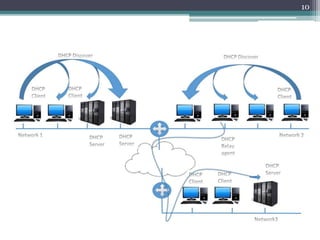
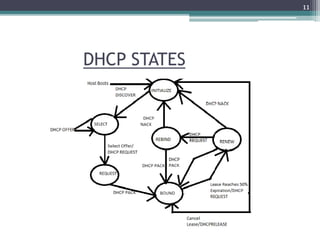
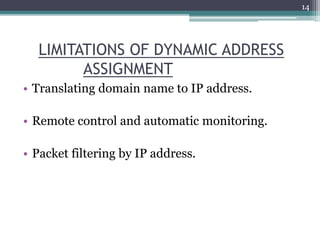
This document discusses DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). It describes DHCP's function of automated IP address assignment and allowing clients to obtain configuration information quickly. It outlines DHCP modes including manual assignment of static addresses, automatic assignment of static addresses, and automatic distribution of dynamic addresses. It also describes DHCP states a client can be in like initialize, select, request, bound, renew, and rebind. Key DHCP messages are discussed like discover, offer, request, and acknowledgment. Limitations of dynamic address assignment are also noted.