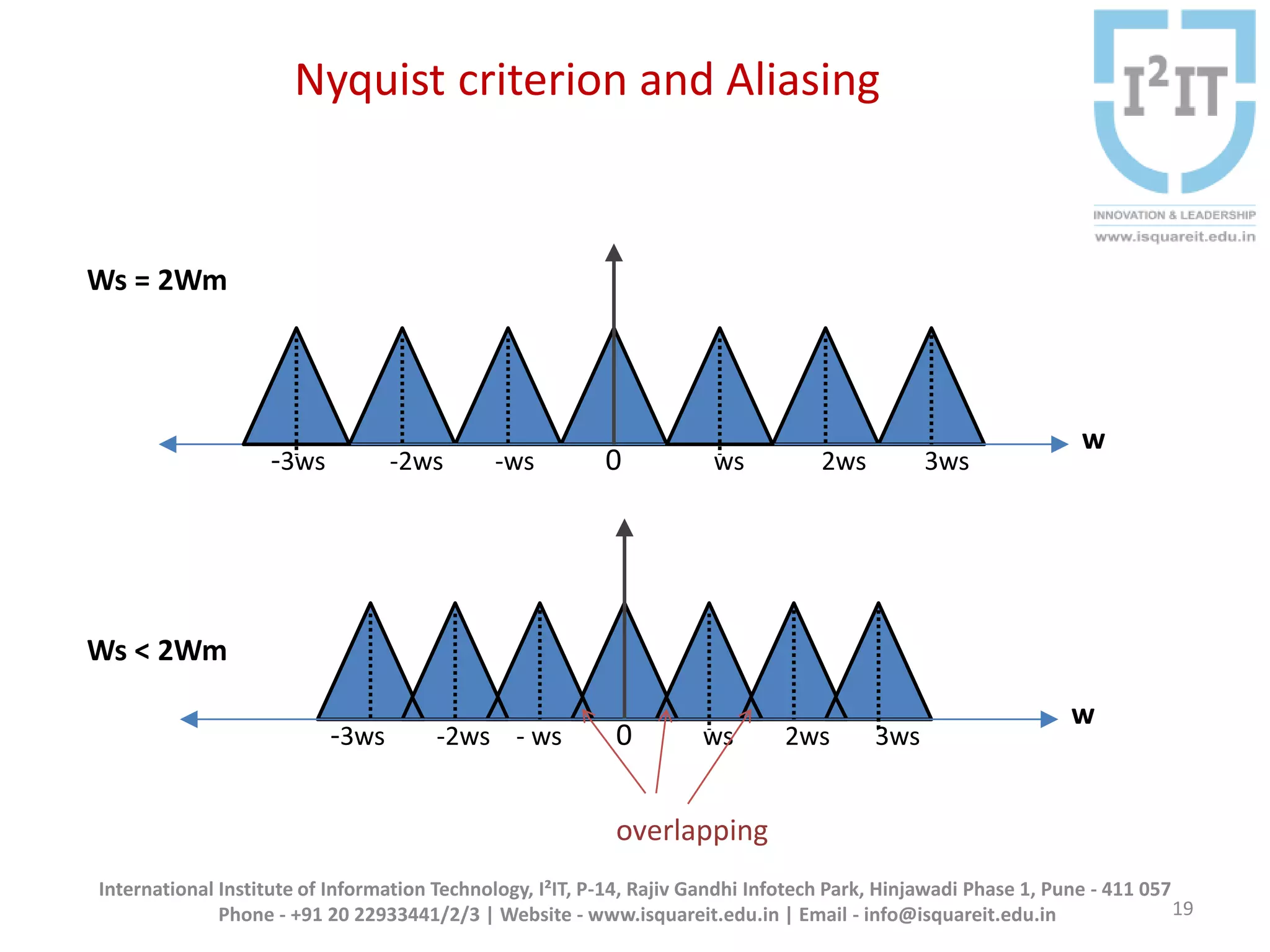
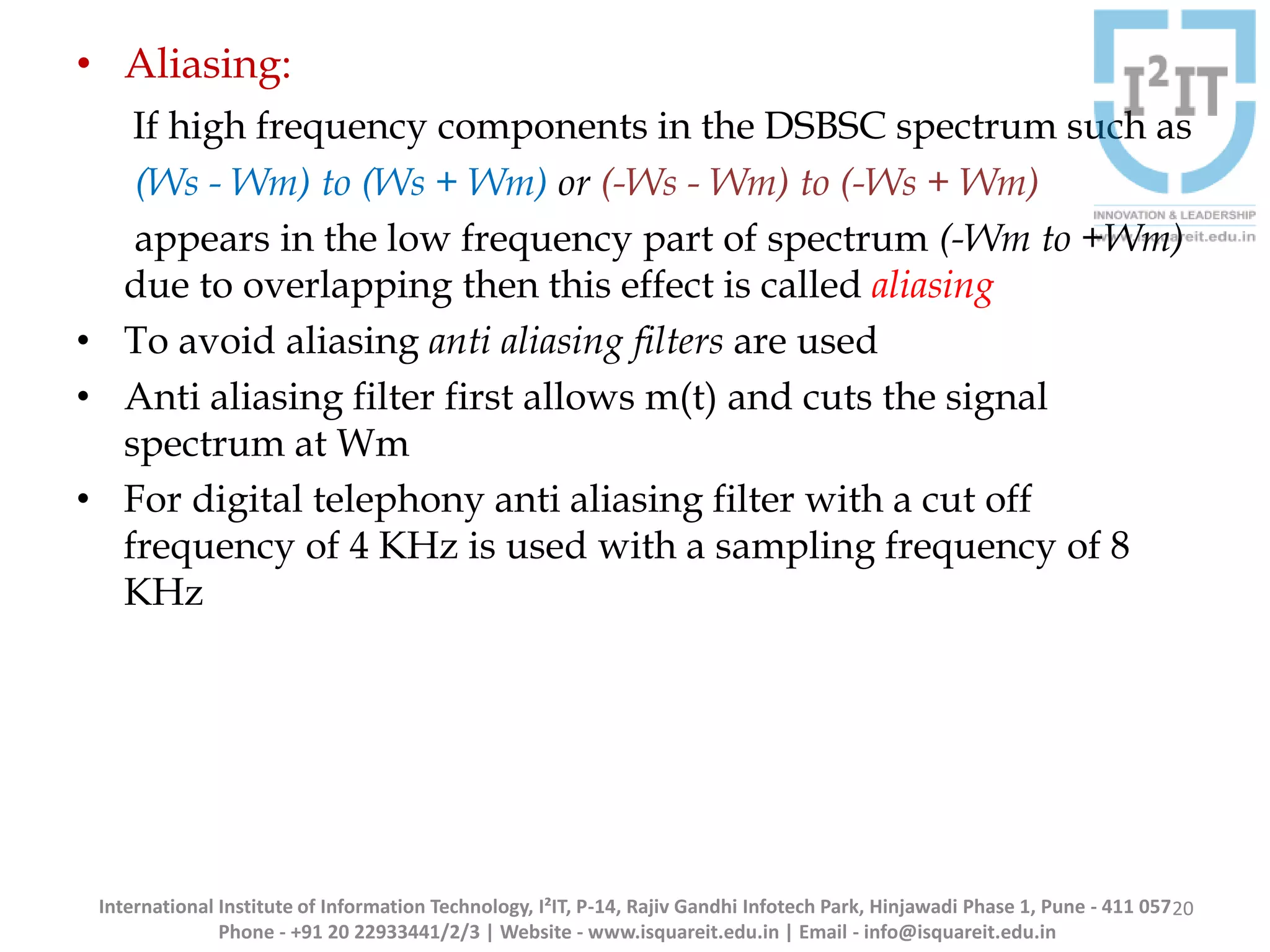
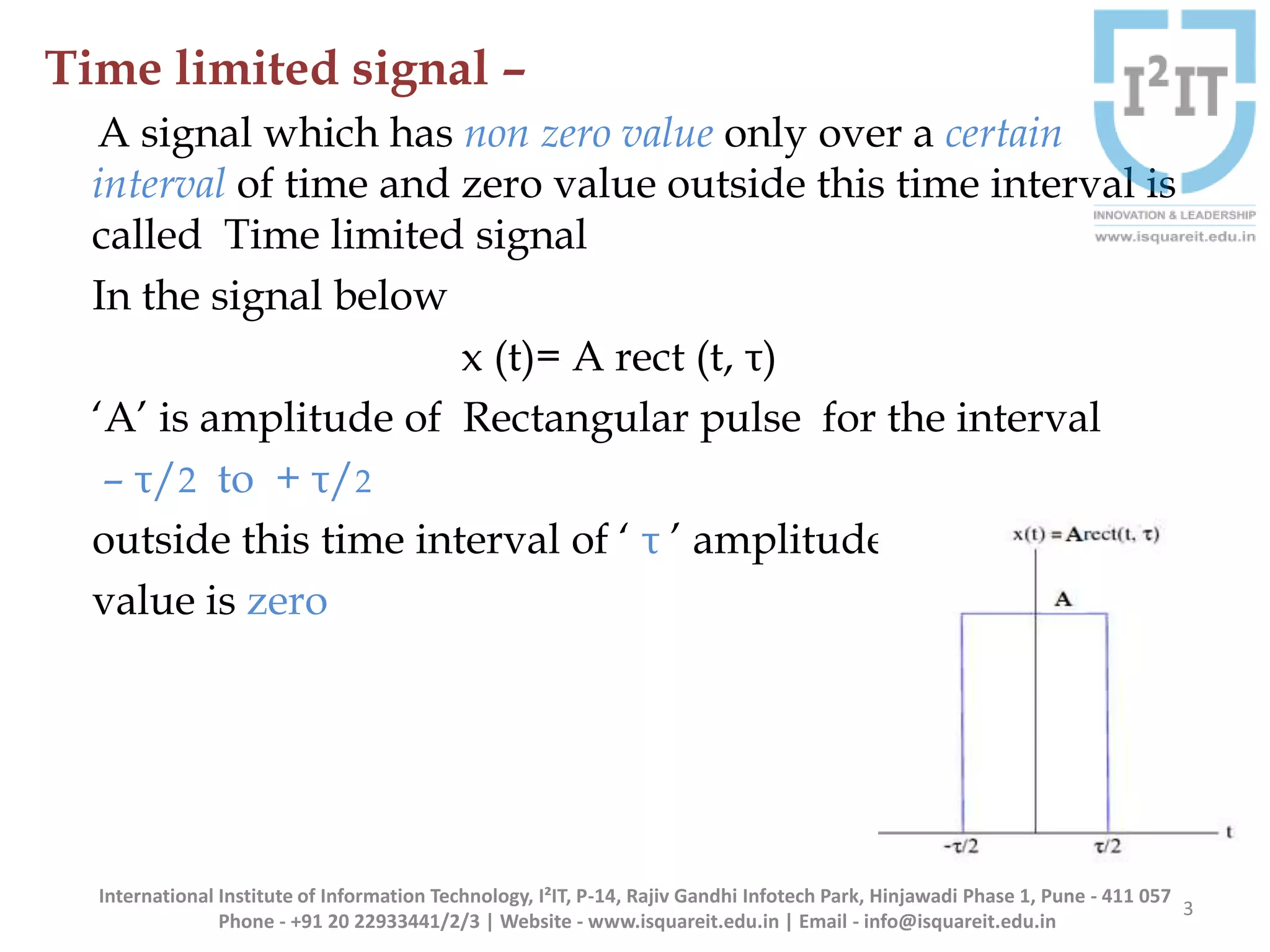
