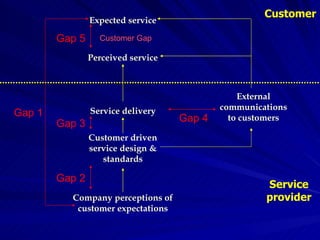
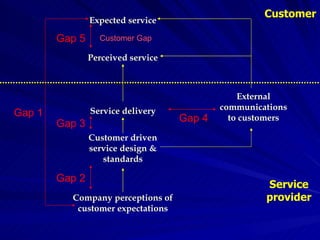
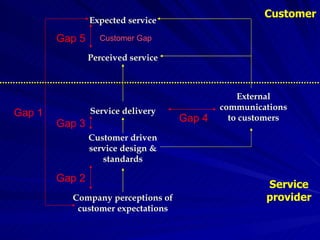
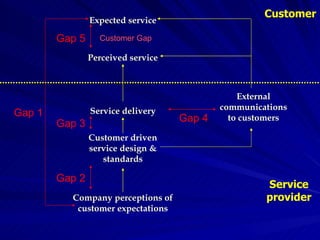
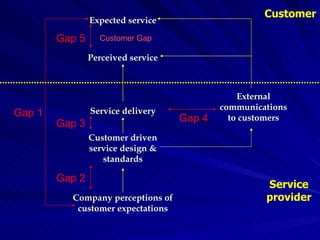
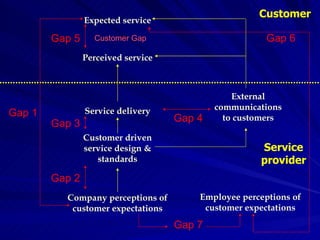
The Gaps Model proposes that there are 5 gaps between a customer's expected service and their perceived service. Gap 1 is between customer expectations and a company's understanding of those expectations. Gap 2 is between a company's understanding and their service design standards. Gap 3 is between service standards and actual service delivery. Gap 4 is between a company's marketing communications and the service delivered. Gap 5 is between customer expectations and their perceptions of the service received. More recently, 2 additional gaps were proposed regarding employees' perceptions of customer expectations.