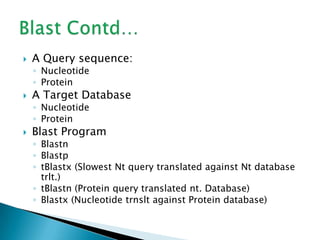
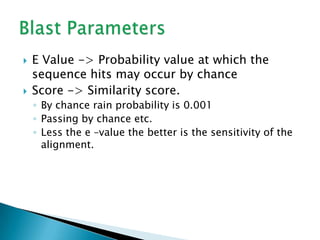
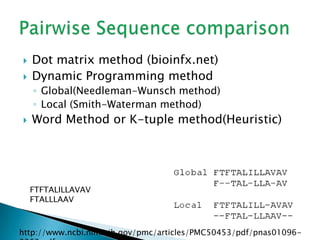
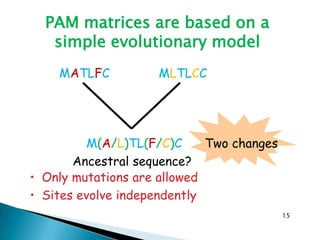
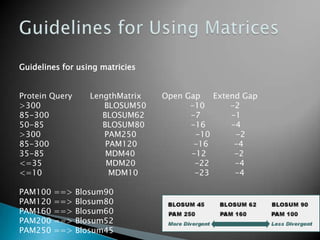
The document discusses various bioinformatics tools and methods for protein sequence analysis, including the use of BLAST and FASTA for sequence alignment. It covers concepts like score and e-value, the significance of conserved motifs, and different scoring matrices such as PAM and BLOSUM for evaluating sequence similarities. Additionally, it highlights methods like dynamic programming and tree-building techniques for phylogenetic analysis.











![Scoring Matrices
S = [sij] gives score of aligning character i
with character j for every pair i, j.
STPP
CTCA
0 + 3 + (-3) + 1
=1
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/msa-motiffinding-121116031725-phpapp02/85/Sequence-Alignment-Blast-Fasta-MSA-17-320.jpg)