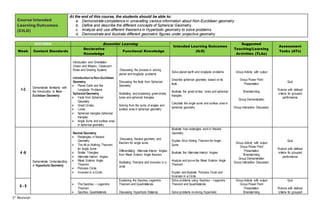
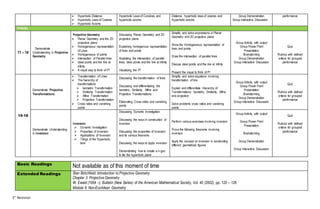
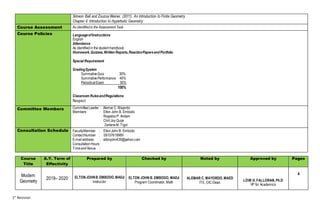
This document outlines the course plan for a Modern Geometry course. The course aims to discuss non-Euclidean geometries like finite, non-Euclidean, and projective geometry. Over 18 weeks, topics will include spherical, hyperbolic, and projective geometry as well as transformations and inversions. Assessment will include quizzes, group activities, and exams worth 100% of the grade. The course intends for students to demonstrate understanding of key concepts in non-Euclidean geometries.