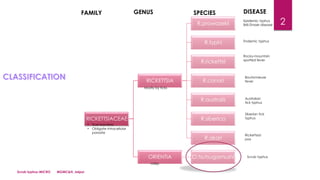
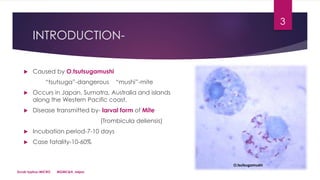
This document discusses scrub typhus, caused by the bacteria Orientia tsutsugamushi, which is transmitted by the larval form of the trombiculid mite. Key points include:
- Scrub typhus occurs in parts of Asia and the Western Pacific and has a mortality rate of 10-60% if untreated.
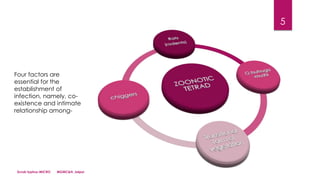
- The bacteria are transmitted via the bites of larval mites (chiggers) that feed on rodents and birds, which act as reservoirs.
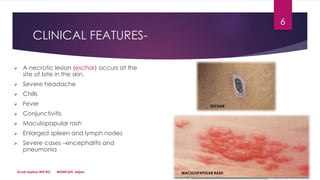
- Clinical features include a necrotic skin lesion (eschar) at the bite site, fever, rash, and potentially severe complications like pneumonia or encephalitis.
- Diagnosis involves