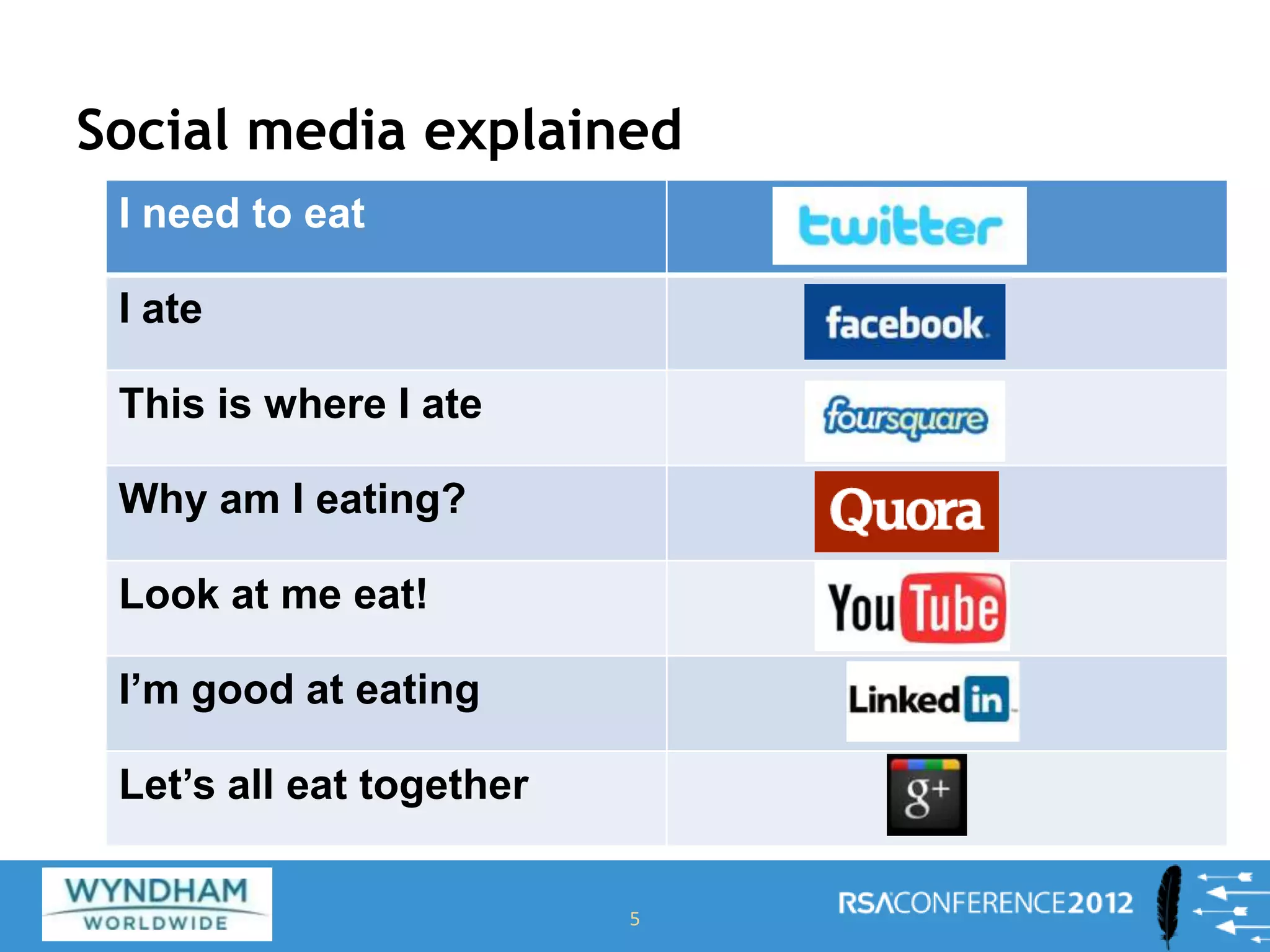
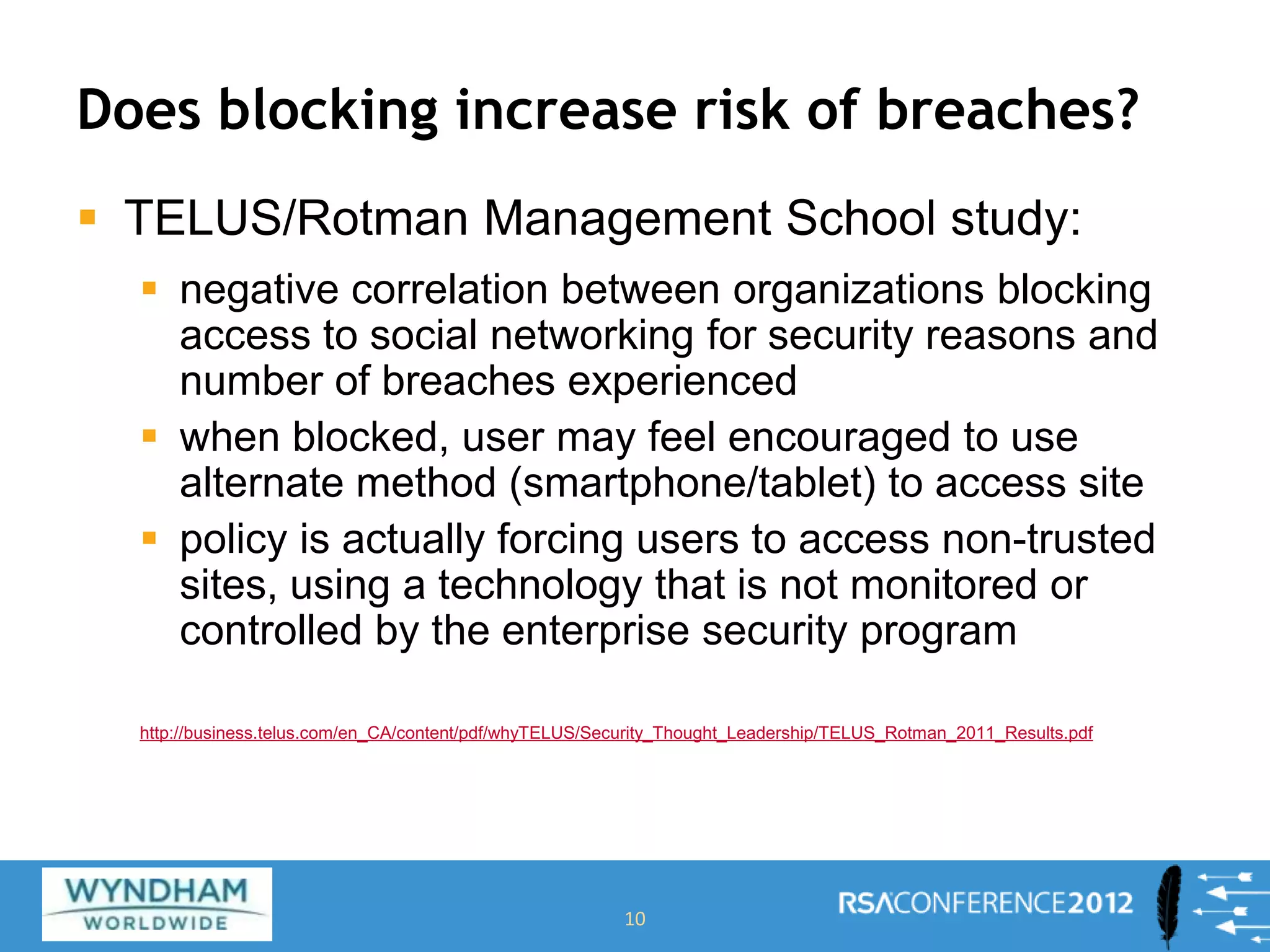
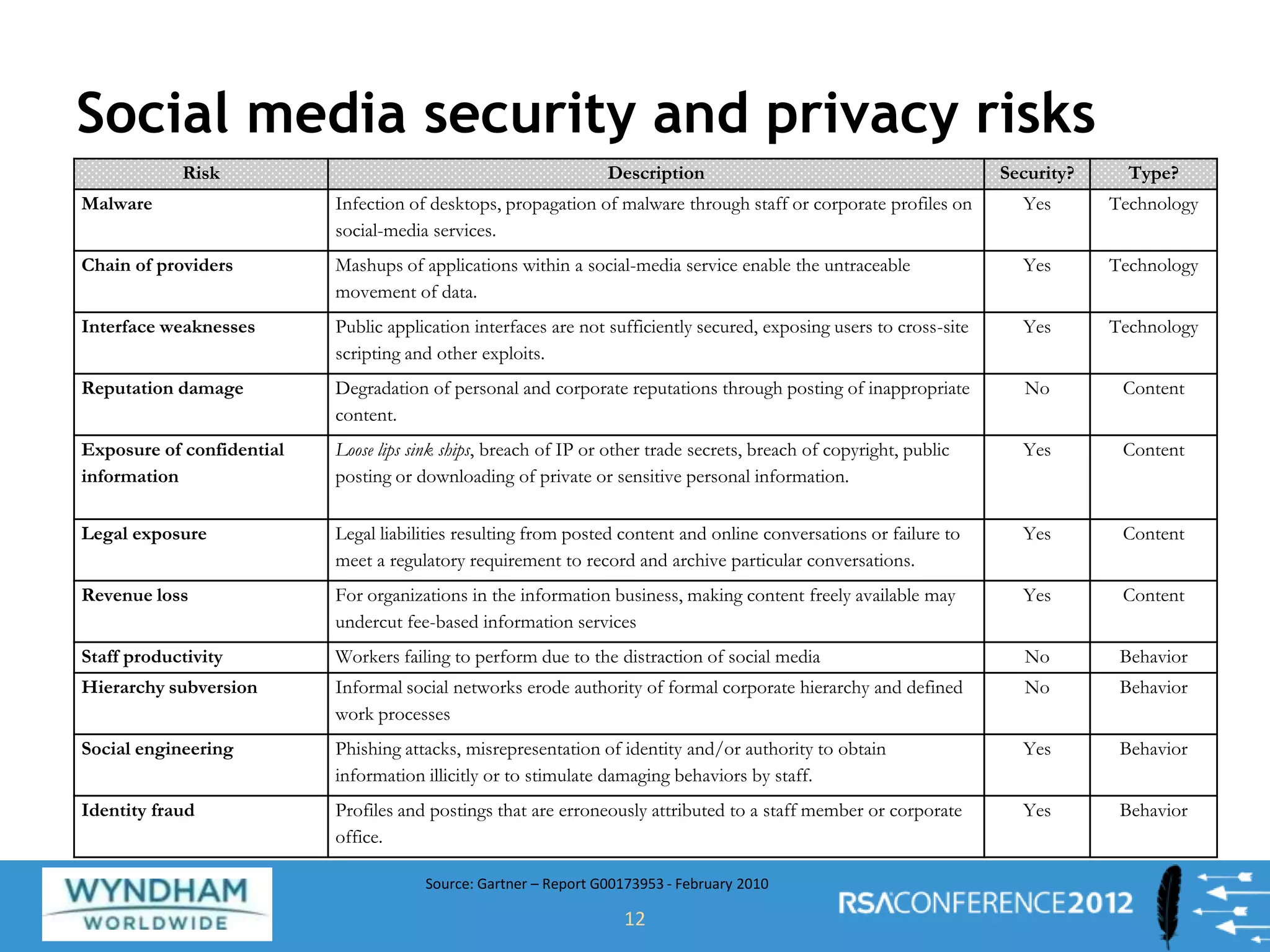
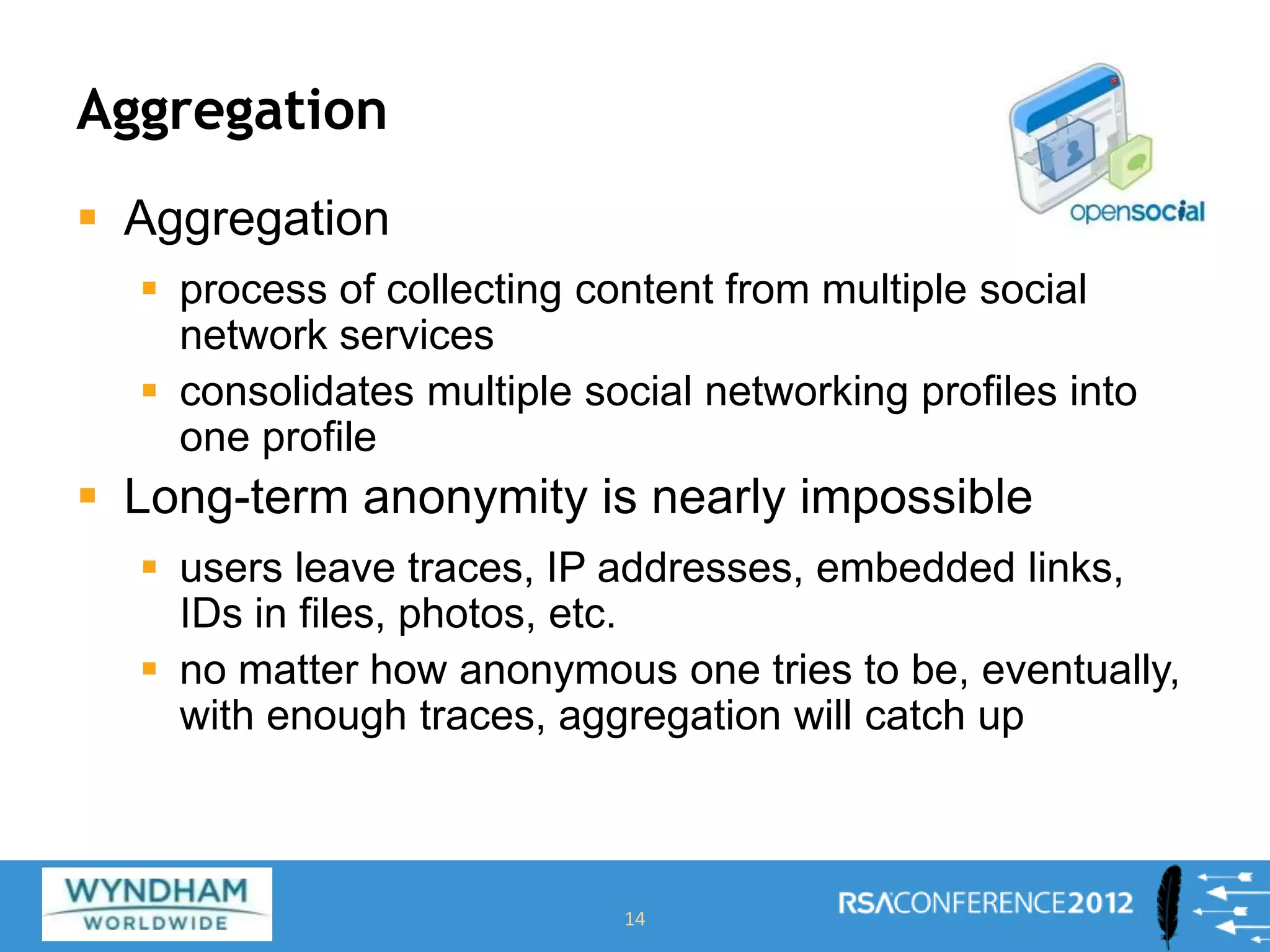
