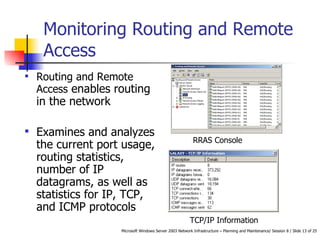
The document discusses maintaining server availability by monitoring performance, network services, and system bottlenecks. It also covers planning a backup strategy. Specifically, it outlines:
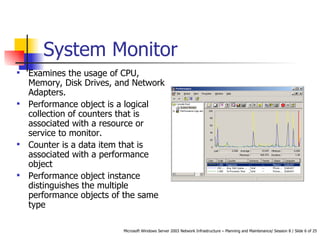
- Tools for analyzing server performance including the Performance Console and Network Monitor
- Services to monitor like DHCP, DNS, WINS, and routing/remote access
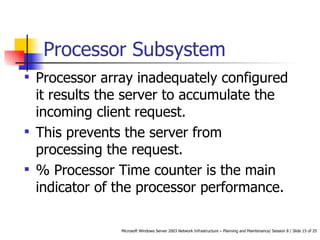
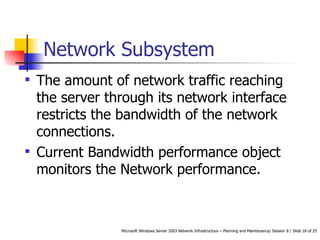
- Areas that could cause bottlenecks: processor, memory, storage, and network
- Components of a backup strategy: hardware, software, and plan
- Backup types and restoring options available in software
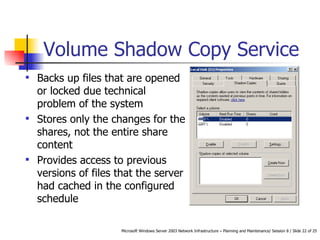
- How Volume Shadow Copy Service works