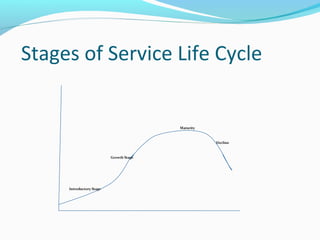
The document outlines the four stages of a service life cycle: introductory, growth, maturity, and decline. The introductory stage involves small-scale launches of new services with few competitors. The growth stage sees rapid industry expansion and emerging market segments. During maturity, sales level off amid intense competition. Finally, the decline stage is marked by falling sales and profits due to new technologies or decreased demand.