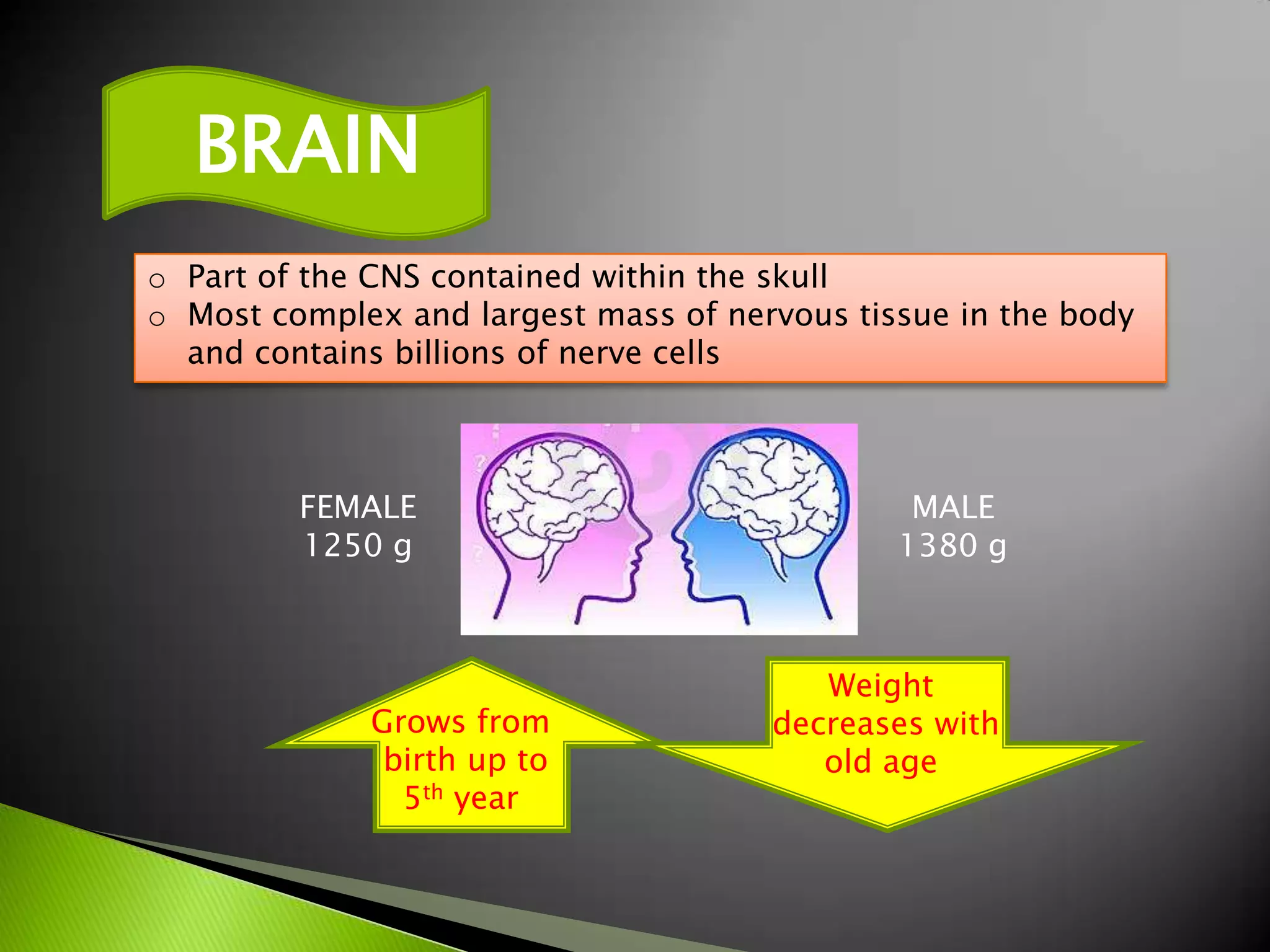
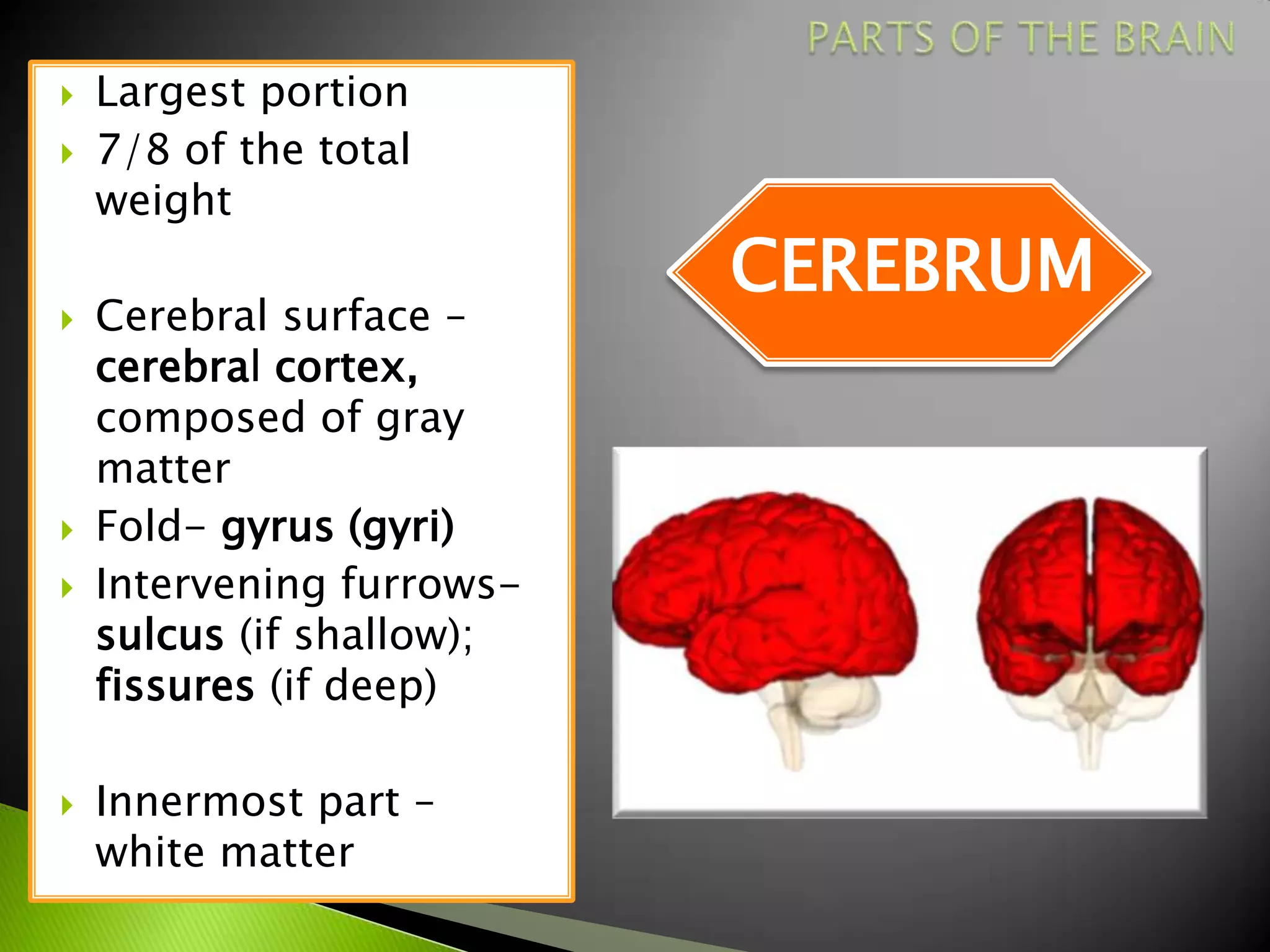
