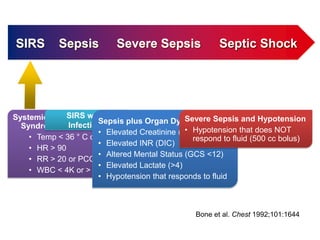
The document summarizes updated guidelines from the 41th Society of Critical Care Medicine Meeting for treating sepsis. Key changes include recommending crystalloids like saline for initial fluid resuscitation; using norepinephrine as the first choice vasopressor; considering corticosteroids for refractory shock; using higher PEEP and recruitment maneuvers for ARDS; and considering procalcitonin to determine if antibiotics can be stopped. The Surviving Sepsis guidelines were previously criticized for being funded primarily by Eli Lilly without disclosure.