This document provides an overview of sepsis, including definitions, epidemiology, pathophysiology, treatment guidelines, and outcomes data from a hospital sepsis protocol. Key points:
- Sepsis is defined as a systemic inflammatory response due to infection plus signs of organ dysfunction. It exists on a spectrum from systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) to septic shock.
- Sepsis accounts for a large portion of ICU costs and mortality. Early goal-directed therapy including antibiotics, fluids, and vasopressors can improve outcomes.
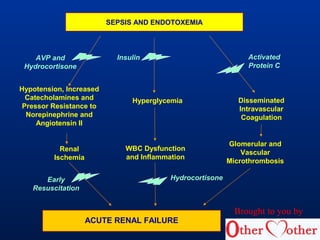
- The pathophysiology involves an initial pro-inflammatory response that can become dysregulated, resulting in organ damage. Bacterial factors like endotoxin and host factors contribute.