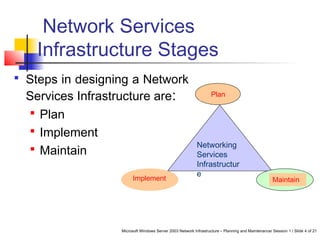
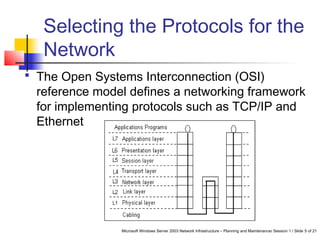
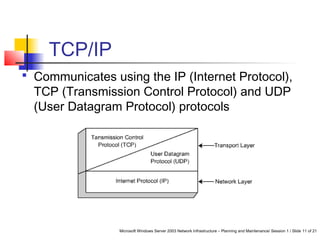
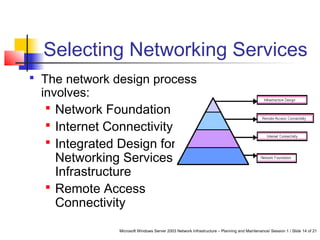
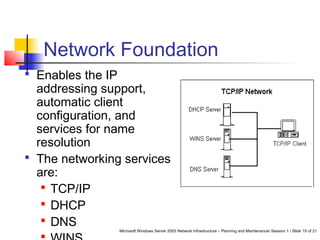
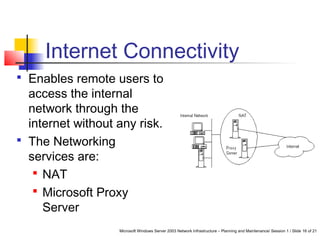
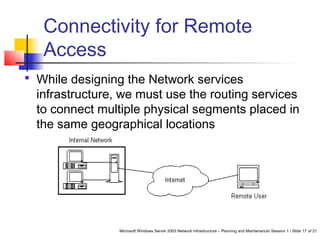
This document discusses planning a network services infrastructure. It explains that an infrastructure consists of physical and logical elements and follows a plan-implement-maintain process. Key aspects covered include selecting protocols like TCP/IP, Ethernet, and DHCP/DNS for networking services. Design considerations involve goals like functionality, security, availability and performance. The document provides an overview of important network infrastructure concepts.