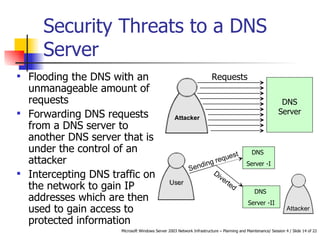
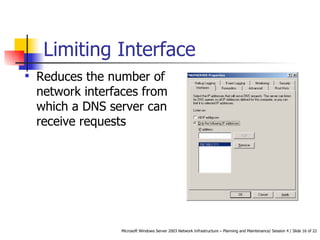
DNS servers convert web addresses to IP addresses and vice versa. A DNS zone is a contiguous portion of the DNS namespace containing domains and subdomains. Resource records within zonal databases contain address mappings. Using multiple DNS servers improves performance and availability through load balancing and redundancy. Threats to DNS servers include flooding, request hijacking, and traffic interception. Security measures involve restricting dynamic updates, network interfaces, and zone transfers.