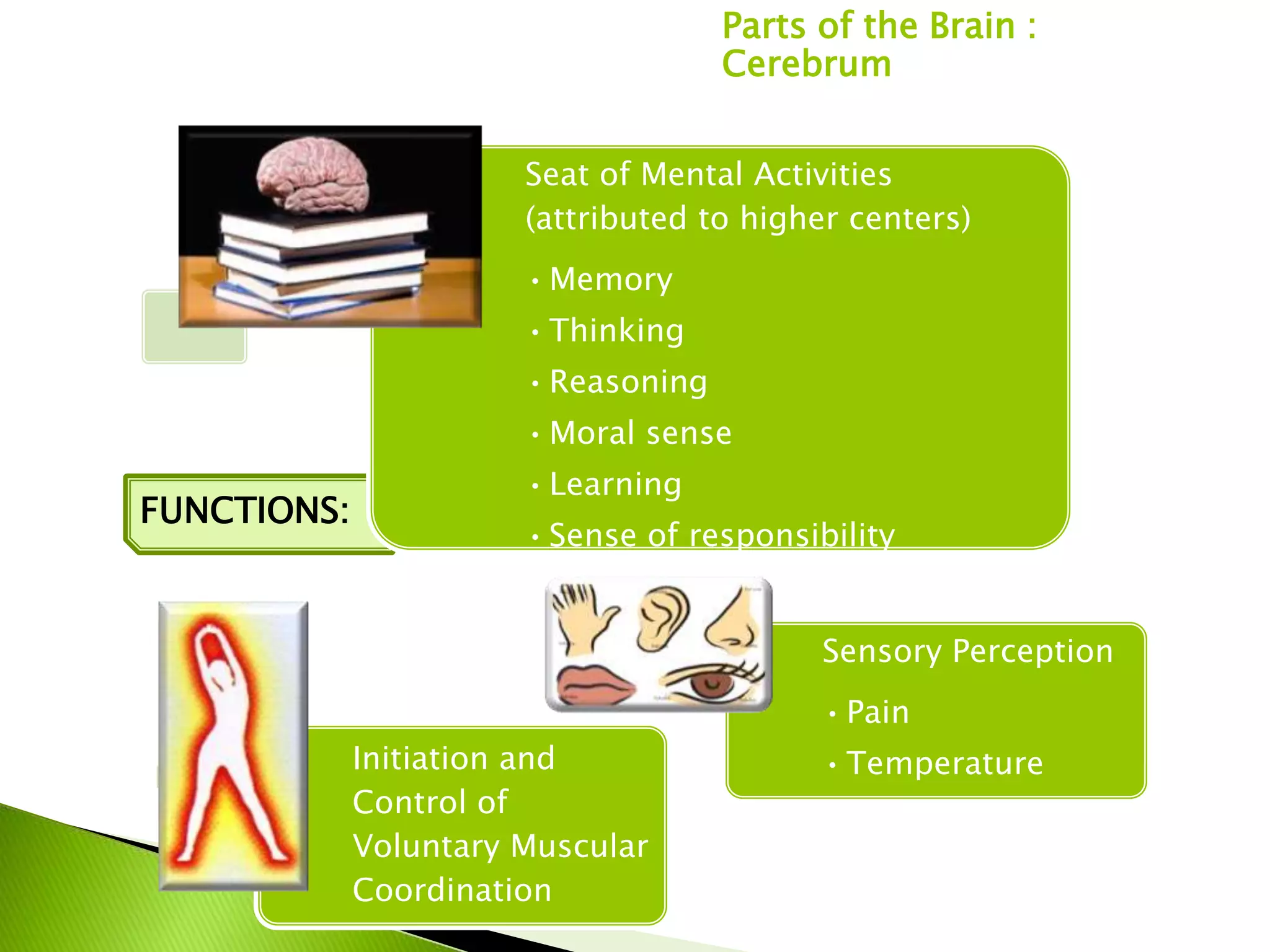
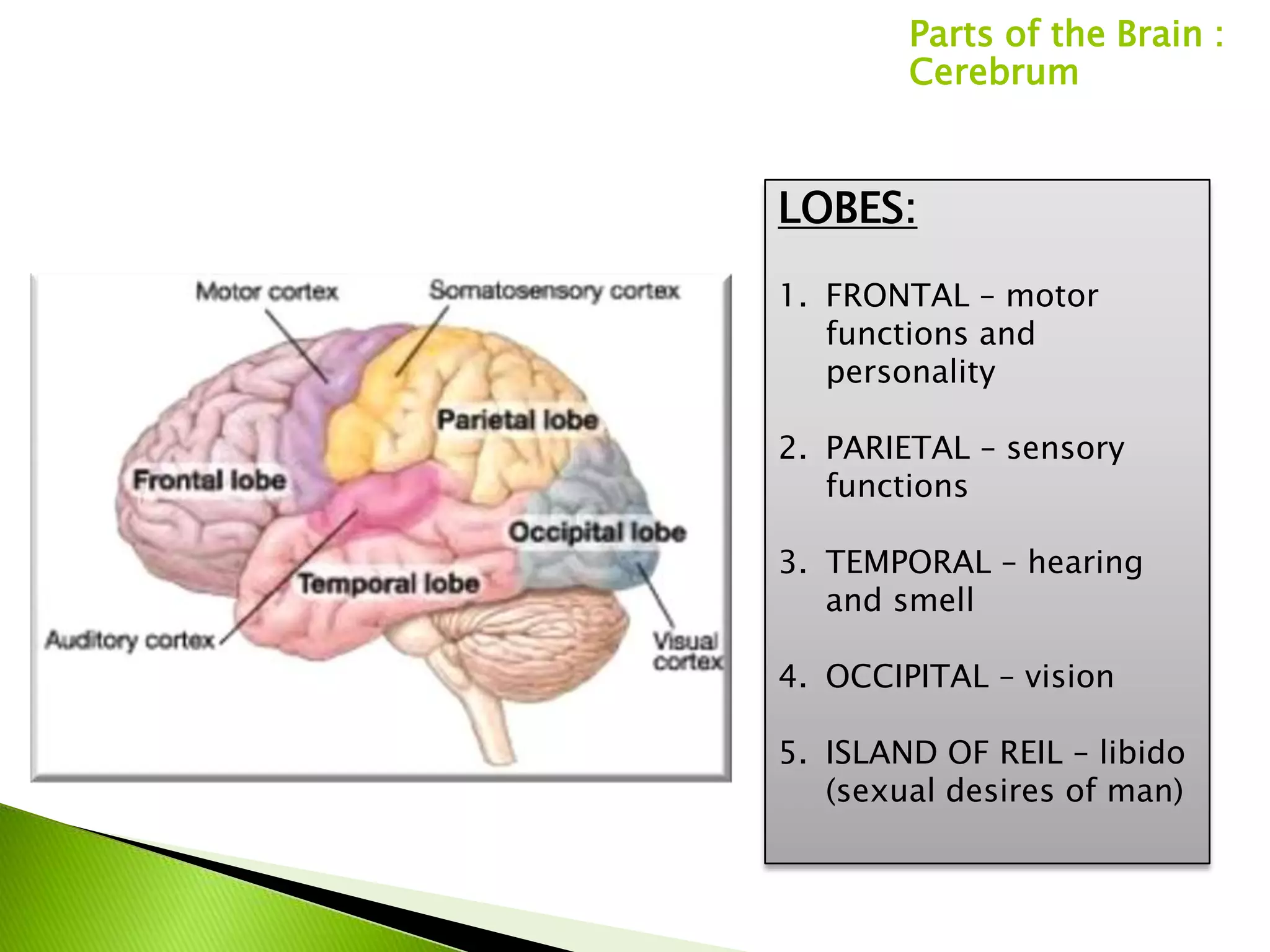
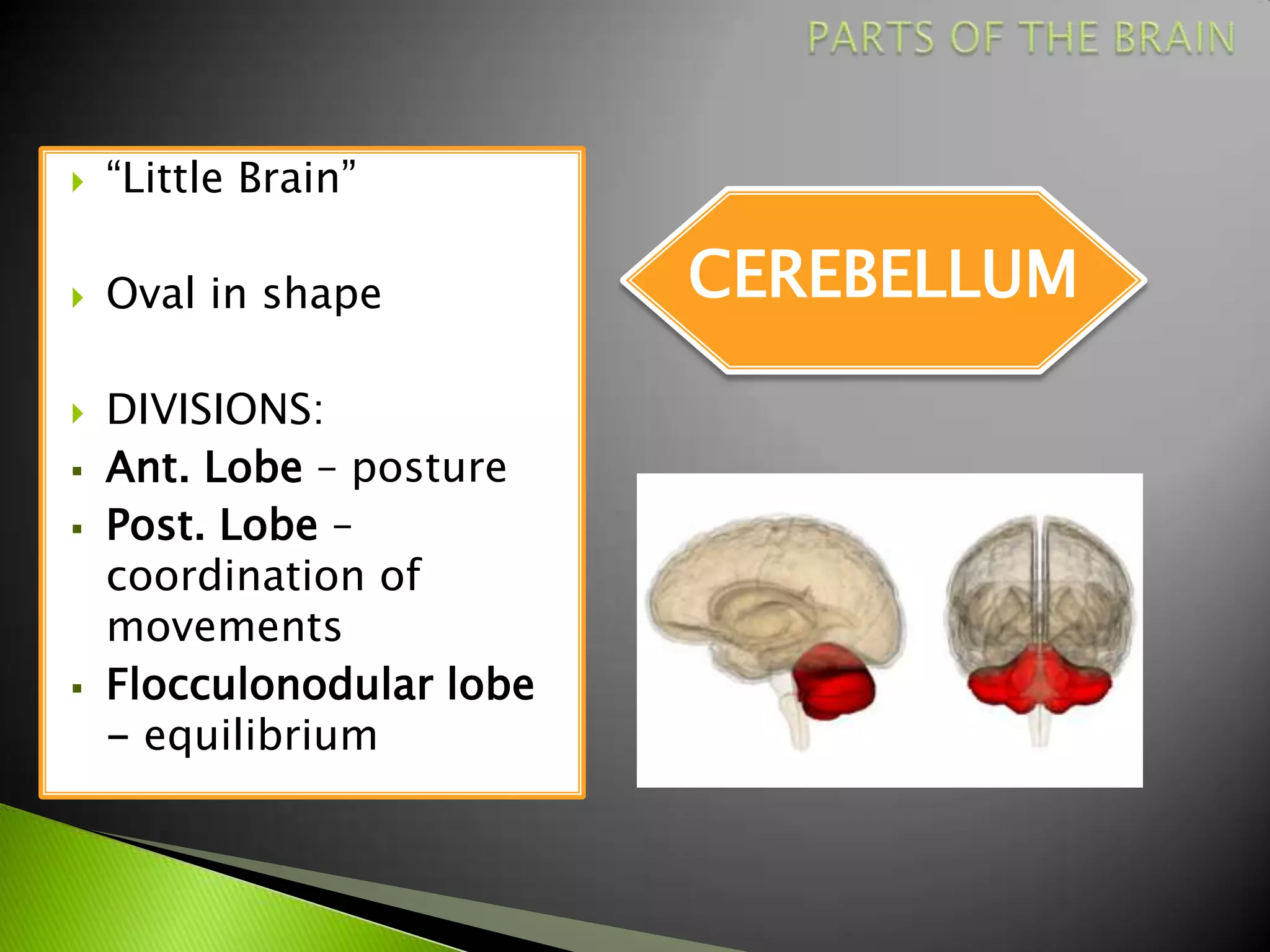
