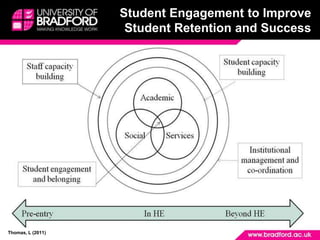
1. Understanding why students doubt continuing their education and feel like leaving is important to improve retention. Building a sense of community and belonging can help address feelings of isolation that contribute to doubting.
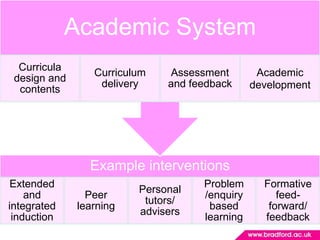
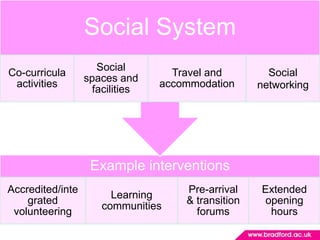
2. Program teams play a key role in retention through improving communication, academic integration, social integration, and helping students align their goals. Identifying students at risk of leaving and intervening early is important.
3. Institutional culture and policies should actively nurture belonging, student development, high quality learning and teaching, and use data to support student success. Reflecting on practices can help implement changes to improve the student experience.