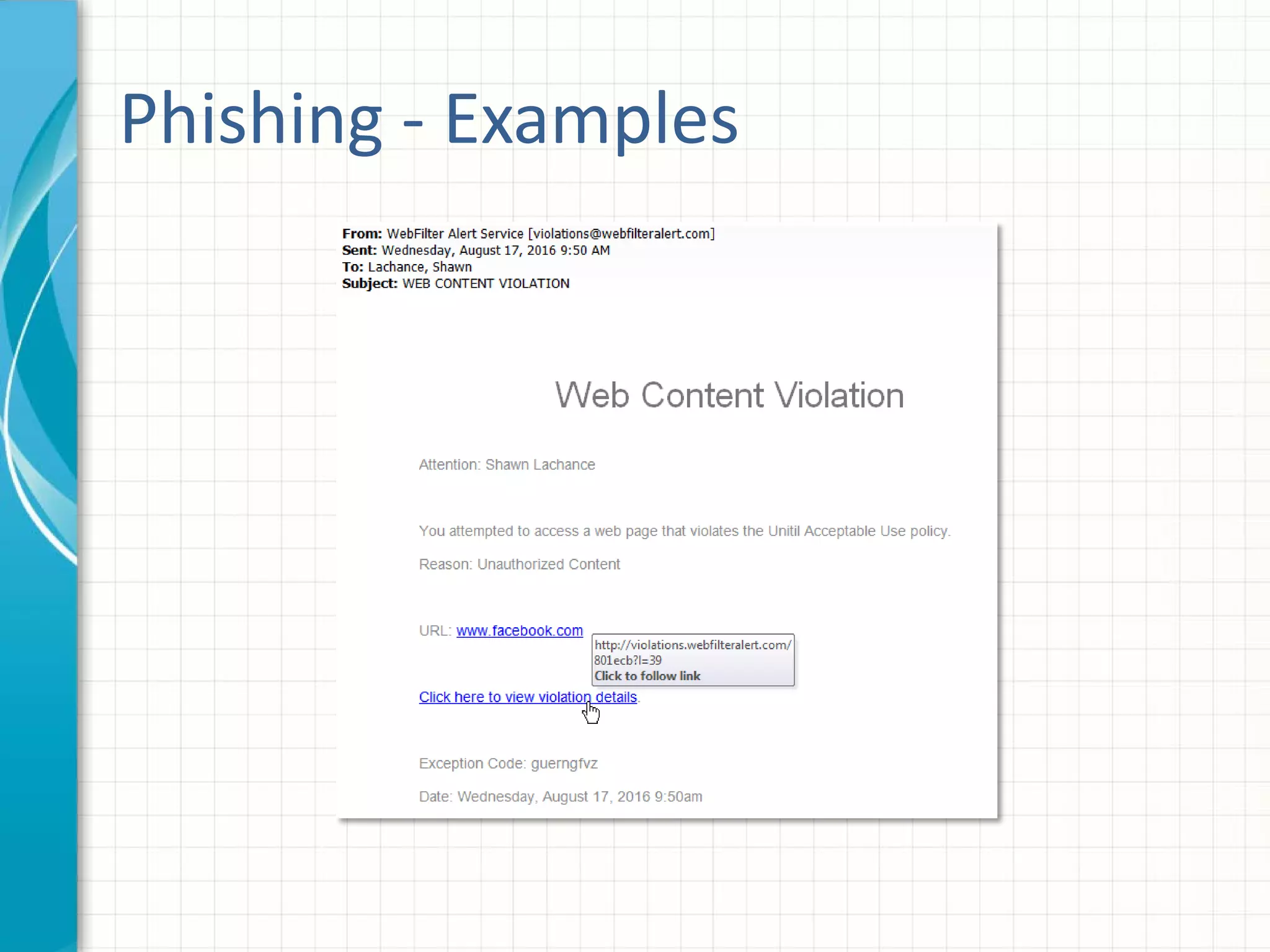
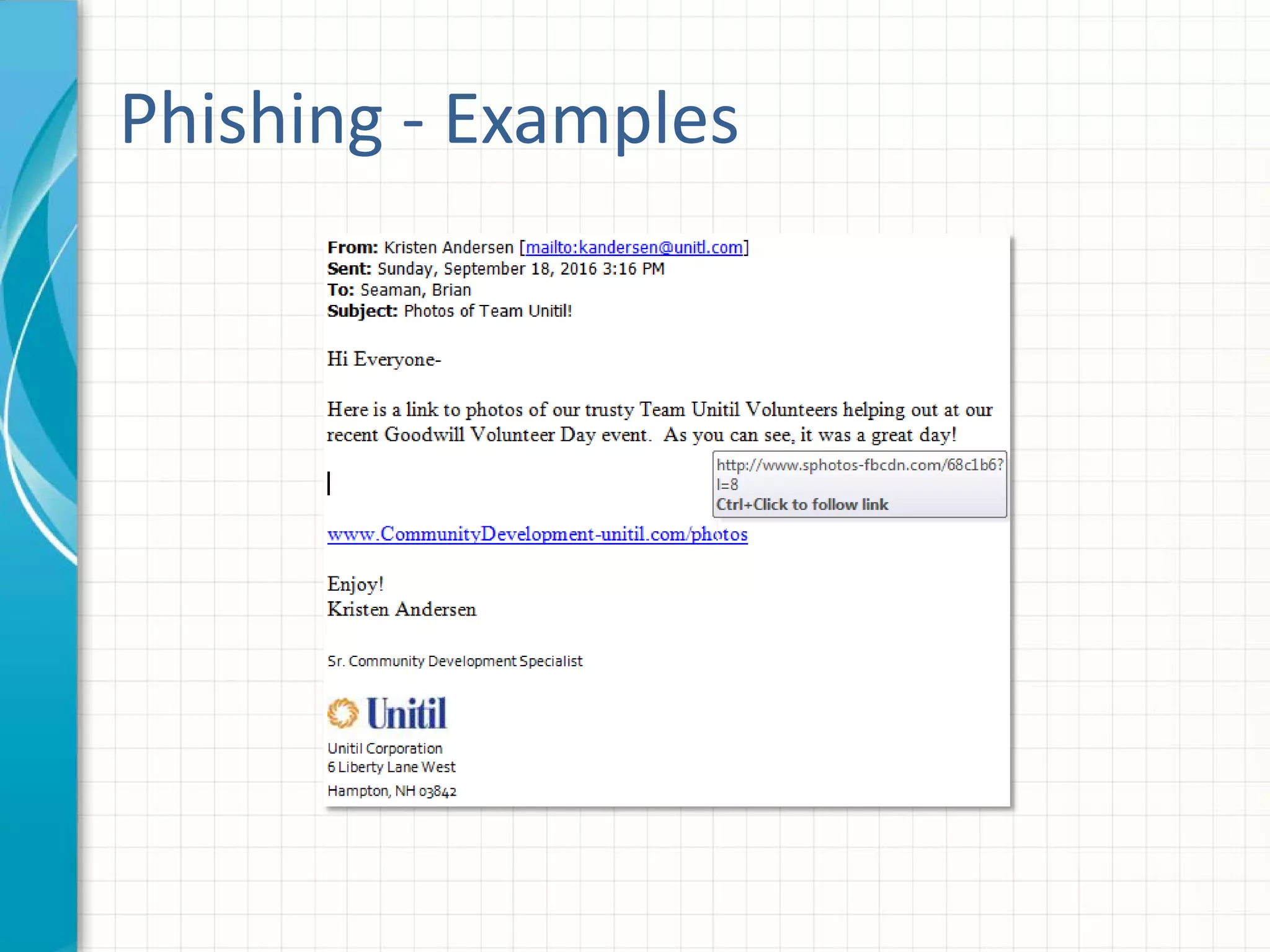
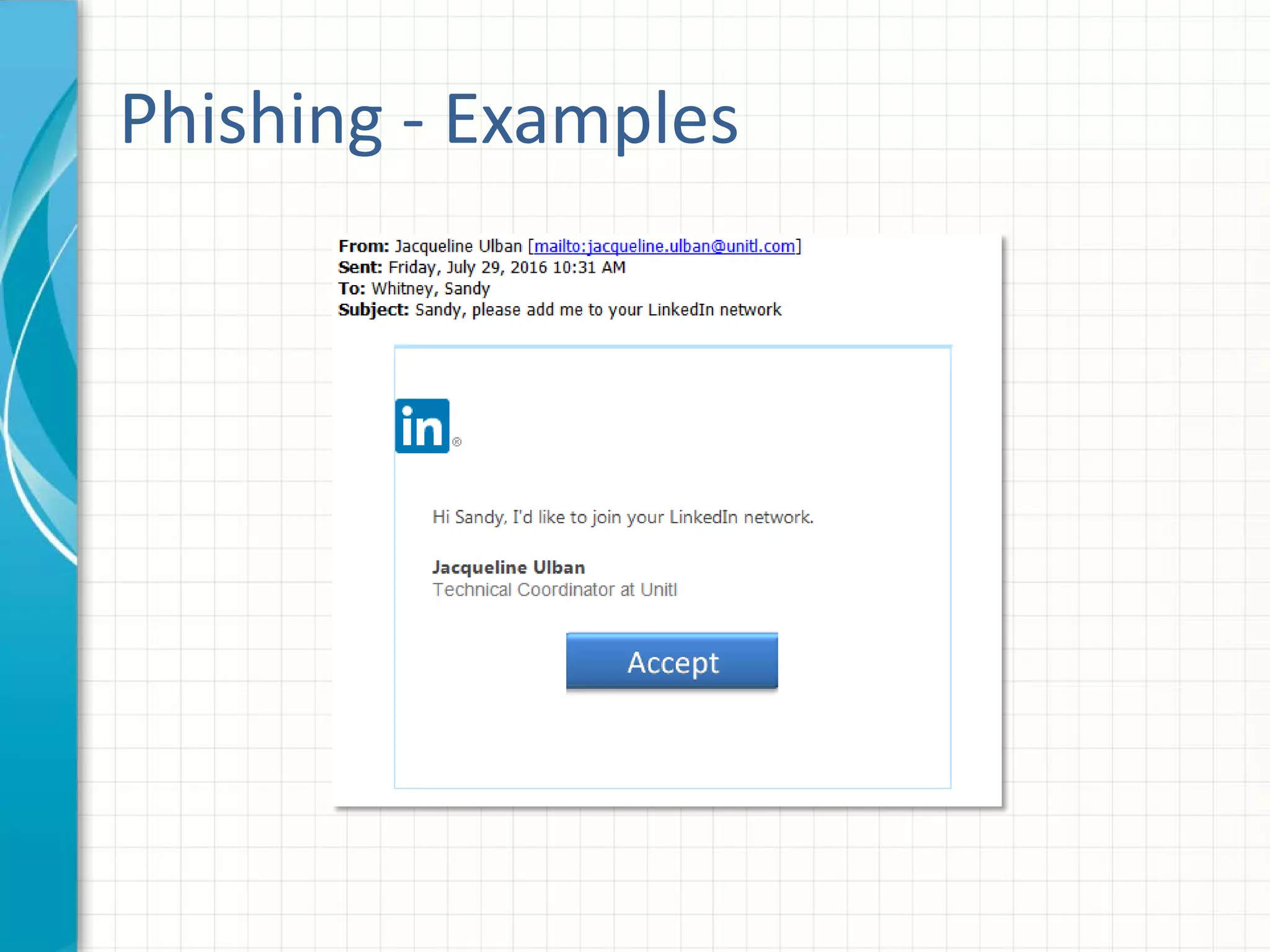
This document discusses building an effective security awareness program. It emphasizes that the biggest risk to an organization's security is the actions or inactions of employees, so training is important. Effective training uses real examples, feedback, and individualized lessons. Compliance standards like PCI DSS, ISO, and HIPAA require awareness training. Building a security culture requires buy-in from executives and employees. Enforcing policies through graduated penalties helps change behavior. Measuring effectiveness through metrics like compliance and data breaches allows improvement. Social engineering tests and phishing simulations can train employees while easing security fatigue.