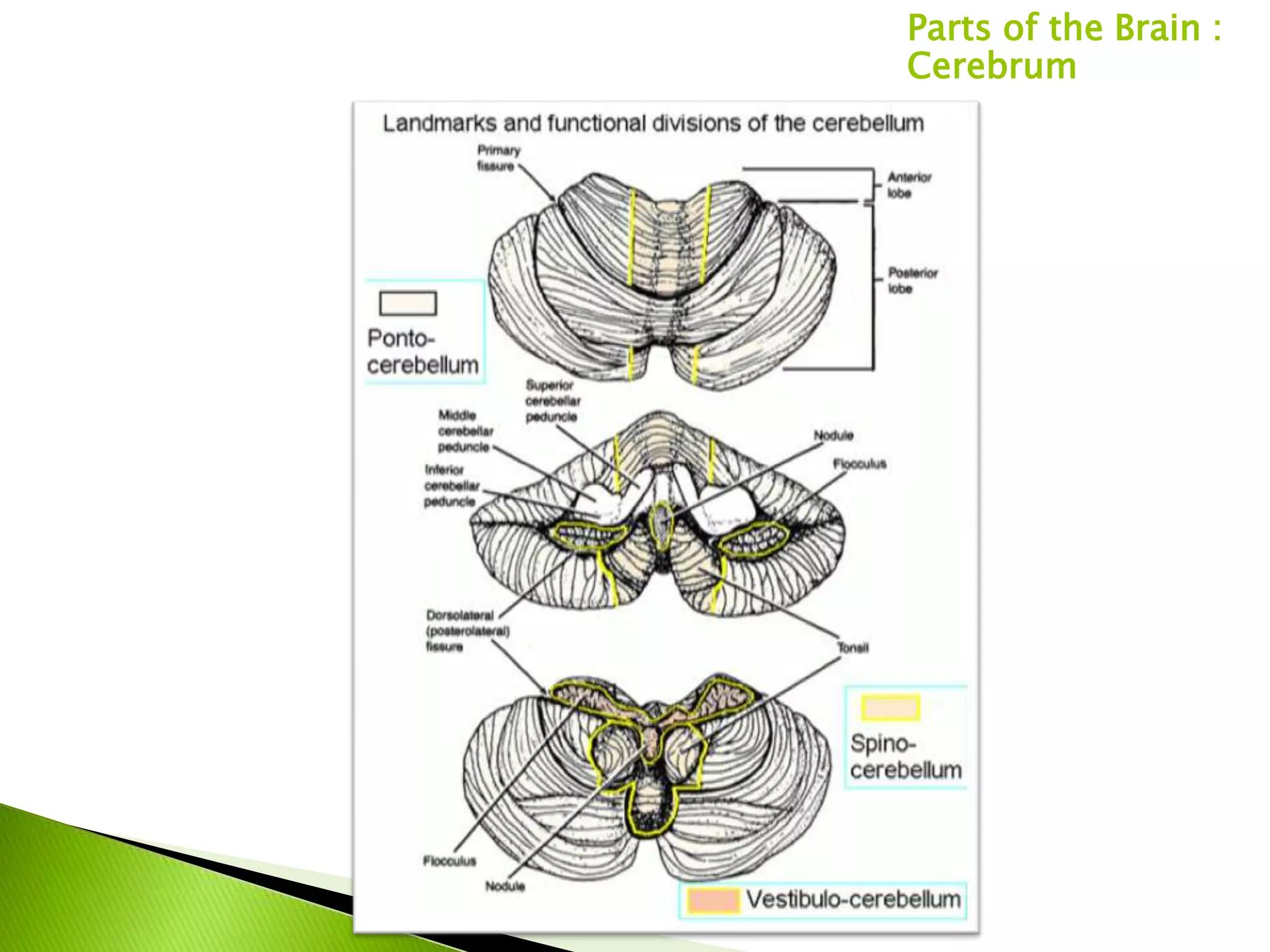
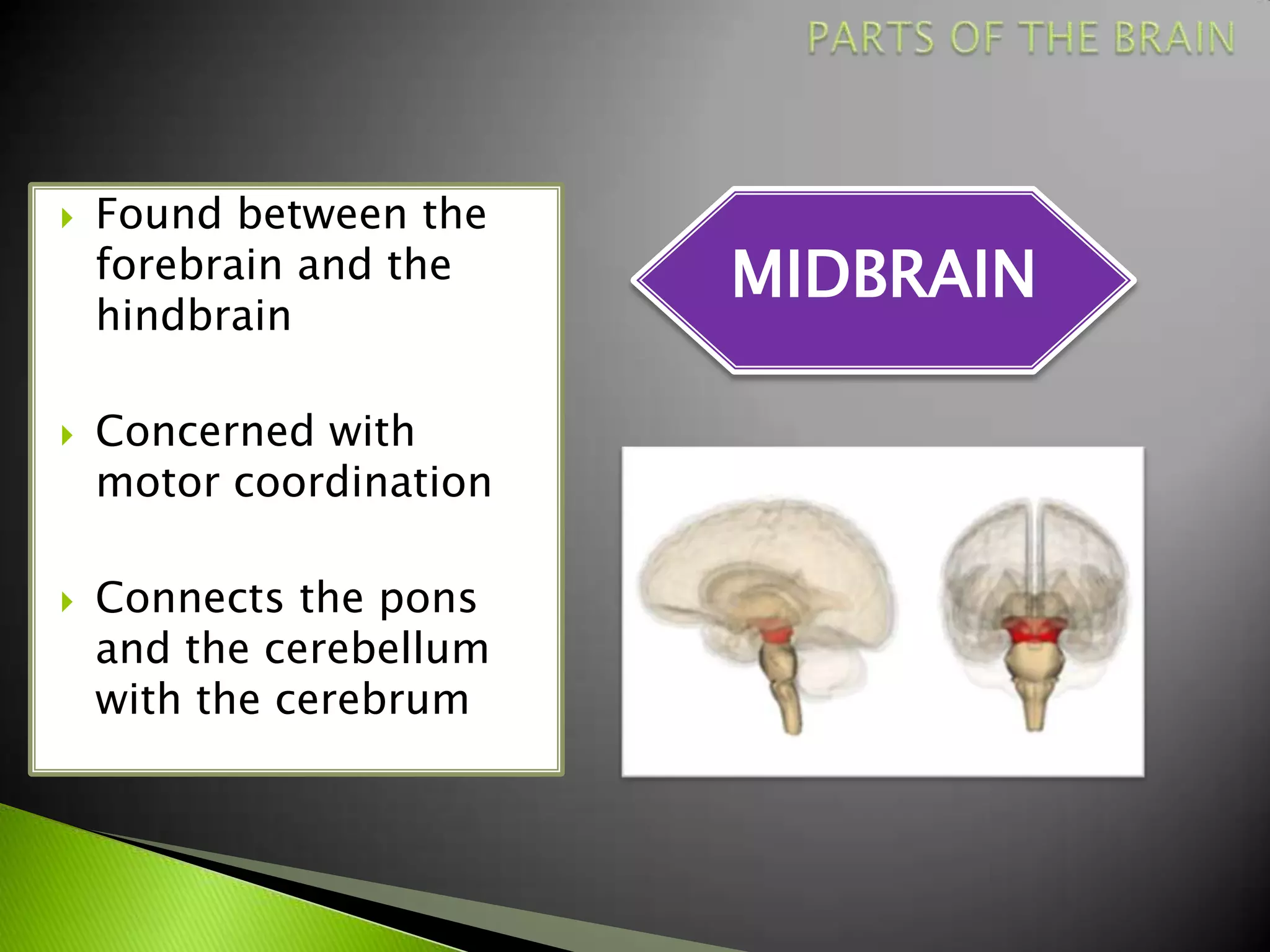
