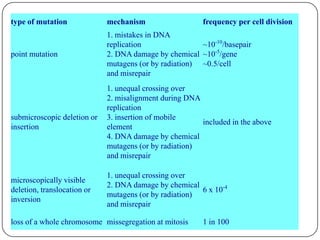
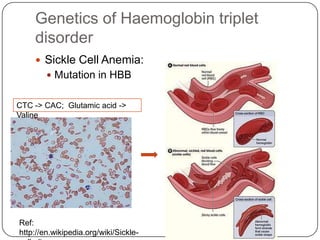
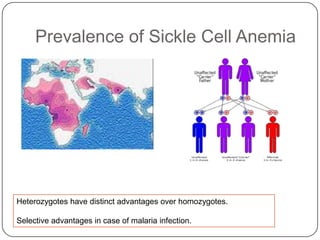
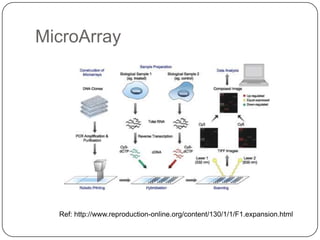
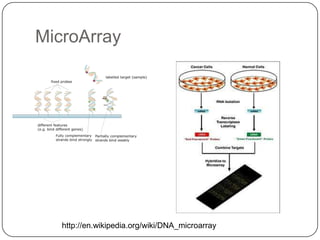
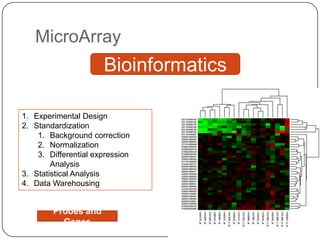
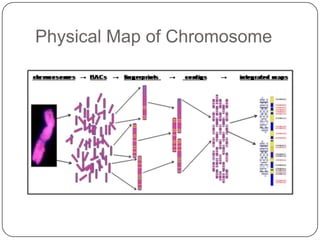
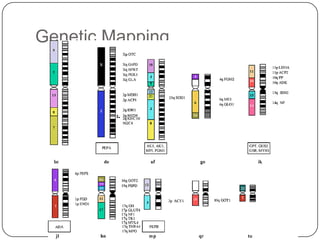
Pharmacogenetics refers to how genetic differences affect individuals' responses to drugs. It influences different metabolic pathways and is responsible for over 106,000 deaths annually in the US. Certain genetic mutations can determine how effectively drugs are processed in the body. Microarrays are DNA chips that allow researchers to analyze large numbers of genes simultaneously, helping to identify genetic factors influencing drug responses and diseases.