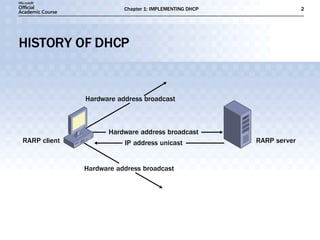
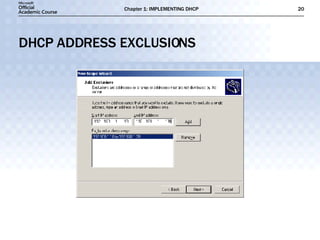
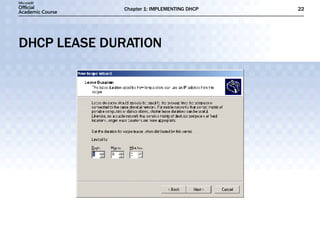
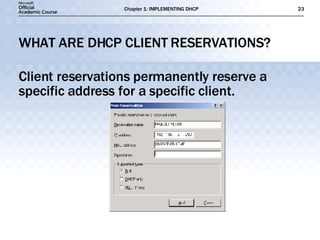
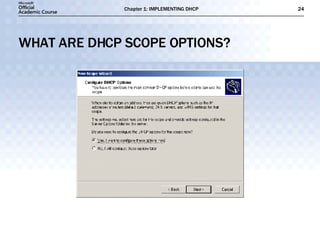
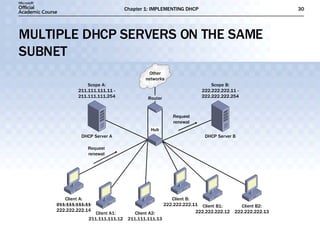
The document discusses the implementation of DHCP including:
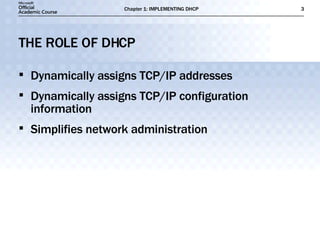
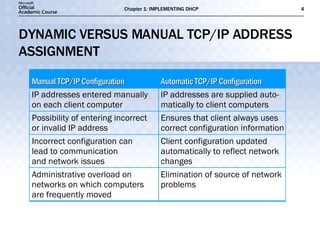
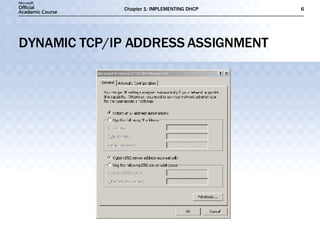
- DHCP dynamically assigns TCP/IP addresses and configuration information to simplify network administration compared to manual configuration.
- DHCP servers require a supported server OS and DHCP service, while clients require supported Windows or other OS versions.
- The key benefits of DHCP include centralized administration, dynamic host configuration, seamless IP configuration, flexibility and scalability.
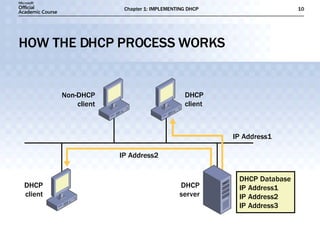
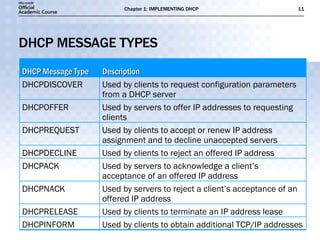
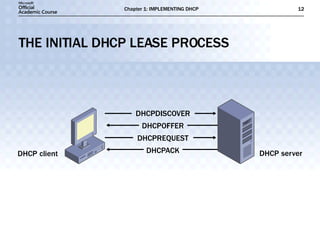
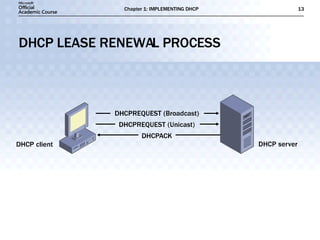
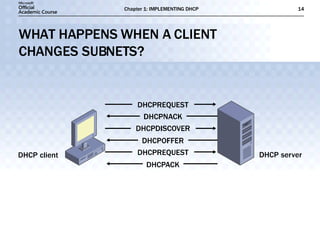
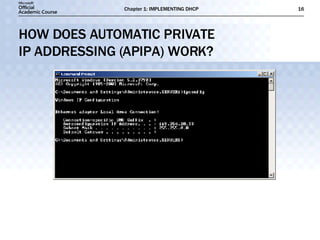
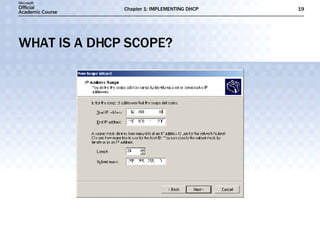
- DHCP uses message types like DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPOFFER, and DHCPACK to dynamically assign IP addresses and configure clients on the network.