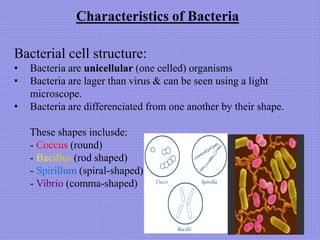
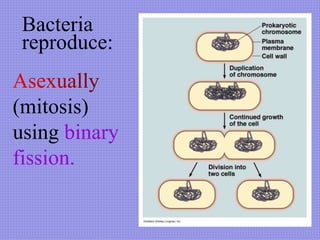
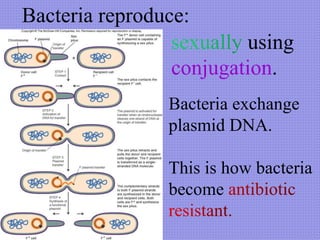
This document discusses the key characteristics of bacteria. It states that bacteria are unicellular organisms found everywhere on Earth that come in different shapes. It describes bacteria as containing DNA, ribosomes, and sometimes plasmids or flagella. The document outlines the different types of cell walls and structures bacteria can have. It categorizes bacteria based on how they obtain energy, such as heterotrophs, photosynthetic bacteria, and chemoautotrophs. The document also mentions that bacteria reproduce through binary fission and gene transfer through conjugation.