Embed presentation
Downloaded 298 times




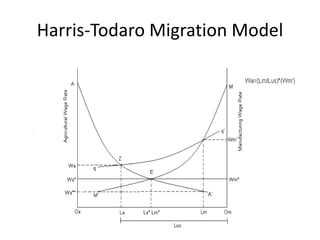


Rural-urban migration has both positive and negative effects on the economy. While it initially withdrew surplus rural labor to provide labor for urban sectors, economists later realized that rural-urban migration rates often exceeded urban job creation rates, leading to higher urban unemployment. According to the 2001 Indian census, rural-urban migration was 20.5 million people. This disproportionately increases the urban job seeking population compared to overall urban population growth, putting pressure on the labor force. It also makes urban job creation more difficult due to rising wages and employee benefits. Both the short and long term effects are an imbalance of resources and rising surplus urban labor. The Harris-Todaro model explains how migration is stimulated by rational considerations of relative costs and benefits






