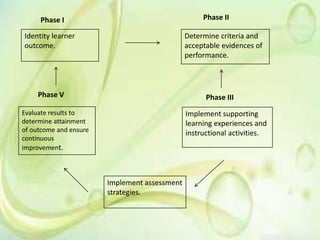
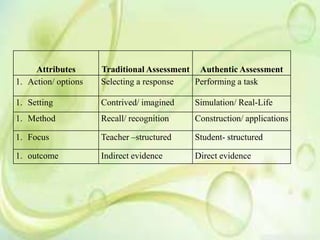
This document discusses authentic assessment, including its meaning, characteristics, and practices. Authentic assessment aims to evaluate students' ability to apply knowledge to real-world tasks, rather than just recall facts. It is characterized by clear performance criteria, emphasis on skills over memorization, and requiring students to demonstrate learning through tasks like projects and portfolios. The document outlines five phases of authentic assessment: identifying outcomes, determining criteria, implementing instruction, measuring performance, and evaluating results for improvement. In contrast to traditional assessment focused on selecting answers, authentic assessment centers on students performing meaningful tasks that simulate real-world challenges.