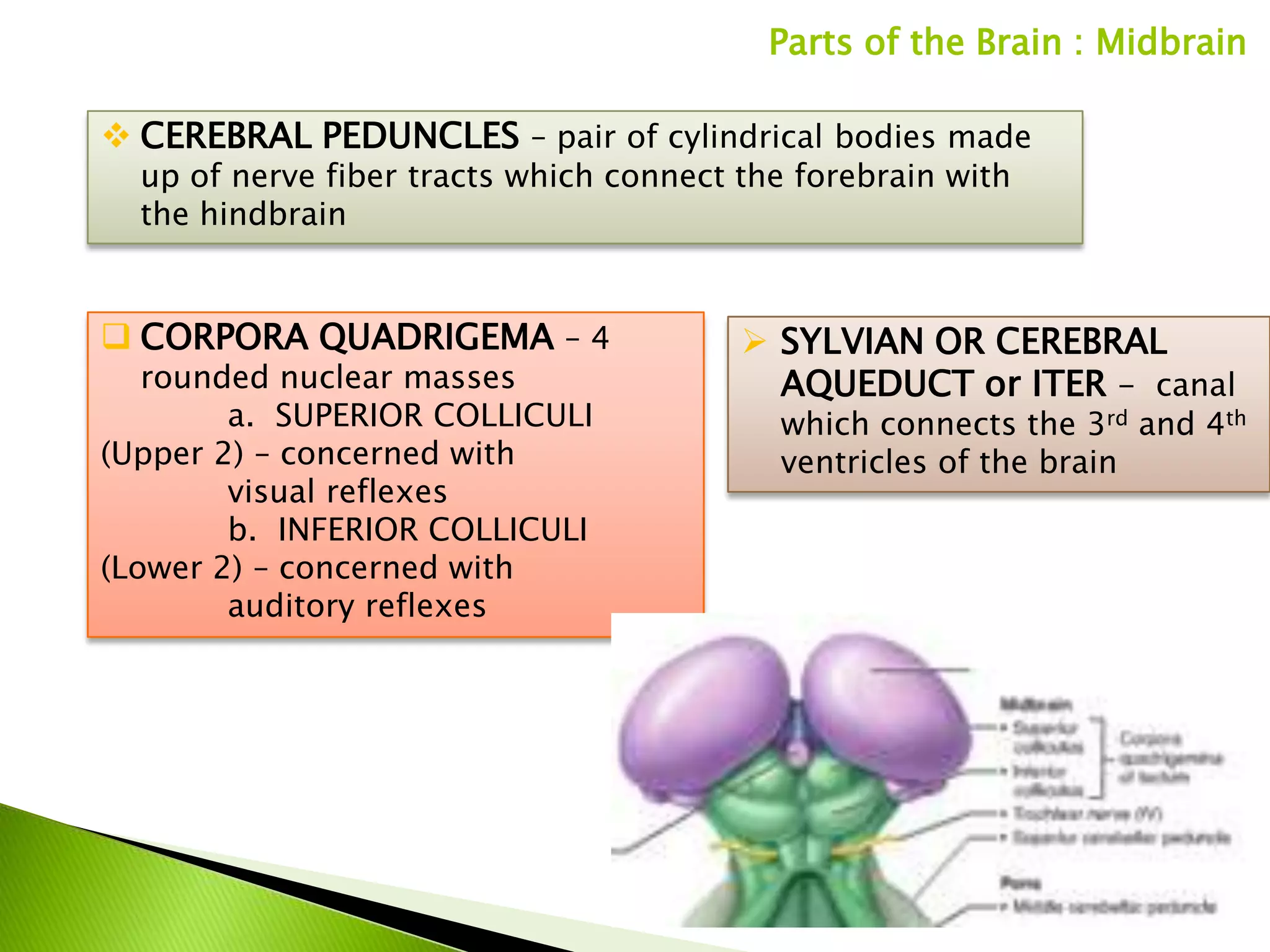
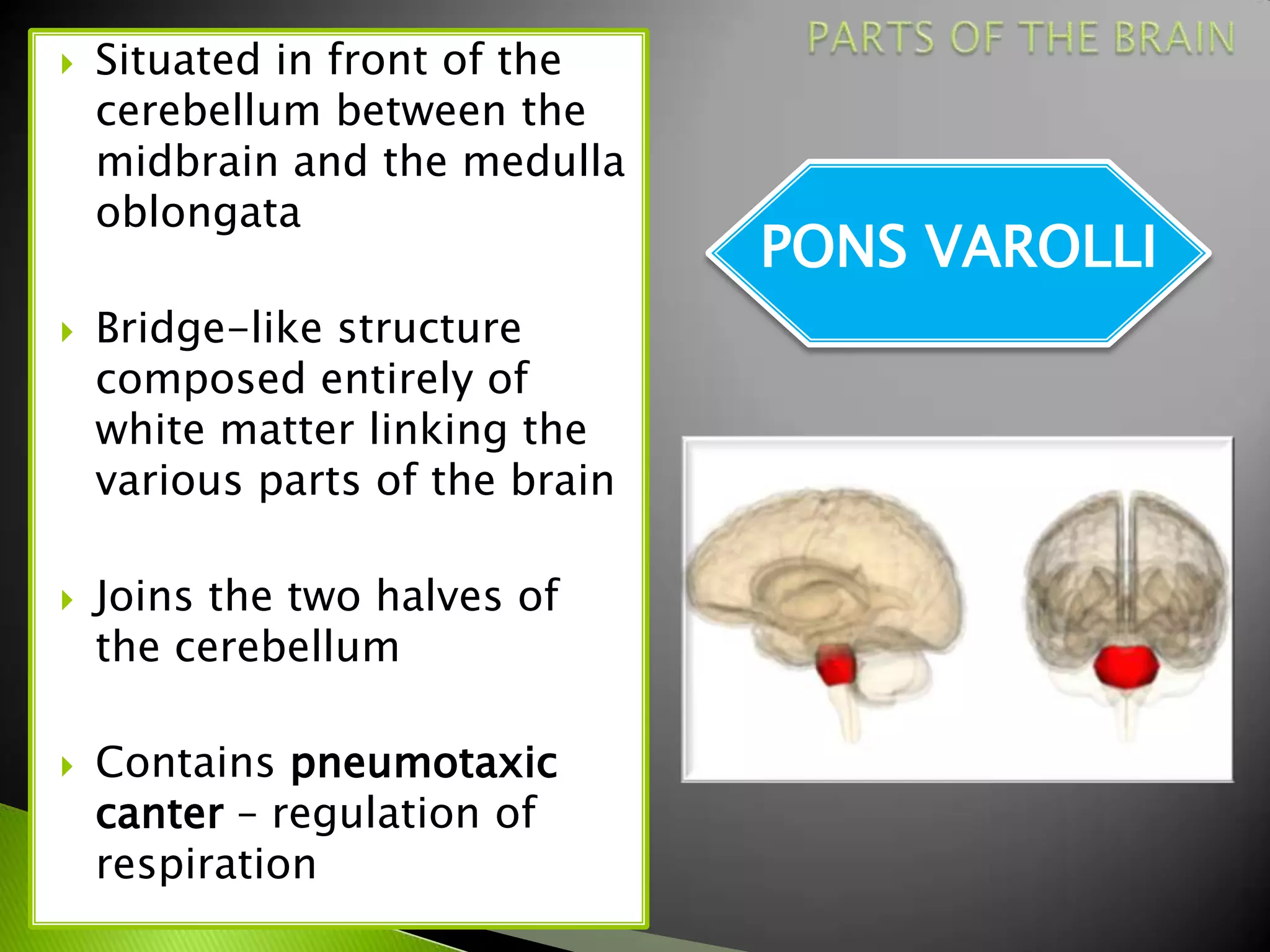
