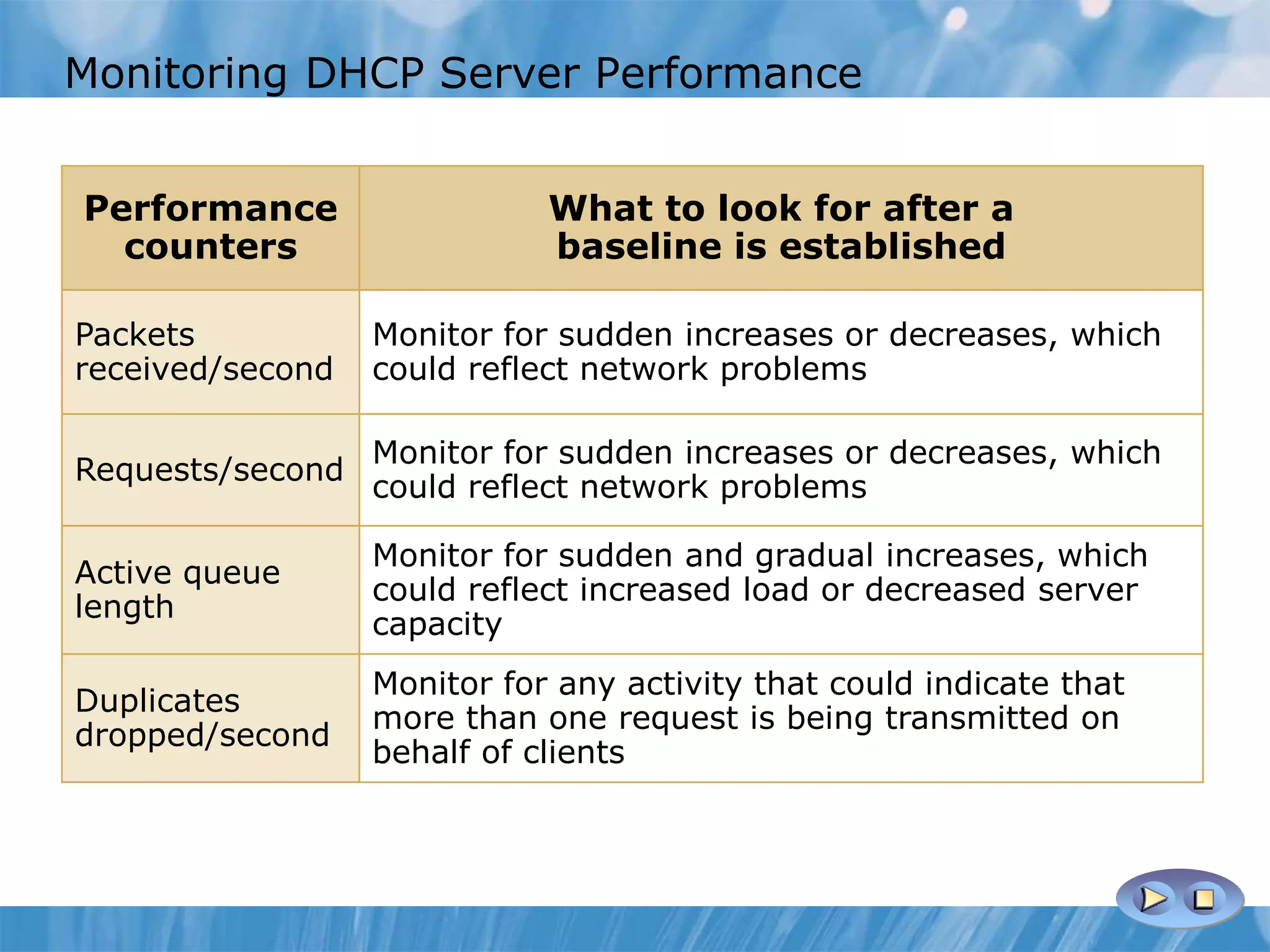
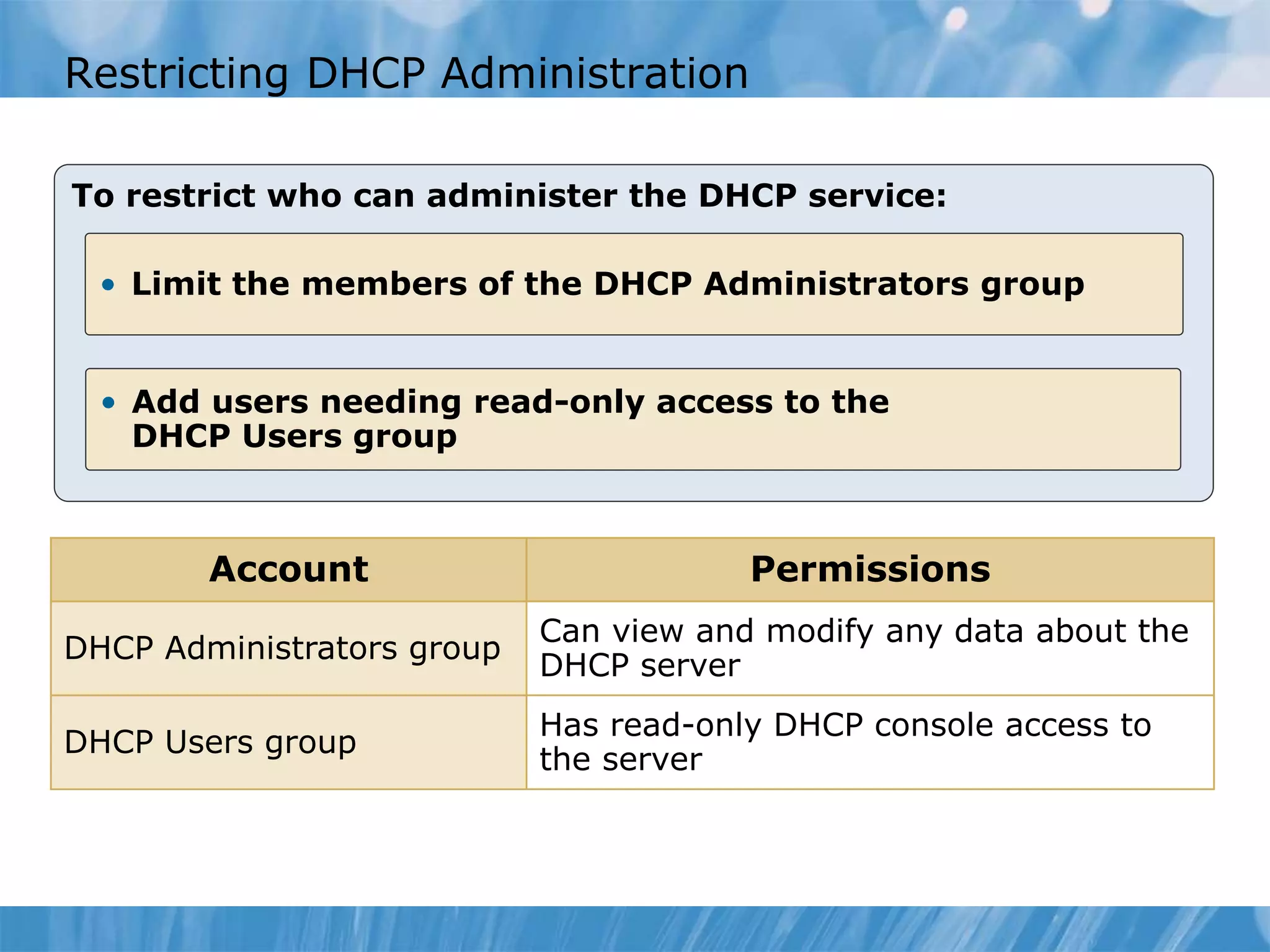
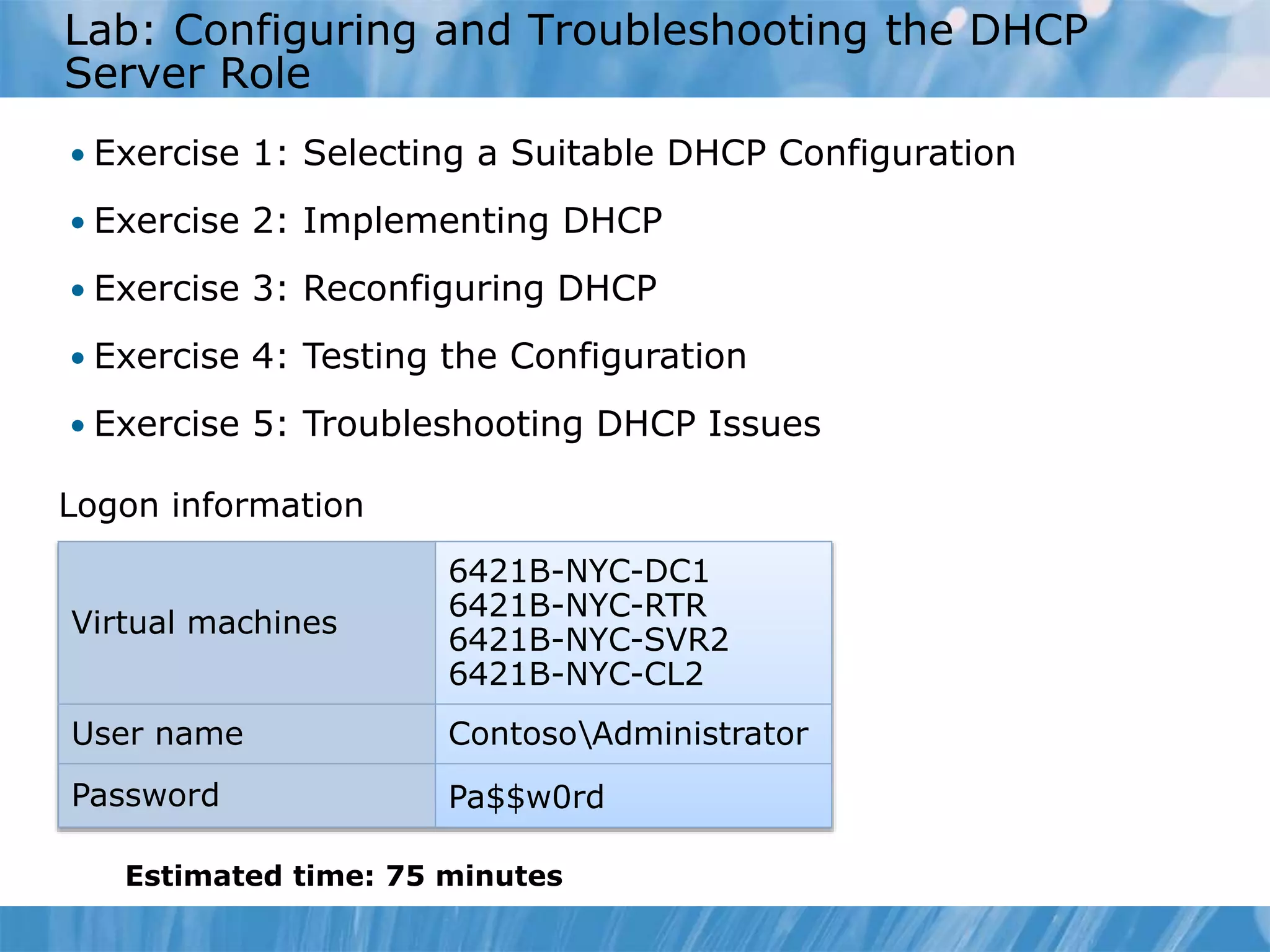
This document provides an overview and lessons for configuring and troubleshooting DHCP. It covers DHCP server roles, configuring scopes and options, managing the DHCP database, monitoring DHCP, and security configuration. A lab scenario tasks the user with implementing a fault-tolerant DHCP configuration across multiple offices to support network requirements.