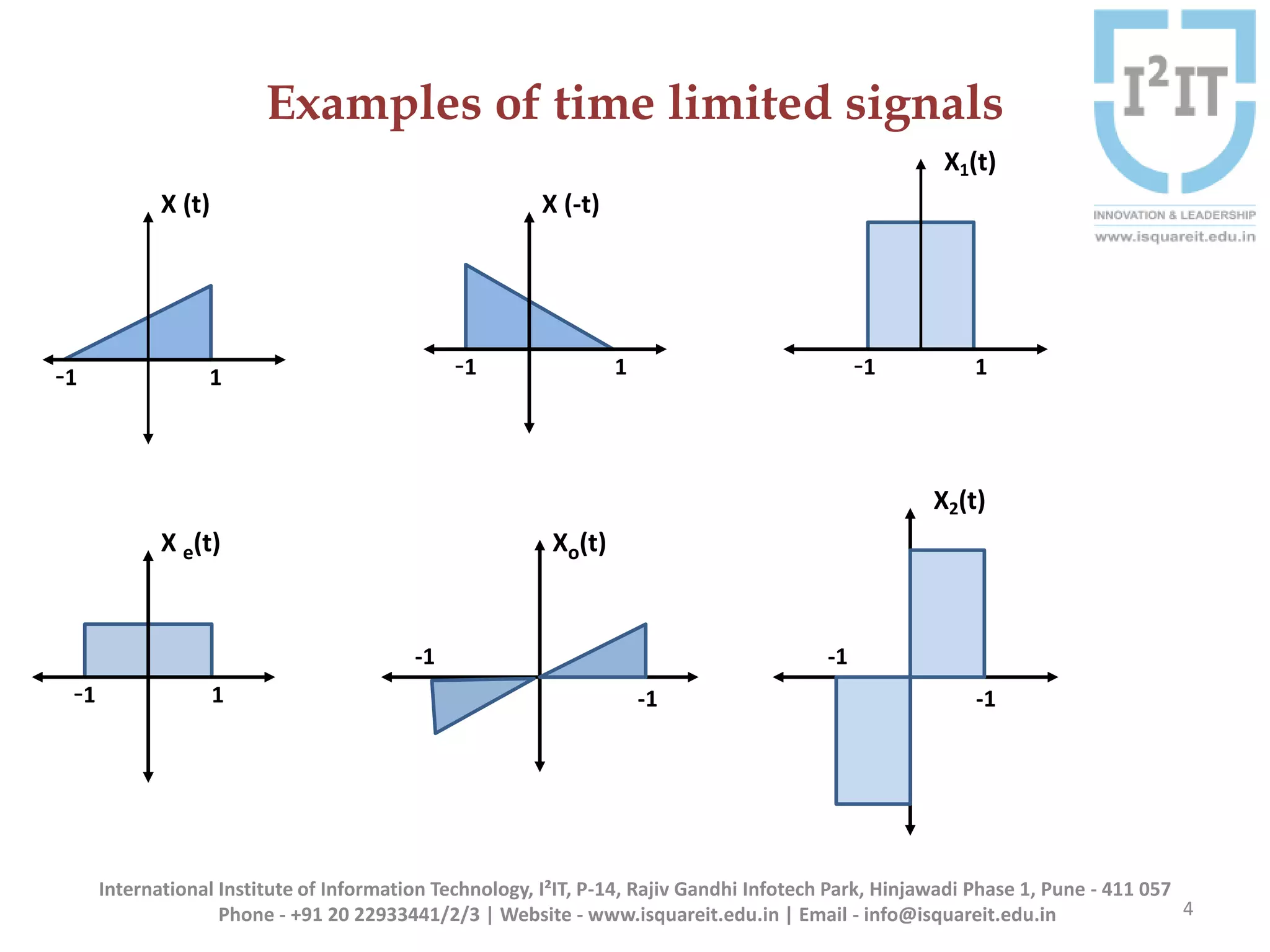
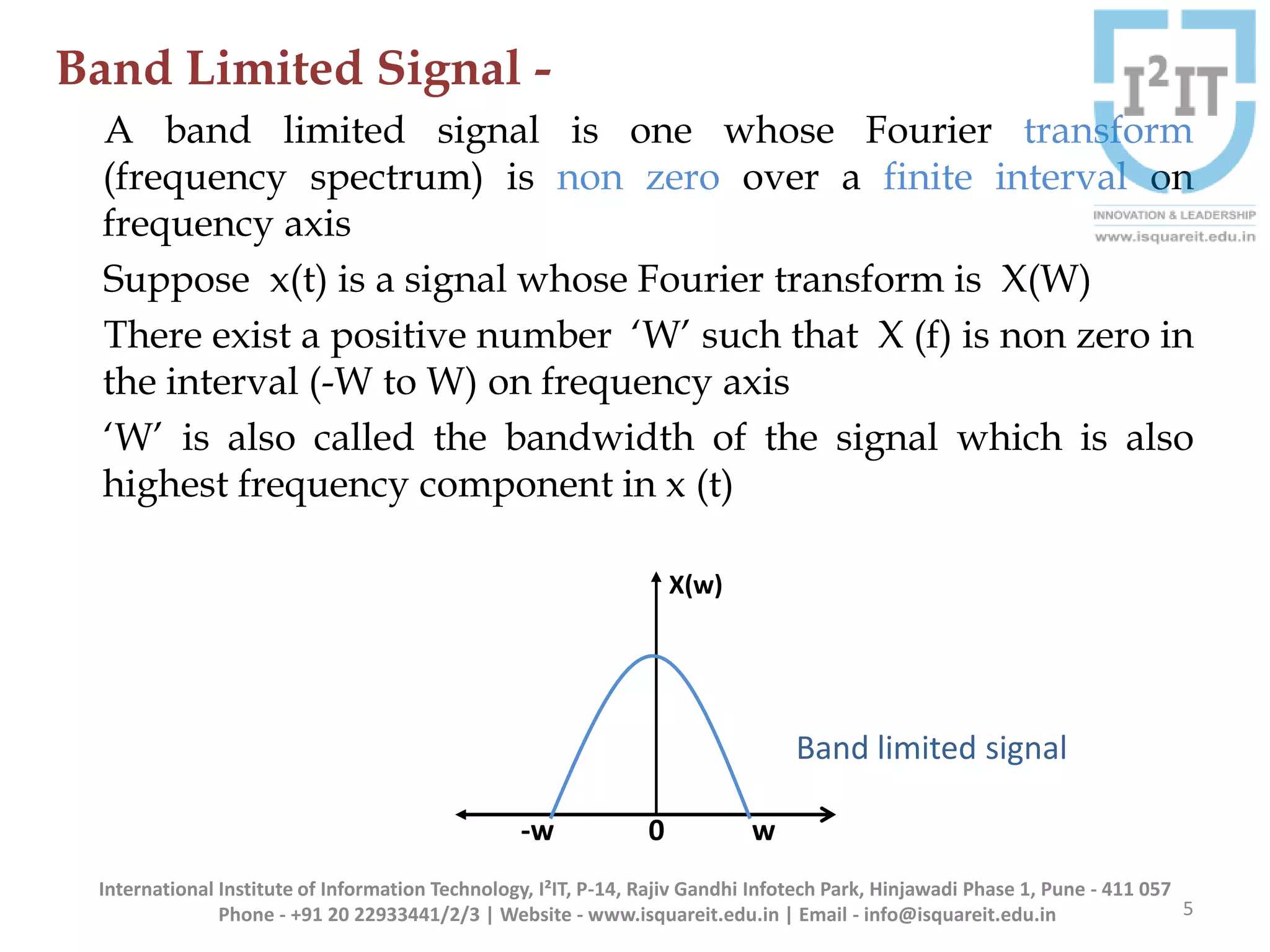
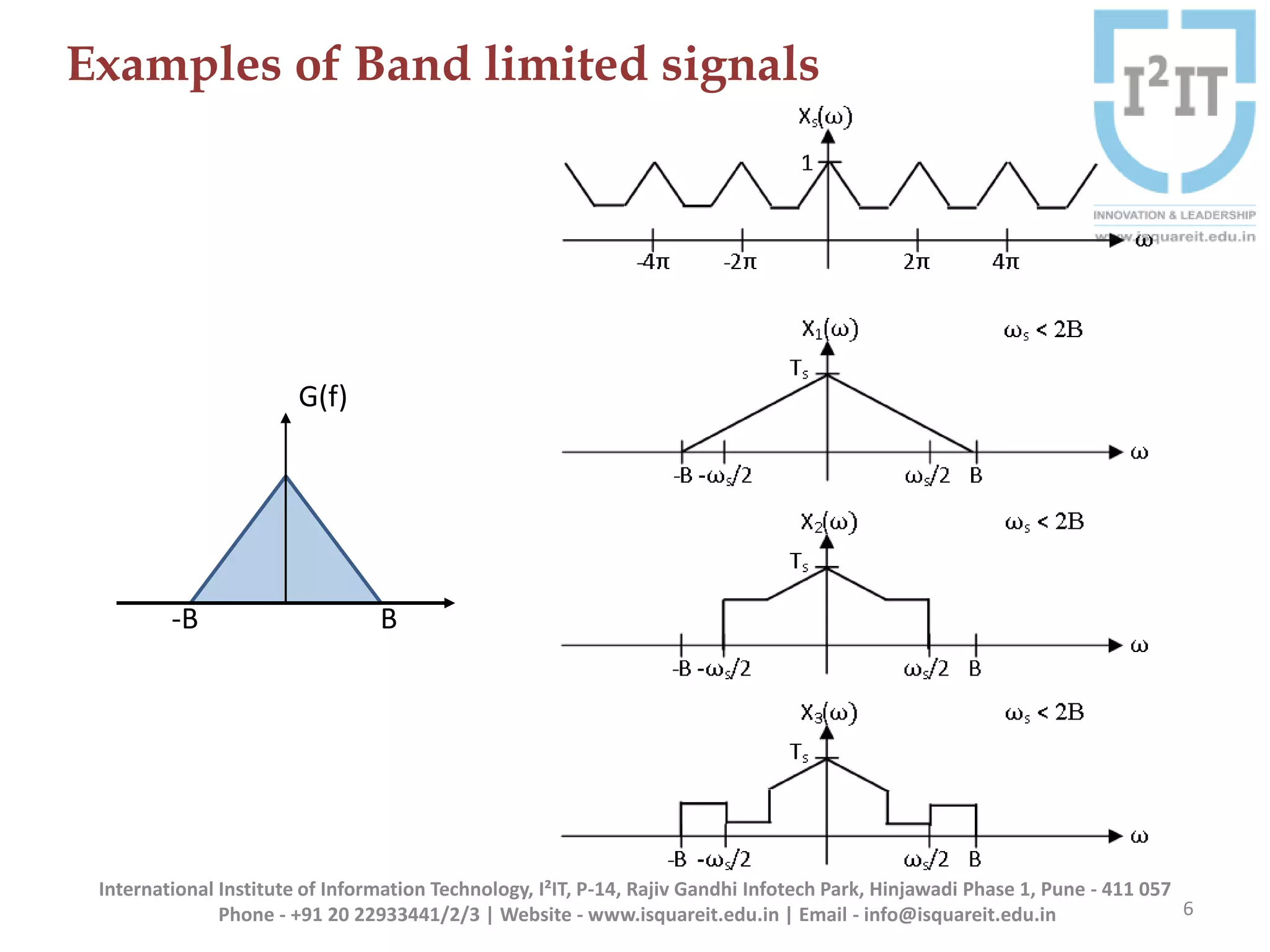