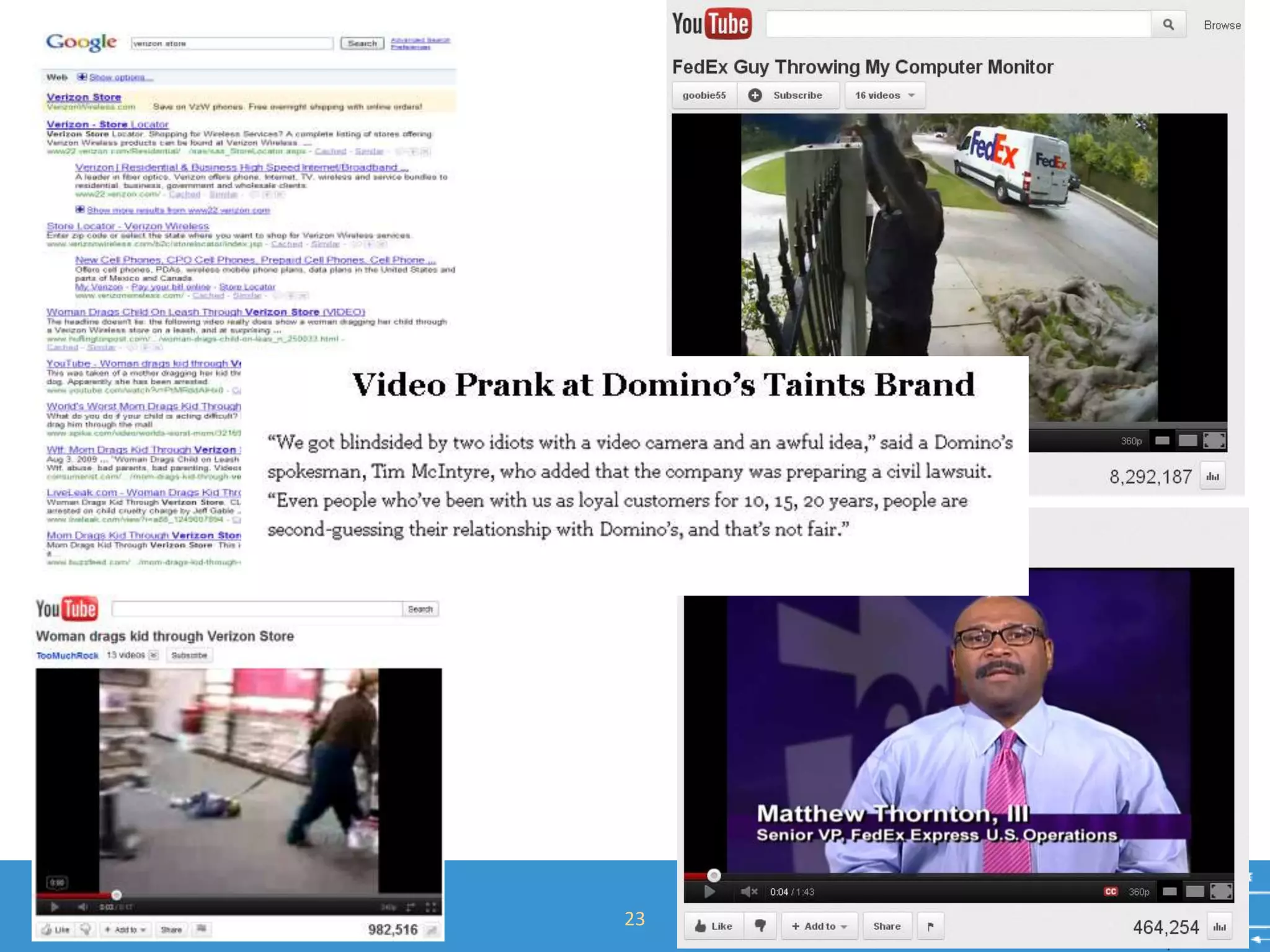
Ben Rothke presented on securely using social networks. He discussed the risks of social media like exposure of confidential information and malware infection. However, blocking social networks completely is ineffective; organizations need governance through risk assessments, policies and reputation management. Education of employees is also key to raise awareness of risks like data leakage. Monitoring of social networks and tools is important for management, but policies must consider privacy regulations. Information security must work with HR and PR to securely enable social media use.