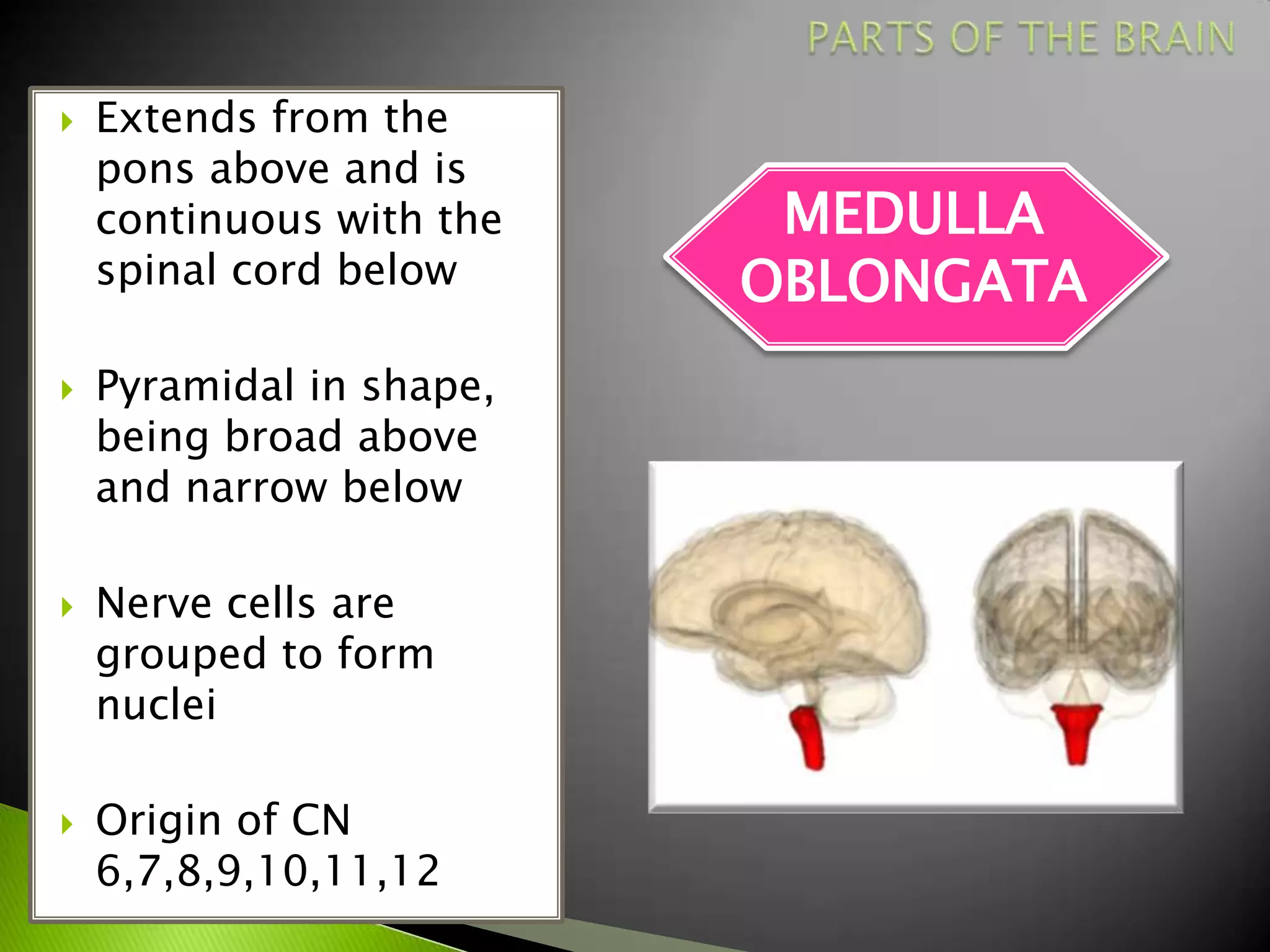
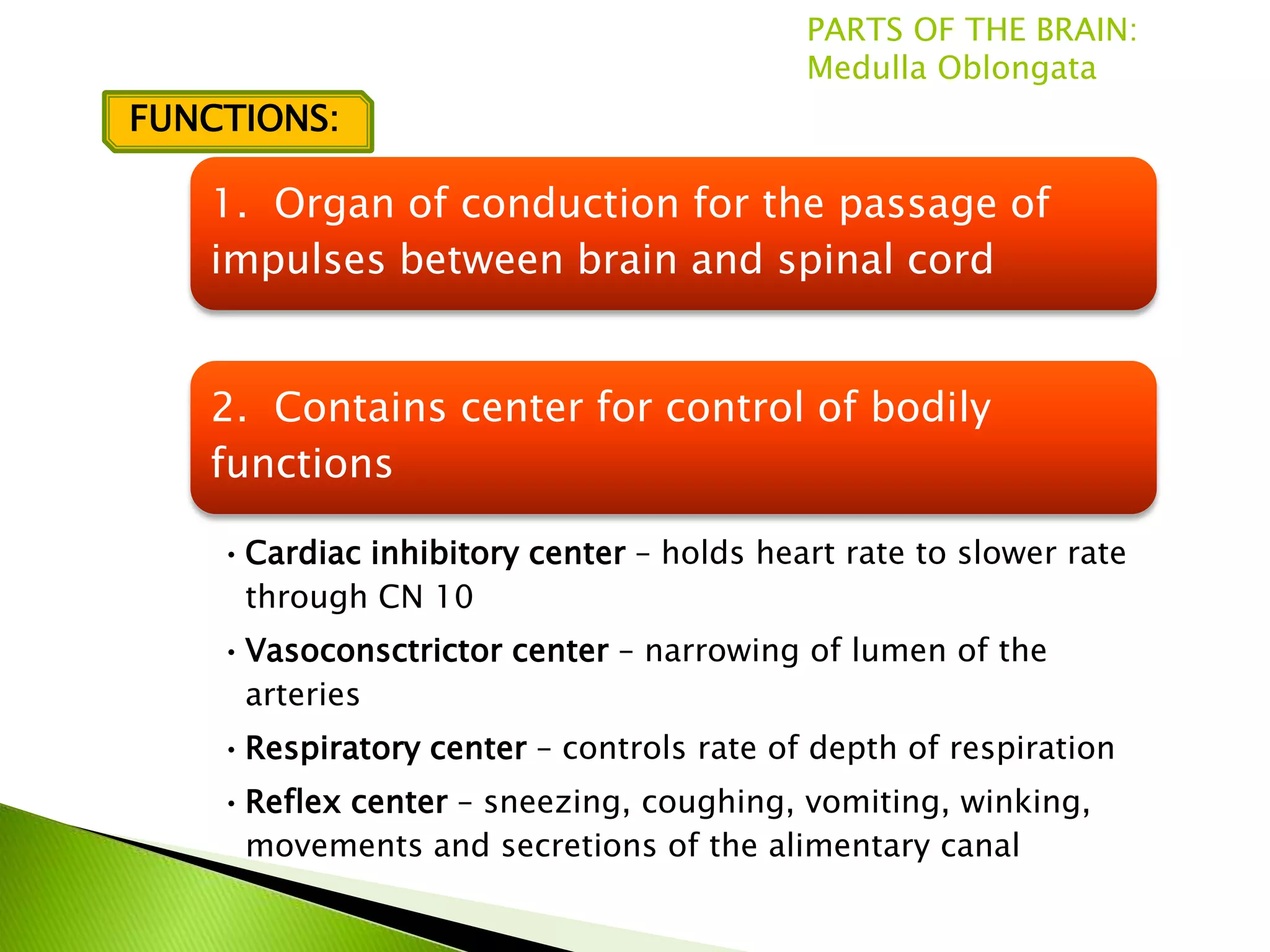
The document summarizes the main parts of the human brain including the cerebrum, cerebellum, midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. It describes the location, weight, lobes, and key functions of each part such as memory, sensory perception, motor coordination, and control of vital bodily functions.