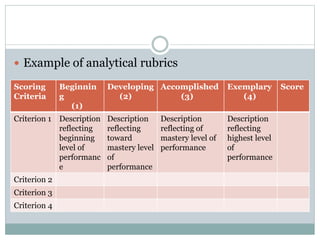
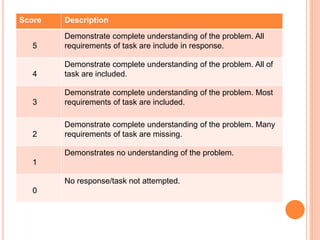
This document discusses two types of rubrics used for performance assessment: analytical rubrics and holistic rubrics. Analytical rubrics assess multiple criteria separately and provide a total score, allowing for detailed feedback. Holistic rubrics use a single overall score based on general impression rather than separate criteria. The document provides examples of each type and discusses their advantages and disadvantages, such as analytical rubrics taking more time but providing more specific feedback than holistic rubrics.