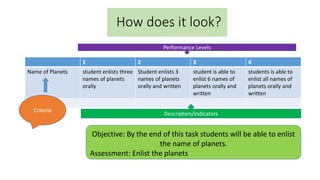
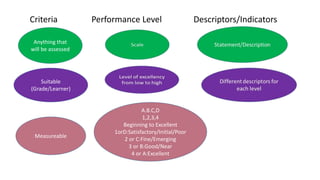
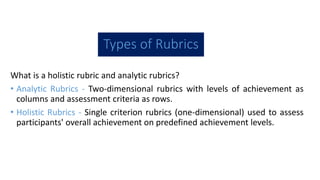
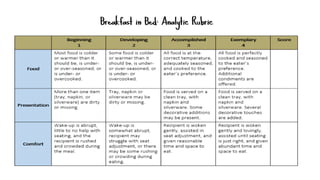
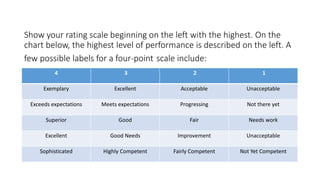
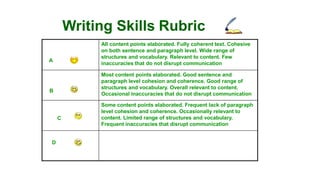
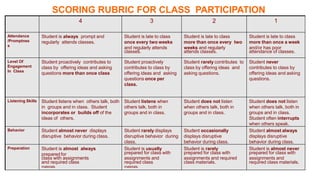
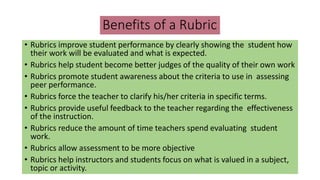
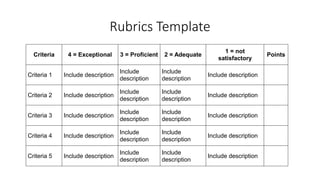
The document discusses rubrics as assessment tools essential for educational evaluation, outlining their definitions, types, components, and differences between holistic and analytic rubrics. It emphasizes the importance of clear learning objectives and how rubrics can improve student performance and guide effective teaching. Additionally, it provides examples of various rubrics for different skills such as listening, speaking, reading, writing, and class participation.