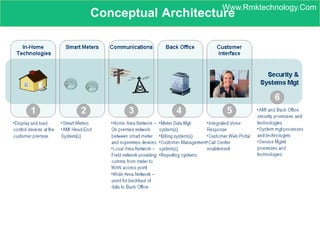
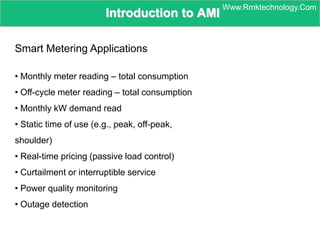
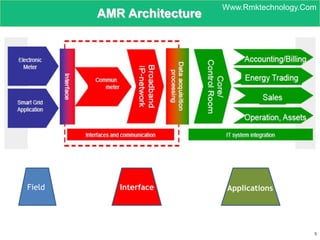
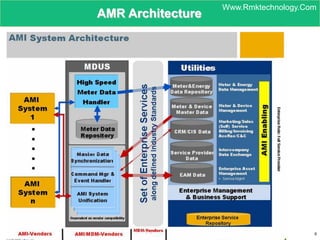
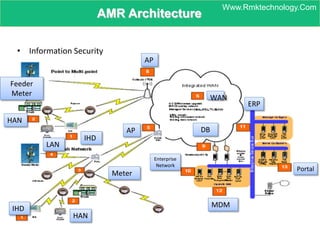
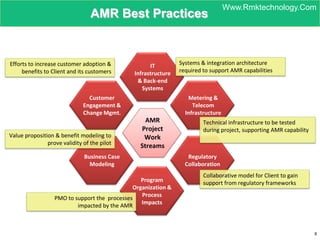
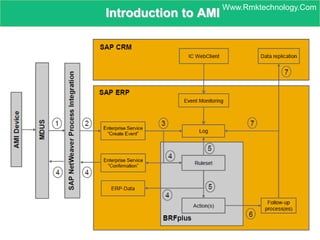
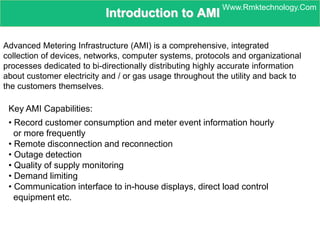
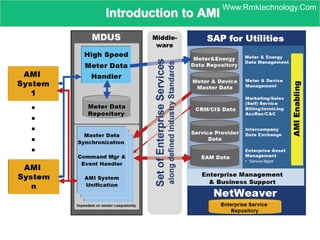
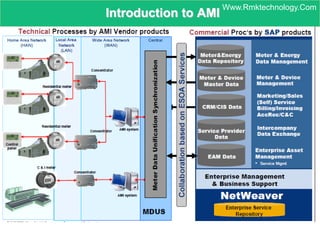
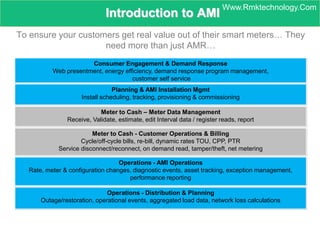
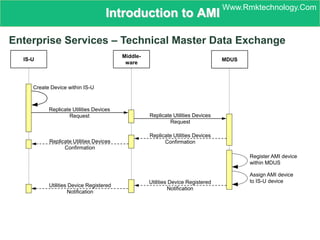
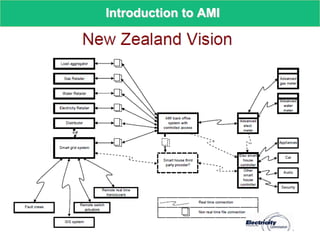
Smart metering, also called advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), allows utilities to remotely monitor customers' energy consumption in near real-time. It provides data to both utilities and customers to make smarter energy choices. AMI improves utility operations by identifying energy use patterns, detecting outages, and locating potential energy theft. It also eliminates the need for manual meter readings and allows for variable pricing plans. The key capabilities of AMI include high-frequency recording of usage, remote disconnection and reconnection, outage detection, and enabling communication with in-home displays and demand response equipment.