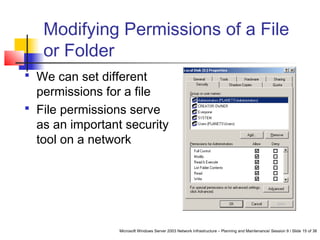
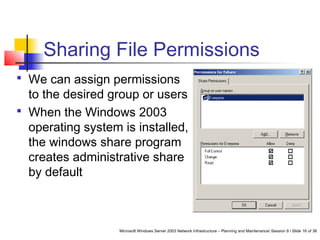
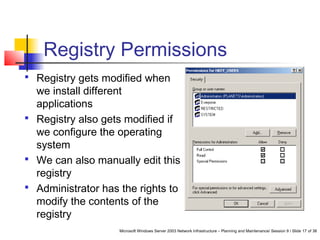
This document discusses planning a secure Windows Server 2003 network. It covers selecting server and desktop computers, operating systems, and security features. Some key points include categorizing computers by role, standardizing hardware, selecting an operating system based on applications and costs, and configuring security permissions for files, folders, and the registry. Domain controllers require additional security as the failure of one could disrupt the whole network. The document also discusses infrastructure servers like DNS and DHCP and how to secure them.