Embed presentation
Downloaded 307 times






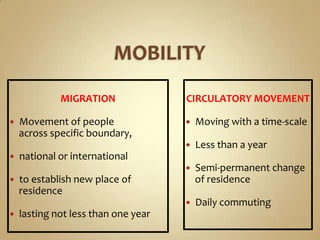

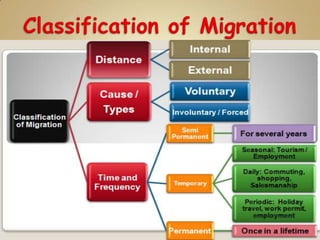
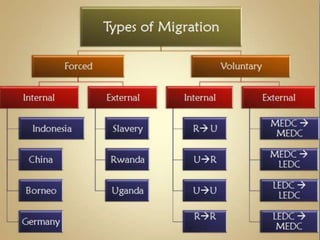
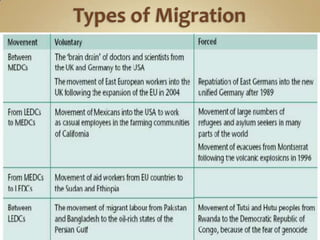



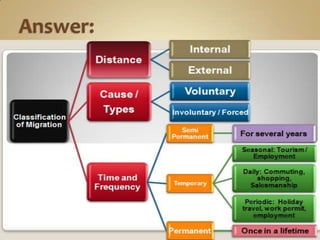
The document defines and compares different types of migration such as internal vs external migration, migration vs circulatory movement, and forced vs voluntary migration. It also discusses factors that influence migrability and provides examples of types of migration like immigration, emigration, in-migration and out-migration. Government controls on immigration are also mentioned.