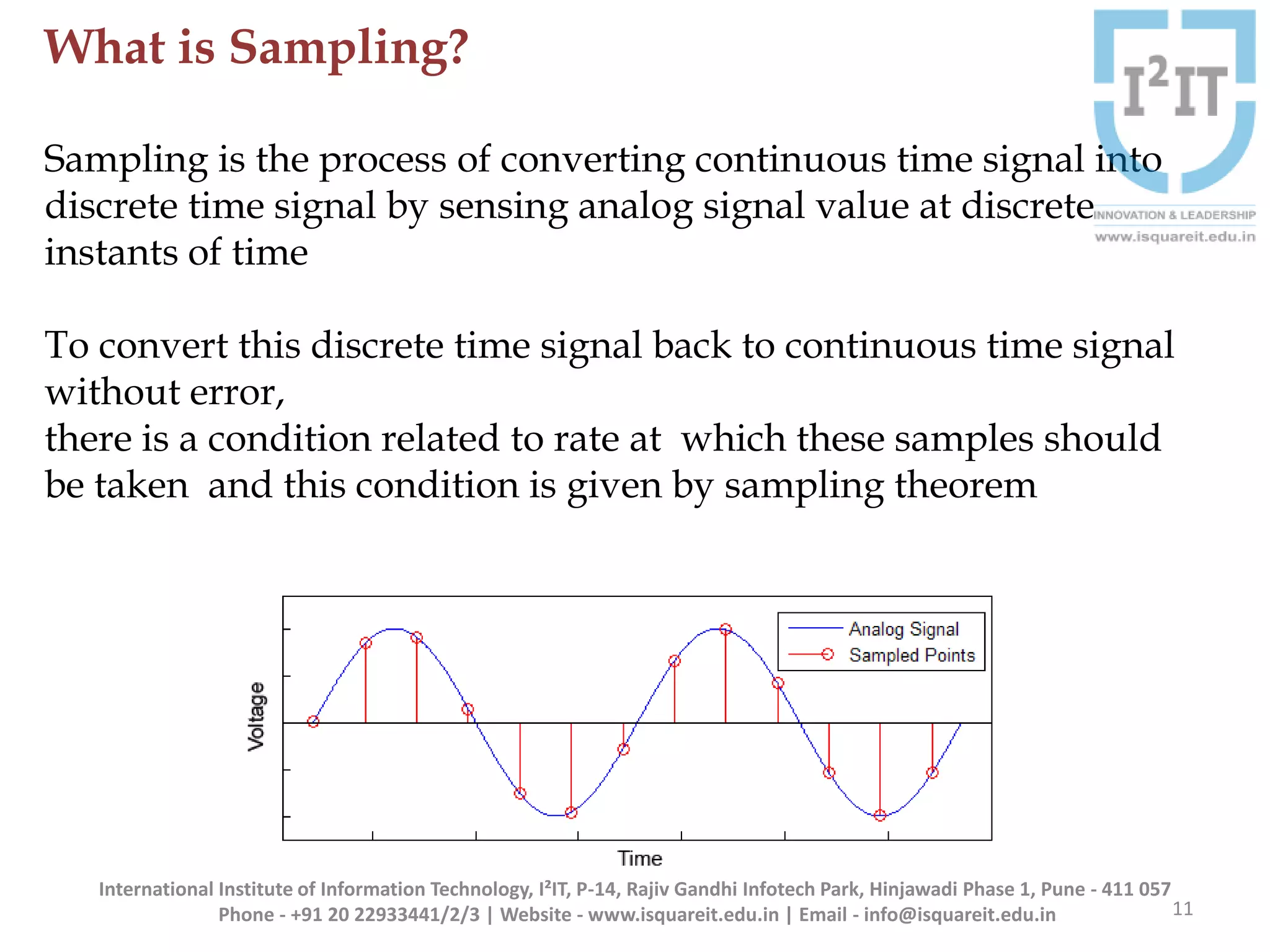
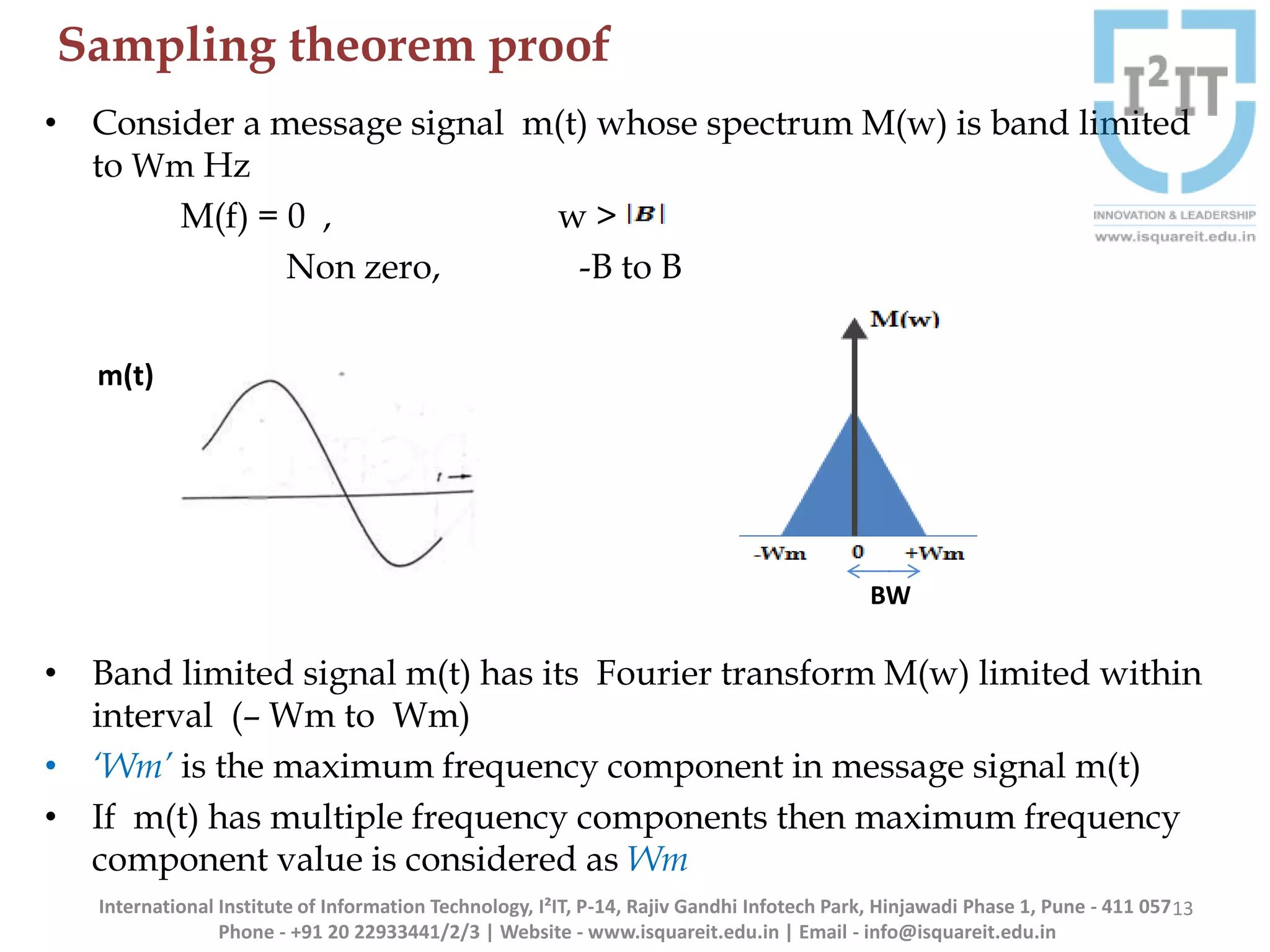
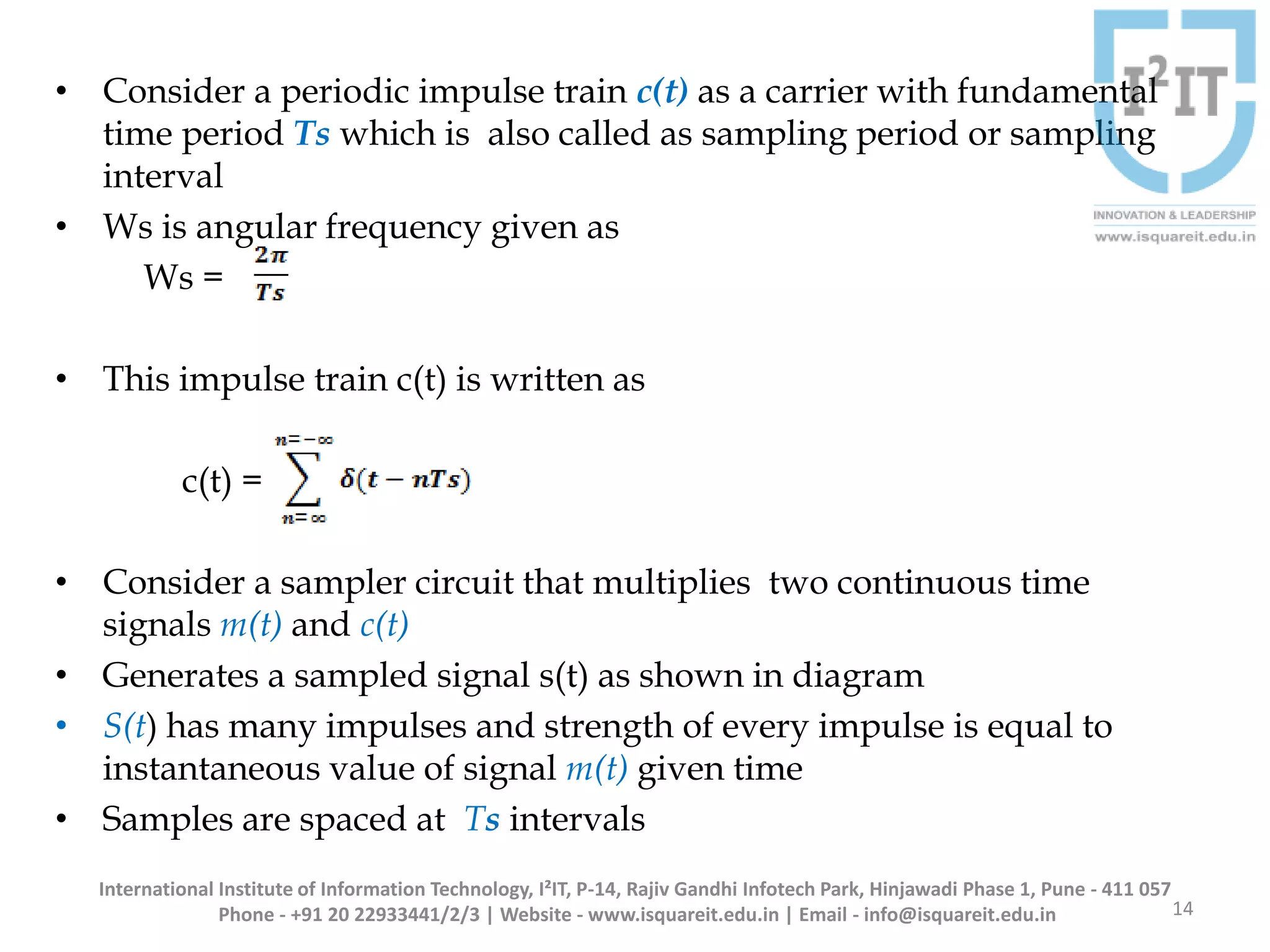
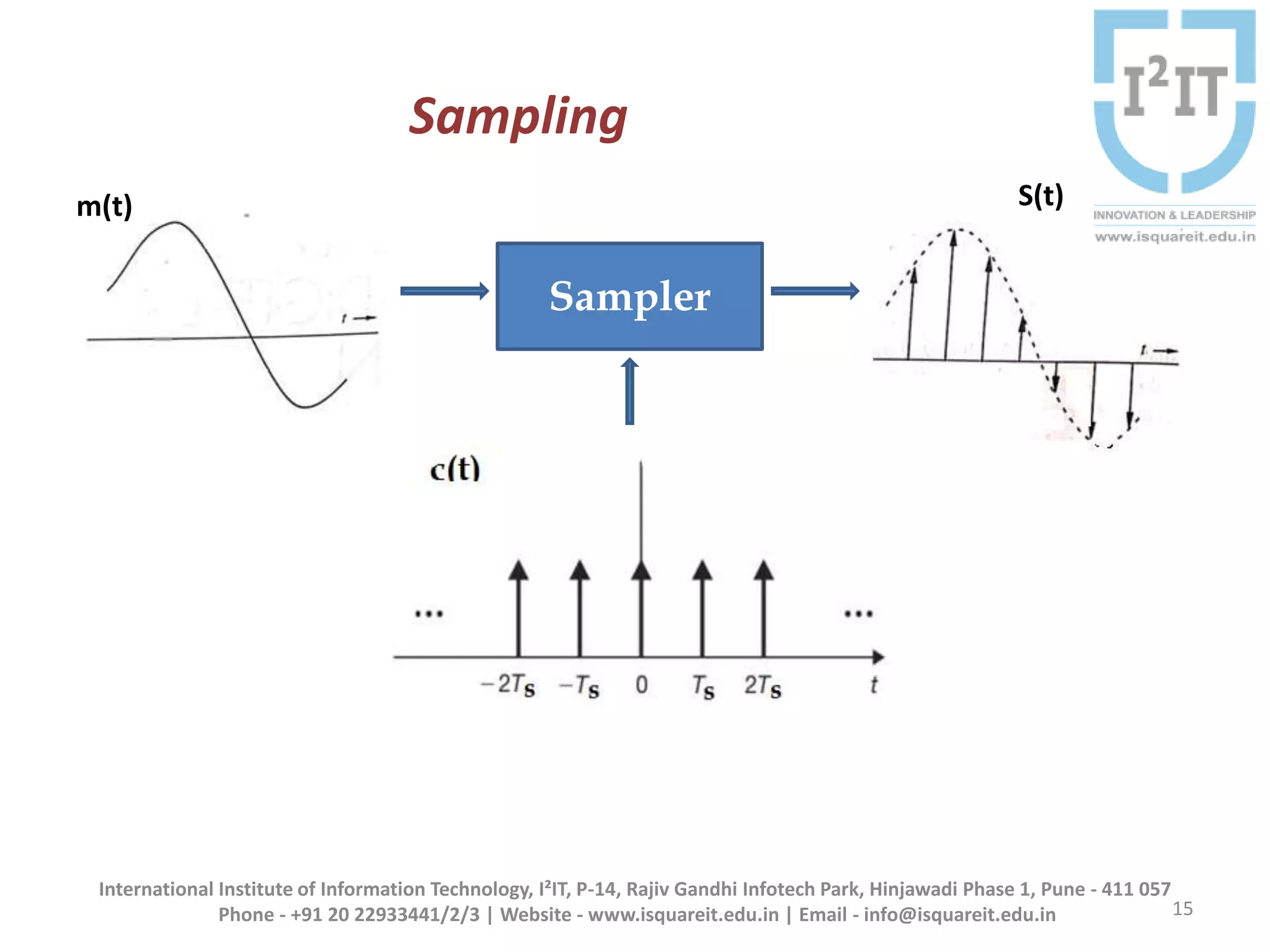
The document discusses the concepts of band-limited and time-limited signals, emphasizing their importance in sampling and signal processing. It explains that for a continuous-time signal to be accurately represented and recovered from samples, it must be band-limited, and details the sampling theorem which states the necessary conditions for the sampling frequency. Additionally, it covers narrowband signals and systems, highlighting their applications and the principle of avoiding aliasing in signal sampling.





