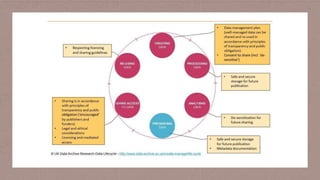
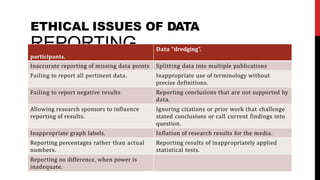
Selective reporting and misrepresentation of data undermine the integrity of academic research. Selective reporting refers to intentionally presenting or omitting certain information, data, or results in a biased manner to support a particular viewpoint. There are several types of selective reporting and misrepresentation, including publication bias, outcome reporting bias, data dredging, spin, and selective citation. Upholding honesty, objectivity, and integrity in experimental design, data analysis, and reporting is important. Fabrication, falsification, or misrepresentation of data is unethical. Journals should verify consent forms and data sources if concerns about accuracy or legitimacy arise.