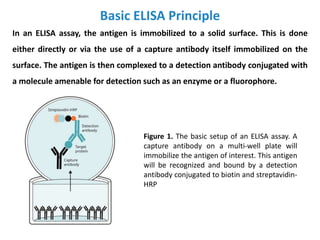
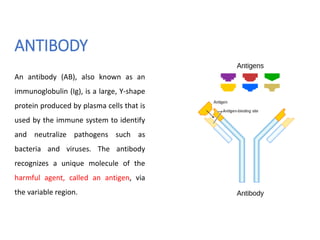
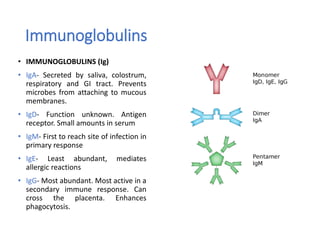
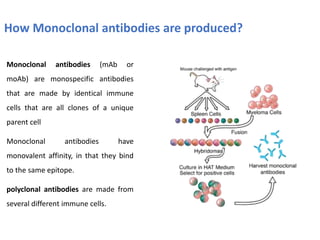
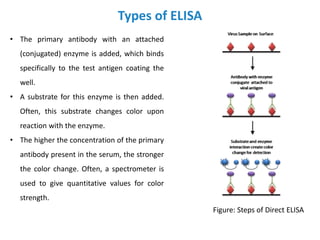
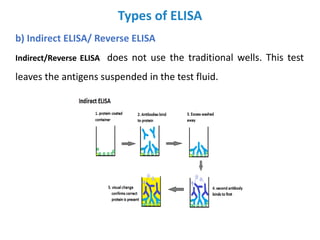
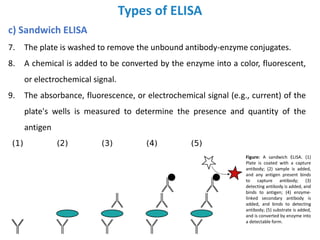
The document discusses ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), a commonly used analytical technique for detecting antigens, antibodies, and proteins. It describes the basic principles of ELISA, including immobilizing an antigen and detecting it using an enzyme-linked antibody. There are four main types of ELISA discussed: direct ELISA, indirect ELISA, sandwich ELISA, and competitive ELISA. Sandwich ELISA is most common and involves capturing the antigen between two antibodies, followed by detection with enzyme-linked secondary antibodies.













![Commonly Used Enzymatic Markers
The following enzymatic markers commonly used in ELISA assays, which allow
the results of the assay to be measured upon completion.
1. OPD (o-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride) turns amber to detect HRP
(Horseradish Peroxidase), which is often used to as a conjugated protein.
2. TMB (3,3',5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine) turns blue when detecting HRP and
turns yellow after the addition of sulfuric or phosphoric acid.
3. ABTS (2,2'-Azinobis [3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid]-diammonium
salt) turns green when detecting HRP.
4. PNPP (p-Nitrophenyl Phosphate, Disodium Salt) turns yellow when
detecting alkaline phosphatase.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elisaai15092023-231030002827-0641ff3c/85/ELISA_AI_15092023-pptx-21-320.jpg)