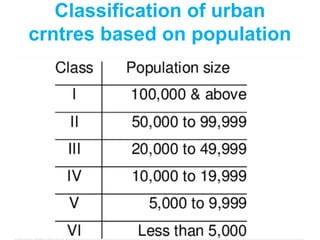
Urban settlements are characterized by high population densities, populations engaged mostly in non-agricultural sectors, and nucleated settlements with distinct economic and cultural characteristics compared to rural areas. India's urban population was 31.16% in 2011, with large variation between states from 62.17% in Goa to 10.04% in Himachal Pradesh. Urban areas are officially defined as settlements with over 5,000 people, density over 400/sq km, and at least 75% engaged in non-farm work. Urban centers are further classified based on population as towns (<100k), cities (100k-1m), metropolises (>1m), and megacities (>5m people). Problems faced