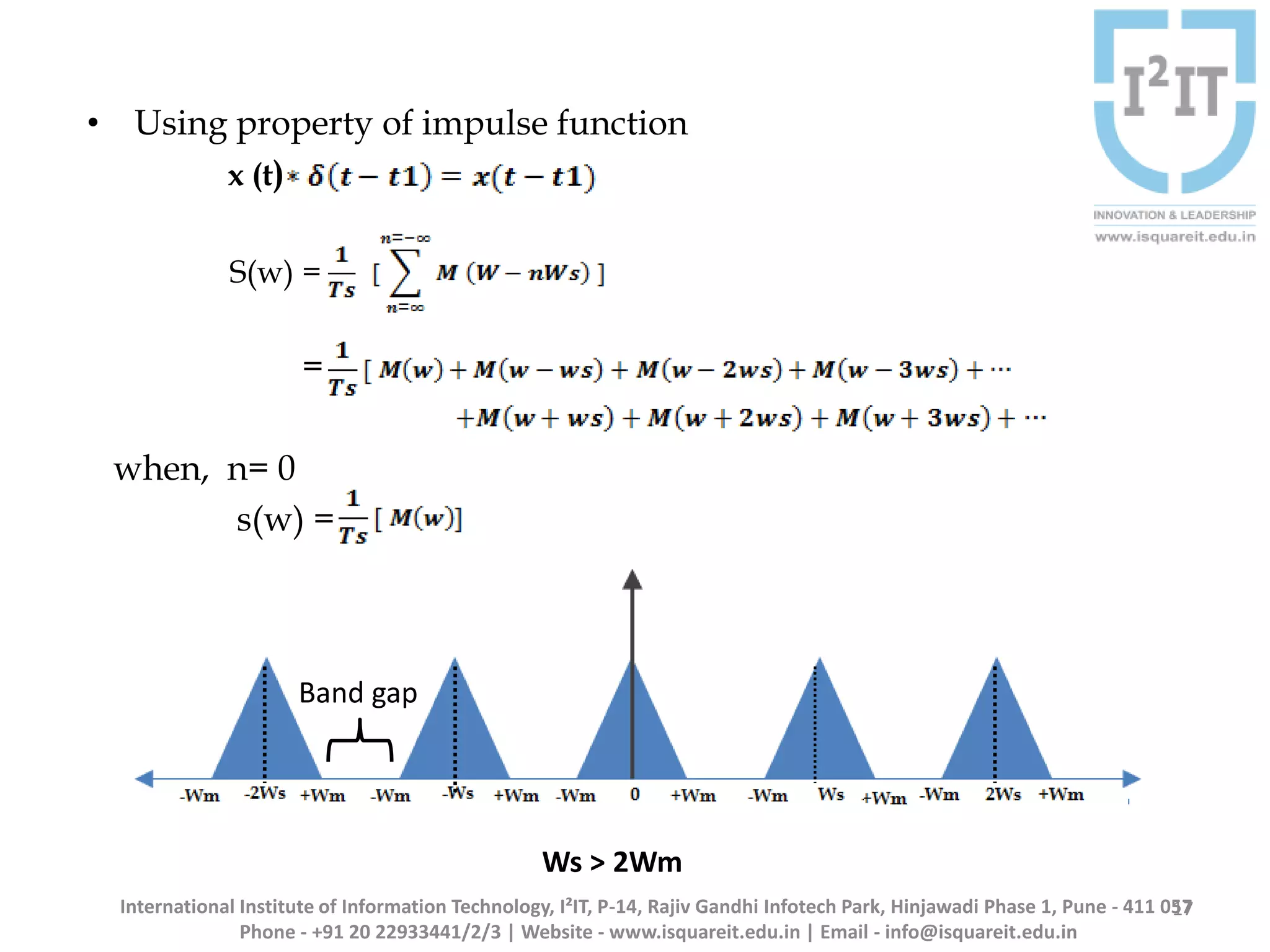
![• S(w) is spectrum of signal s(t) given by
s(t) = m(t) δTs(t)
• As per the property of Fourier transform multiplication of two
signals in time domain is equal to convolution in frequency domain
which can be written as
S(w)= [ M(w)* C(w) ]
• Fourier transform of periodic pulse train c(t) is written as
• S(w) = [ M(w) * ]
=
=
16International Institute of Information Technology, I²IT, P-14, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Hinjawadi Phase 1, Pune - 411 057
Phone - +91 20 22933441/2/3 | Website - www.isquareit.edu.in | Email - info@isquareit.edu.in](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smitakadam2etc-200612130741/75/Sampling-Theorem-and-Band-Limited-Signals-16-2048.jpg)